查找重复的电子邮箱
编写一个 SQL 查询,查找 Person 表中所有重复的电子邮箱。
+----+---------+
| Id | Email |
+----+---------+
| 1 | a@b.com |
| 2 | c@d.com |
| 3 | a@b.com |
+----+---------+
根据以上输入,你的查询应返回以下结果:
+---------+
| Email |
+---------+
| a@b.com |
+---------+
说明:所有电子邮箱都是小写字母。
select Email
from Person
group by Email
having count(Email) > 1;
合作过至少三次的演员导演
ActorDirector 表:
±------------±--------+
| Column Name | Type |
±------------±--------+
| actor_id | int |
| director_id | int |
| timestamp | int |
±------------±--------+
timestamp 是这张表的主键.
写一条SQL查询语句获取合作过至少三次的演员和导演的 id 对 (actor_id, director_id)
SELECT
actor_id, director_id
FROM
actordirector
GROUP BY actor_id, director_id
HAVING COUNT(*) >= 3;
销售分析
Table: Product
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| product_id | int |
| product_name | varchar |
| unit_price | int |
+--------------+---------+
Product_id是该表的主键。
该表的每一行显示每个产品的名称和价格。
Table: Sales
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| seller_id | int |
| product_id | int |
| buyer_id | int |
| sale_date | date |
| quantity | int |
| price | int |
+------ ------+---------+
这个表没有主键,它可以有重复的行。
product_id 是 Product 表的外键。
该表的每一行包含关于一个销售的一些信息。
编写一个SQL查询,报告2019年春季才售出的产品。即仅在2019-01-01至2019-03-31(含)之间出售的商品
select product_id,product_name
from product
where product_id not in(
select product_id
from sales
where datediff (sale_date,'2019-01-01')<0
or datediff(sale_date,'2019-03-31')>0
)and product_id in (
select distinct product_id from sales
);
银行账户概要
表: Users
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| account | int |
| name | varchar |
+--------------+---------+
account 是该表的主键.
表中的每一行包含银行里中每一个用户的账号.
表: Transactions
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| trans_id | int |
| account | int |
| amount | int |
| transacted_on | date |
+---------------+---------+
trans_id 是该表主键.
该表的每一行包含了所有账户的交易改变情况.
如果用户收到了钱, 那么金额是正的; 如果用户转了钱, 那么金额是负的.
所有账户的起始余额为 0.
写一个 SQL, 报告余额高于 10000 的所有用户的名字和余额. 账户的余额等于包含该账户的所有交易的总和.
select NAME, sum(T.amount) as BALANCE
from Users as U
inner join
Transactions as T
on U.account=T.account
group by T.account
having sum(T.amount)>10000
腐烂的橘子
在给定的 m x n 网格 grid 中,每个单元格可以有以下三个值之一:
值 0 代表空单元格;
值 1 代表新鲜橘子;
值 2 代表腐烂的橘子。
每分钟,腐烂的橘子 周围 4 个方向上相邻 的新鲜橘子都会腐烂。
返回 直到单元格中没有新鲜橘子为止所必须经过的最小分钟数。如果不可能,返回 -1 。
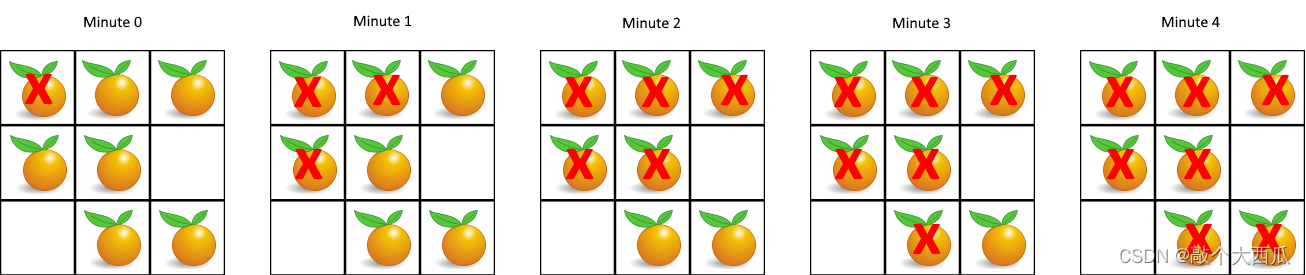
输入:grid = [[2,1,1],[1,1,0],[0,1,1]]
输出:4
class Solution {
public int orangesRotting(int[][] grid) {
// 第一感觉用广度优先遍历
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
boolean[][] seen = new boolean[m][n];
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int count = 0; // 用来记录新鲜橘子的个数
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 2) {
queue.offer(new int[]{i, j}); // 先找出所有的腐烂橘子入队
} else if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
count++; // 新鲜橘子+1
}
}
}
int[] dx = {1, 0, 0, -1};
int[] dy = {0, 1, -1, 0};
int round = 0; // 用来记录遍历的层数或轮数或橘子腐烂的时间
while (count > 0 && !queue.isEmpty()) {
round++;
int size = queue.size();
for (int p = 0; p < size; ++p) {
int[] temp = queue.poll();
int x = temp[0], y = temp[1];
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int i = x + dx[k], j = y + dy[k];
// 如果在边界内且某个方向有新鲜橘子,则遍历
if (i >= 0 && i < m && j >= 0 && j < n && grid[i][j] == 1) {
grid[i][j] = 2; // 新鲜橘子 变为腐烂橘子
count--; // 新鲜橘子腐烂掉 相应减少新鲜橘子
queue.offer(new int[]{i, j}); // 腐烂橘子入队
}
}
}
}
// 在能腐烂的新鲜橘子都腐烂后,如果count还大于0,说明有新鲜橘子没法腐烂 则返回-1
return count > 0 ? -1 : round;
}
}
矩阵
给定一个由 0 和 1 组成的矩阵 mat ,请输出一个大小相同的矩阵,其中每一个格子是 mat 中对应位置元素到最近的 0 的距离。
两个相邻元素间的距离为 1 。
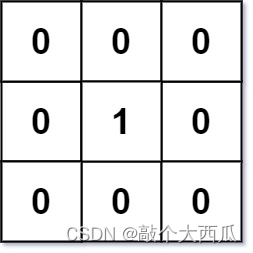
输入:mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
输出:[[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
class Solution {
static int[][] dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
public int[][] updateMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int[][] dist = new int[m][n];
boolean[][] seen = new boolean[m][n];
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<int[]>();
// 将所有的 0 添加进初始队列中
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (matrix[i][j] == 0) {
queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});
seen[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
// 广度优先搜索
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] cell = queue.poll();
int i = cell[0], j = cell[1];
for (int d = 0; d < 4; ++d) {
int ni = i + dirs[d][0];
int nj = j + dirs[d][1];
if (ni >= 0 && ni < m && nj >= 0 && nj < n && !seen[ni][nj]) {
dist[ni][nj] = dist[i][j] + 1;
queue.offer(new int[]{ni, nj});
seen[ni][nj] = true;
}
}
}
return dist;
}
}
二叉树的层序遍历
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 层序遍历 。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
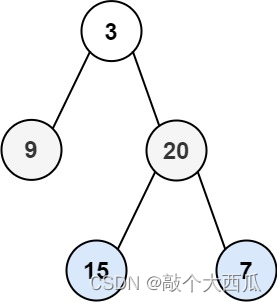
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:[[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list=new LinkedList<>( );
if (root==null){
return list;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>( );
queue.offer( root );
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
int size=queue.size();
List<Integer> le=new LinkedList<>( );
for (int i=0;i<size;i++){
TreeNode node=queue.poll();
le.add( node.val );
if (node.left!=null){
queue.offer( node.left );
}
if (node.right!=null){
queue.offer( node.right );
}
}
list.add( le );
}
return list;
}}
二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。、
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
} else {
int leftHeight = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightHeight = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
}
}
堆成二叉树
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return check(root, root);
}
public boolean check(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q == null) {
return true;
}
if (p == null || q == null) {
return false;
}
return p.val == q.val && check(p.left, q.right) && check(p.right, q.left);
}
}
赎金信
给你两个字符串:ransomNote 和 magazine ,判断 ransomNote 能不能由 magazine 里面的字符构成。
如果可以,返回 true ;否则返回 false 。
magazine 中的每个字符只能在 ransomNote 中使用一次。
class Solution {
public boolean canConstruct(String ransomNote, String magazine) {
if (ransomNote.length()>magazine.length()){
return false;
}
int[] cnt=new int[26];
for (char c:ransomNote.toCharArray()){
cnt[c-'a']++;
}
for (char c:magazine.toCharArray()) {
cnt[c-'a']--;
if(cnt[c-'a']<0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}}
有效的字母异位词
给定两个字符串 s 和 t ,编写一个函数来判断 t 是否是 s 的字母异位词。
注意:若 s 和 t 中每个字符出现的次数都相同,则称 s 和 t 互为字母异位词。
class Solution {
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
if (s.length()!=t.length()){
return false;
}
int[] cat=new int[26];
for (char c:s.toCharArray()){
cat[c-'a']++;
}
for (char c:t.toCharArray()){
cat[c-'a']--;
}
for (int a:cat){
if (a!=0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
二叉树的前序遍历
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它节点值的 前序 遍历。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans=new LinkedList<>( );
pro( root,ans );
return ans;
}
public void pro(TreeNode root,List<Integer> ans){
if (root==null){
return;
}
pro( root.left,ans );
ans.add( root.val );
pro( root.right,ans );
}
}
中序遍历
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回 它的 中序 遍历 。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans=new LinkedList<>( );
pro( root,ans );
return ans;
}
public void pro(TreeNode root,List<Integer> ans){
if (root==null){
return;
}
pro( root.left,ans );
ans.add( root.val );
pro( root.right,ans );
}
}
二叉树的后序遍历
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 后序遍历 。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans=new LinkedList<>( );
pro( root,ans );
return ans;
}
public void pro(TreeNode root,List<Integer> ans){
if (root==null){
return;
}
pro( root.left,ans );
pro( root.right,ans );
ans.add( root.val );
}
}
翻转二叉树
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
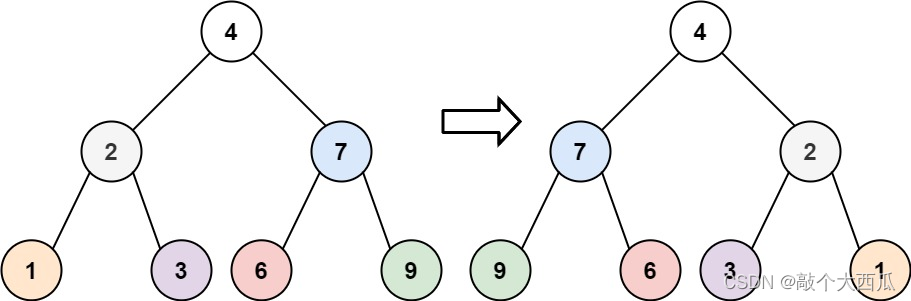
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root==null){
return null;
}
TreeNode left=invertTree( root.left );
TreeNode right=invertTree( root.right );
root.left=right;
root.right=left;
return root;
}
}
路经总和
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum 。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root==null){
return false;
}
if (root.left==null&&root.right==null){
return targetSum==root.val;
}
return hasPathSum( root.right,targetSum-root.val )||hasPathSum( root.left,targetSum-root.val );
}
}
用栈实现队列
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 推到队列的末尾
int pop() 从队列的开头移除并返回元素
int peek() 返回队列开头的元素
boolean empty() 如果队列为空,返回 true ;否则,返回 false
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stackin=new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> stackout=new Stack<>();
public MyQueue() {
}
public void push(int x) {
stackin.push( x );
}
public int pop() {
if (stackout.empty()){
while (!stackin.empty()){
stackout.push( stackin.pop() );
}
}
return stackout.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if (stackout.empty()){
while (!stackin.empty()){
stackout.push( stackin.pop() );
}
}
return stackout.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
if (stackout.empty()&&stackin.empty()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
有效的括号
给定一个只包括 ‘(’,‘)’,‘{’,‘}’,‘[’,‘]’ 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
int n = s.length();
if (n % 2 == 1) {
return false;
}
Map<Character, Character> pairs = new HashMap<Character, Character>() {{
put(')', '(');
put(']', '[');
put('}', '{');
}};
Deque<Character> stack = new LinkedList<Character>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char ch = s.charAt(i);
if (pairs.containsKey(ch)) {
if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.peek() != pairs.get(ch)) {
return false;
}
stack.pop();
} else {
stack.push(ch);
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
删除排序链表中的重复元素
给定一个已排序的链表的头 head , 删除所有重复的元素,使每个元素只出现一次 。返回 已排序的链表 。
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return head;
}
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur.next!=null){
if (cur.val==cur.next.val){
cur.next=cur.next.next;
}else {
cur= cur.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
题目解析:本题中的已排序决定我们可以用双指针
反转链表
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}
}





 本文涵盖多个SQL查询案例,包括查找重复电子邮件、合作频繁的演员导演等,同时提供了多种数据结构如矩阵、二叉树的操作方法,以及相关算法如广度优先搜索的应用实例。
本文涵盖多个SQL查询案例,包括查找重复电子邮件、合作频繁的演员导演等,同时提供了多种数据结构如矩阵、二叉树的操作方法,以及相关算法如广度优先搜索的应用实例。
















 842
842

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








