There is an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1 and n - 1 edges.
You are given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1 where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree. You are also given an integer array restricted which represents restricted nodes.
Return the maximum number of nodes you can reach from node 0 without visiting a restricted node.
Note that node 0 will not be a restricted node.
Example 1:
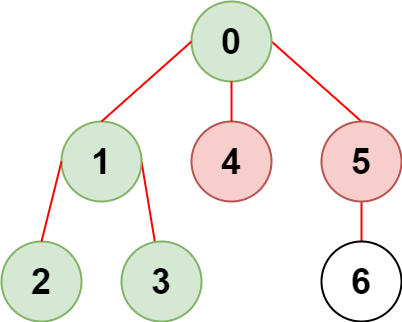
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[3,1],[4,0],[0,5],[5,6]], restricted = [4,5]
Output: 4
Explanation:
The diagram above shows the tree.
We have that [0,1,2,3] are the only nodes that can be reached from node 0 without visiting a restricted node.
Example 2:
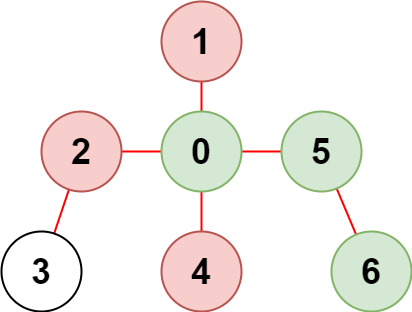
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,5],[0,4],[3,2],[6,5]], restricted = [4,2,1]
Output: 3
Explanation:
The diagram above shows the tree.
We have that [0,5,6] are the only nodes that can be reached from node 0 without visiting a restricted node.
Constraints:
- 2 <= n <= 105
- edges.length == n - 1
- edges[i].length == 2
- 0 <= ai, bi < n
- ai != bi
- edges represents a valid tree.
- 1 <= restricted.length < n
- 1 <= restricted[i] < n
- All the values of restricted are unique.
既然说是一棵树了, 那我们就把 0 作为 root,dfs 向下遍历整棵树就好了, 实现写的有些麻烦了, 因为这是棵树,所以任意两个 node 之间一定是只有唯一一条 edge 的, 所以检查的时候不需要 visited,只需要检查上一个 node 就可以了。
use std::collections::{HashMap, HashSet};
impl Solution {
fn dfs(
n: i32,
edges: &HashMap<i32, Vec<i32>>,
restricted: &HashSet<i32>,
visited: &mut HashSet<i32>,
ans: &mut i32,
) {
if restricted.contains(&n) || visited.contains(&n) {
return;
}
visited.insert(n);
*ans += 1;
for &e in edges.get(&n).unwrap() {
Solution::dfs(e, edges, restricted, visited, ans);
}
}
pub fn reachable_nodes(n: i32, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>, restricted: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let edges = edges.into_iter().fold(HashMap::new(), |mut m, v| {
m.entry(v[0]).or_insert(Vec::new()).push(v[1]);
m.entry(v[1]).or_insert(Vec::new()).push(v[0]);
m
});
let mut ans = 0;
Solution::dfs(
0,
&edges,
&restricted.into_iter().collect(),
&mut HashSet::new(),
&mut ans,
);
ans
}
}







 本文介绍了一种基于深度优先搜索(DFS)的方法来计算在给定的无向树中,从节点0出发不经过限制节点所能到达的最大节点数量。通过构建边的映射关系,并利用哈希集合进行快速查找,该算法有效地避免了访问限制节点。
本文介绍了一种基于深度优先搜索(DFS)的方法来计算在给定的无向树中,从节点0出发不经过限制节点所能到达的最大节点数量。通过构建边的映射关系,并利用哈希集合进行快速查找,该算法有效地避免了访问限制节点。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








