Given a binary tree where node values are digits from 1 to 9. A path in the binary tree is said to be pseudo-palindromic if at least one permutation of the node values in the path is a palindrome.
Return the number of pseudo-palindromic paths going from the root node to leaf nodes.
Example 1:
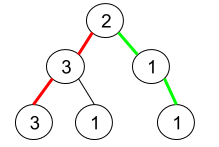
Input: root = [2,3,1,3,1,null,1]
Output: 2
Explanation: The figure above represents the given binary tree. There are three paths going from the root node to leaf nodes: the red path [2,3,3], the green path [2,1,1], and the path [2,3,1]. Among these paths only red path and green path are pseudo-palindromic paths since the red path [2,3,3] can be rearranged in [3,2,3] (palindrome) and the green path [2,1,1] can be rearranged in [1,2,1] (palindrome).
Example 2:
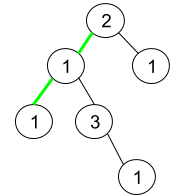
Input: root = [2,1,1,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,1]
Output: 1
Explanation: The figure above represents the given binary tree. There are three paths going from the root node to leaf nodes: the green path [2,1,1], the path [2,1,3,1], and the path [2,1]. Among these paths only the green path is pseudo-palindromic since [2,1,1] can be rearranged in [1,2,1] (palindrome).
Example 3:
Input: root = [9]
Output: 1
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 105].
- 1 <= Node.val <= 9
既然是任意组合能形成回文就可以,那其实就是只对数量有限制,对位置没限制, 形成回文对数量的限制无非就是奇数数量的字符最多只能有 1 个, 其他字符都必须是偶数个, 就这道题而言, 我们只需要维护对每一个数字的计数, 同时维护这些计数里面奇数数量的个数就可以了, 只要这个奇数计数<=1, 那就可以认定当前路径是可以形成回文的。
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {
fn rc(
root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
mut odd_count: i32,
mut counts: Vec<i32>,
ans: &mut i32,
) {
if let Some(node) = root {
let val = node.borrow().val;
counts[val as usize - 1] += 1;
if counts[val as usize - 1] % 2 == 1 {
odd_count += 1;
} else {
odd_count -= 1;
}
if node.borrow().left.is_none() && node.borrow().right.is_none() {
if odd_count == 0 || odd_count == 1 {
*ans += 1;
}
return;
}
Solution::rc(
node.borrow_mut().left.take(),
odd_count,
counts.clone(),
ans,
);
Solution::rc(
node.borrow_mut().right.take(),
odd_count,
counts.clone(),
ans,
);
}
}
pub fn pseudo_palindromic_paths(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
let mut ans = 0;
Solution::rc(root, 0, vec![0; 9], &mut ans);
ans
}
}







 该博客介绍了如何使用递归和深度优先搜索策略解决二叉树中伪回文路径的问题。在给定的二叉树中,如果节点值的任意排列可以形成回文串,则称该路径为伪回文路径。文章通过具体例子解释了算法的实现过程,包括维护每个数字出现次数的计数,并检查奇数数量是否不超过1,以确定路径是否能形成回文。最后,给出了基于Rust语言的解决方案代码片段,展示了如何遍历树并计算伪回文路径的数量。
该博客介绍了如何使用递归和深度优先搜索策略解决二叉树中伪回文路径的问题。在给定的二叉树中,如果节点值的任意排列可以形成回文串,则称该路径为伪回文路径。文章通过具体例子解释了算法的实现过程,包括维护每个数字出现次数的计数,并检查奇数数量是否不超过1,以确定路径是否能形成回文。最后,给出了基于Rust语言的解决方案代码片段,展示了如何遍历树并计算伪回文路径的数量。
















 1124
1124

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








