1. package access class with public constructor
// hiding/packageaccess/PublicConstructor.java
// (c)2017 MindView LLC: see Copyright.txt
// We make no guarantees that this code is fit for any purpose.
// Visit http://OnJava8.com for more book information.
package hiding.packageaccess;
class PublicConstructor {
public PublicConstructor() {}
}
2. access public construtor above
// hiding/CreatePackageAccessObject.java
// (c)2017 MindView LLC: see Copyright.txt
// We make no guarantees that this code is fit for any purpose.
// Visit http://OnJava8.com for more book information.
// {WillNotCompile}
import hiding.packageaccess.*;
public class CreatePackageAccessObject {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new PublicConstructor();// compile error
}
}
my compiler error message:
CreatePackageAccessObject.java:7: error: package hiding.packageaccess does not exist
import hiding.packageaccess.*;
^
CreatePackageAccessObject.java:11: error: cannot access PublicConstructor
new PublicConstructor();
^
bad source file: ./packageaccess/PublicConstructor.java
file does not contain class PublicConstructor
Please remove or make sure it appears in the correct subdirectory of the sourcepath.
2 errorsSummary, declaring a constructor public inside a packageaccess class doesn't actually make it public, and it should probably be flagged with a compiler error at the point of declaration.
The following table shows the access to members permitted by each modifier.
| Modifier | Class | Package | Subclass | World |
|---|---|---|---|---|
public | Y | Y | Y | Y |
protected | Y | Y | Y | N |
| no modifier | Y | Y | N | N |
private | Y | N | N | N |
Access levels affect you in two ways.
First, when you use classes that come from another source, such as the classes in the Java platform, access levels determine which members of those classes your own classes can use.
Second, when you write a class, you need to decide what access level every member variable and every method in your class should have.
Let's look at a collection of classes and see how access levels affect visibility. The following figure shows the four classes in this example and how they are related.
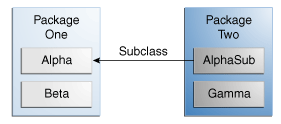
Classes and Packages of the Example Used to Illustrate Access Levels
The following table shows where the members of the Alpha class are visible for each of the access modifiers that can be applied to them.
| Modifier | Alpha | Beta | Alphasub | Gamma |
|---|---|---|---|---|
public | Y | Y | Y | Y |
protected | Y | Y | Y | N |
| no modifier | Y | Y | N | N |
private | Y | N | N | N |
Note the difference in column names between table Access Levels and table Visibility.
references:
1. On Java 8 - Bruce Eckel
2. https://github.com/wangbingfeng/OnJava8-Examples/blob/master/hiding/packageaccess/PublicConstructor.java
3. https://github.com/wangbingfeng/OnJava8-Examples/blob/master/hiding/CreatePackageAccessObject.java
4. https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/javaOO/accesscontrol.html




 本文深入探讨Java中不同访问修饰符对类成员可见性的影响,包括public、protected、默认(包访问)和private的使用场景及限制。通过实例说明如何正确设定类成员的访问级别,以实现良好的封装性和模块间协作。
本文深入探讨Java中不同访问修饰符对类成员可见性的影响,包括public、protected、默认(包访问)和private的使用场景及限制。通过实例说明如何正确设定类成员的访问级别,以实现良好的封装性和模块间协作。
















 814
814

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








