流布局的实现是熟悉自定义控件流程一个比较好的例子,在代码中详细注释:
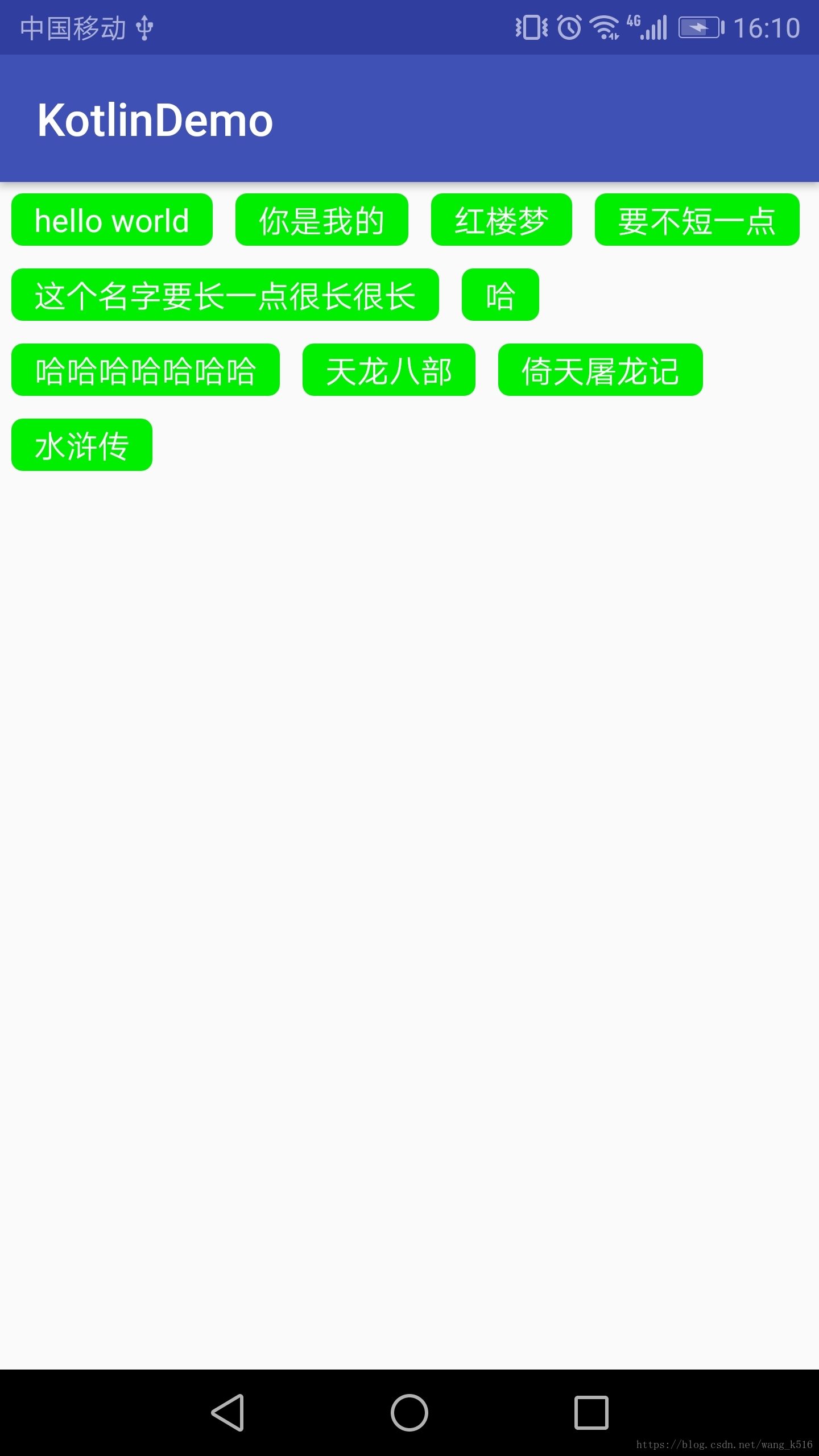
代码:
public class MyFlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
//每一行行高集合
List<Integer> heights = new ArrayList<>();
//每一行子view的集合
List<List<View>> views = new ArrayList<>();
public MyFlowLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public MyFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//从运行机制来讲,在7.0之前布局加载流程调用scheduleTraversals()
// 会依次调用onMeasure-->onLayout,
// 但是在7.0之后我门会发现运行机制发生了改变,
// 如果是第一次的onMeasure那么他不会去调用onLayout,
// 所以这里变成了两次onMeasure一次onLayout 此处清空第一次测量的结果
heights.clear();
views.clear();
//获取父布局的宽高以及自己的测量模式
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
//当前View的宽高
int measureWidth = 0;
int measureHeight = 0;
//记录当前行宽 高
int curLineWidth = 0;
int curLineHeight = 0;
//根据测量模式测量当前控件的尺寸
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {//全部match
measureHeight = heightSize;
measureWidth = widthSize;
} else {
//获取所有的child数量
int childCount = getChildCount();
//记录每一行的view
List<View> childViews = new ArrayList<>();
if (childCount > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);//测量子view
//获取子view的layoutparam 此处使用MarginLayoutParams可以获取其margin值 保证类型强转 需要重写generateLayoutParams方法
MarginLayoutParams childLayoutParam = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
//获取子view需要的尺寸
int iChildWidth = childLayoutParam.leftMargin + childLayoutParam.rightMargin + child.getMeasuredWidth();
int iChildHeight = childLayoutParam.topMargin + childLayoutParam.bottomMargin + child.getMeasuredHeight();
//是否需要换行
if (curLineWidth + iChildWidth > widthSize) {
//测量的当前View的宽高
measureWidth = Math.max(measureWidth, curLineWidth);
measureHeight += curLineHeight;
//记录这一行的子view
views.add(childViews);
//要换行了 记录这一行的行高
heights.add(curLineHeight);
//换行了 新的一行的行宽为当前子view的测量宽
curLineWidth = iChildWidth;
curLineHeight = iChildHeight;
//新的一行的view集合重新创建
childViews = new ArrayList<>();
childViews.add(child);
} else {//不换行 宽叠加 高取最大
childViews.add(child);
curLineWidth += iChildWidth;
curLineHeight = Math.max(iChildHeight, curLineHeight);
}
//最后一行的处理 刚好最后一行
if (i == childCount - 1) {
measureWidth = Math.max(measureWidth, curLineWidth);
measureHeight += curLineHeight;
views.add(childViews);
heights.add(curLineHeight);
}
}
}
}
setMeasuredDimension(measureWidth, measureHeight);//设置宽高
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
//定义左上右下
int left, top, right, bottom;
//定义当前的左和上 作为下一个view的左或者下一行的上
int curLeft = 0;
int curTop = 0;
//获取行数
int lineSize = views.size();
for (int i = 0; i < lineSize; i++) {
//获取每一行的view数量
List<View> childs = this.views.get(i);
int childCount = childs.size();
for (int j = 0; j < childCount; j++) {
View child = childs.get(j);
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
left = curLeft + params.leftMargin;
top = curTop + params.topMargin;
right = left + child.getMeasuredWidth();
bottom = top + child.getMeasuredHeight();
child.layout(left, top, right, bottom);
//记录当前的left top
curLeft += child.getMeasuredWidth() + params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin;
}
//一行结束了 左归位 上叠加
curLeft = 0;
curTop += heights.get(i);
}
//全部布局完成
heights.clear();
views.clear();
}
}
主要运用的自定义控件的测量和布局两个方法。






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








