<think>我们正在使用QCustomPlot在PyQt5中进行数据可视化。QCustomPlot是一个强大的Qt图表库,而PyQt5是Python的Qt绑定。下面将介绍如何在Python中使用QCustomPlot进行图表绘制。
### 步骤1:安装必要的库
首先,确保已经安装了PyQt5和sip。然后,我们需要安装QCustomPlot的Python绑定。可以通过pip安装:
```bash
pip install PyQt5
pip install pyqt5-tools # 可选,提供Qt Designer等工具
pip install PyQt5-sip
# 安装QCustomPlot的Python绑定
pip install qcustomplot_pyqt
```
### 步骤2:创建基本绘图窗口
以下是一个简单的示例,展示如何创建一个窗口并绘制一条曲线:
```python
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt
from PyQt5.QtGui import QPen
from qcustomplot_pyqt import QCustomPlot, QCPGraph, QCP
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("QCustomPlot Example")
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
# 创建QCustomPlot实例
self.customPlot = QCustomPlot()
self.setCentralWidget(self.customPlot)
# 添加一个图形
self.graph = self.customPlot.addGraph()
self.graph.setPen(QPen(Qt.blue)) # 设置线条颜色
# 准备数据
x = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
y = [0, 1, 4, 9, 16]
# 设置数据
self.graph.setData(x, y)
# 设置坐标轴标签
self.customPlot.xAxis.setLabel("x")
self.customPlot.yAxis.setLabel("y")
# 设置坐标轴范围
self.customPlot.xAxis.setRange(0, 4)
self.customPlot.yAxis.setRange(0, 16)
# 重绘图表
self.customPlot.replot()
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
```
### 步骤3:绘制多条曲线和设置样式
我们可以添加多个图形并设置不同的样式:
```python
# 在同一个窗口中添加第二条曲线
graph2 = self.customPlot.addGraph()
graph2.setPen(QPen(Qt.red))
graph2.setData([0,1,2,3,4], [0, 2, 1, 3, 4])
```
### 步骤4:添加交互功能
QCustomPlot支持多种交互操作,如缩放、平移和选择:
```python
# 启用缩放、拖拽和选择
self.customPlot.setInteractions(QCP.iRangeDrag | QCP.iRangeZoom | QCP.iSelectPlottables)
```
### 步骤5:绘制动态数据
动态更新数据需要定时器。以下是一个动态更新的例子:
```python
from PyQt5.QtCore import QTimer
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
# ... 初始化代码同上 ...
self.timer = QTimer()
self.timer.timeout.connect(self.update_plot)
self.timer.start(100) # 每100毫秒更新一次
# 初始化数据
self.x = []
self.y = []
self.count = 0
def update_plot(self):
# 生成新数据点
self.count += 0.1
self.x.append(self.count)
self.y.append(math.sin(self.count))
# 更新数据
self.graph.setData(self.x, self.y)
# 调整坐标轴范围
self.customPlot.xAxis.setRange(self.count-10, self.count)
self.customPlot.replot()
```
### 步骤6:自定义图表样式
QCustomPlot允许高度自定义,例如设置背景网格、标题等:
```python
# 设置背景网格
self.customPlot.xAxis.grid.setVisible(True)
self.customPlot.yAxis.grid.setVisible(True)
self.customPlot.xAxis.grid.setPen(QPen(QColor(200, 200, 200), 1, Qt.DotLine))
self.customPlot.yAxis.grid.setPen(QPen(QColor(200, 200, 200), 1, Qt.DotLine))
# 设置标题
self.customPlot.plotLayout().insertRow(0) # 插入一行用于标题
title = QCPTextElement(self.customPlot, "Sine Wave", QFont("sans", 12, QFont.Bold))
self.customPlot.plotLayout().addElement(0, 0, title)
```
### 注意事项
1. **性能优化**:当数据点很多时,使用`setData`可能会变慢。可以使用`QCPGraph.setData`的重载版本,它接受两个`QVector`(但在Python中我们通常用列表或数组)。对于极大数据量,考虑使用`QCPGraph.setData`的`QCPGraphDataContainer`版本,或者使用`addData`逐步添加数据。
2. **多线程**:如果需要在后台线程更新数据,注意Qt的GUI操作必须在主线程进行。可以使用信号槽机制将数据传递到主线程更新。
3. **资源文件**:如果使用QCustomPlot的样式文件(如.qss),需要按照之前提到的资源路径方法加载。
### 完整示例:动态正弦波
```python
import sys
import math
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow
from PyQt5.QtCore import QTimer, Qt
from PyQt5.QtGui import QPen, QColor, QFont
from qcustomplot_pyqt import QCustomPlot, QCP, QCPTextElement
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("Dynamic Sine Wave")
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
self.customPlot = QCustomPlot()
self.setCentralWidget(self.customPlot)
# 添加图形
self.graph = self.customPlot.addGraph()
self.graph.setPen(QPen(Qt.blue))
# 设置坐标轴标签
self.customPlot.xAxis.setLabel("Time")
self.customPlot.yAxis.setLabel("Amplitude")
# 设置交互
self.customPlot.setInteractions(QCP.iRangeDrag | QCP.iRangeZoom)
# 初始化数据
self.x = []
self.y = []
self.t = 0
# 设置定时器
self.timer = QTimer()
self.timer.timeout.connect(self.update_plot)
self.timer.start(50) # 20 FPS
def update_plot(self):
# 更新数据点
self.t += 0.1
self.x.append(self.t)
self.y.append(math.sin(self.t))
# 只保留最近100个点
if len(self.x) > 100:
self.x = self.x[-100:]
self.y = self.y[-100:]
# 更新图形数据
self.graph.setData(self.x, self.y)
# 调整X轴范围,使最新数据在右侧
self.customPlot.xAxis.setRange(self.t-10, self.t)
self.customPlot.yAxis.setRange(-1.5, 1.5)
# 重绘
self.customPlot.replot()
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
mainWin = MainWindow()
mainWin.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
```
### 常见问题
1. **导入错误**:确保安装的`qcustomplot_pyqt`版本与PyQt5版本兼容。如果遇到导入错误,尝试重新安装或检查依赖。
2. **性能问题**:对于实时数据流,避免每次重绘整个图表。可以只更新新增的数据点,并使用`QCustomPlot.rescaleAxes()`或手动设置范围。
3. **样式问题**:QCustomPlot的样式设置非常灵活,但需要参考其C++文档,因为Python绑定的文档可能不完整。
### 更多资源
- [QCustomPlot官方文档](https://www.qcustomplot.com/documentation/)
- [Python绑定示例](https://github.com/leoncvlt/qcustomplot-pyqt)
§§相关问题§§
1. 如何解决QCustomPlot在PyQt5中绘图时出现的内存泄漏问题?
2. QCustomPlot如何绘制柱状图、散点图等复杂图表?
3. 如何将QCustomPlot图表导出为图片或PDF?
4. 在PyQt5中如何实现多子图布局的QCustomPlot?
5. 如何优化QCustomPlot绘制大量数据点时的性能?</think>### Python中使用QCustomPlot进行数据可视化的完整指南
QCustomPlot是一个强大的C++绘图库,通过PyQt5绑定可在Python中实现高性能数据可视化。以下是详细使用指南:
#### 一、安装与环境配置
```bash
# 安装核心依赖
pip install pyqt5 pyqt5-tools sip
# 安装QCustomPlot Python绑定
pip install qcustomplot_pyqt
```
#### 二、基础绘图示例
```python
import sys
import math
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow
from PyQt5.QtGui import QPen, QColor
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt
from qcustomplot_pyqt import QCustomPlot, QCP
class PlotWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 800, 600)
# 创建QCustomPlot实例
self.customPlot = QCustomPlot()
self.setCentralWidget(self.customPlot)
# 添加两条曲线
self.graph1 = self.customPlot.addGraph()
self.graph2 = self.customPlot.addGraph()
# 设置曲线样式
self.graph1.setPen(QPen(Qt.blue))
self.graph2.setPen(QPen(Qt.red))
self.graph1.setBrush(QColor(0, 0, 255, 20)) # 填充区域
# 生成数据
x = [i/10.0 for i in range(100)]
y1 = [math.sin(val) for val in x]
y2 = [math.cos(val) * 0.5 for val in x]
# 设置数据
self.graph1.setData(x, y1)
self.graph2.setData(x, y2)
# 设置坐标轴
self.customPlot.xAxis.setLabel("X轴")
self.customPlot.yAxis.setLabel("Y轴")
self.customPlot.xAxis.setRange(0, 10)
self.customPlot.yAxis.setRange(-1.5, 1.5)
# 添加交互功能
self.customPlot.setInteractions(
QCP.iRangeDrag | QCP.iRangeZoom | QCP.iSelectPlottables
)
# 添加标题
self.customPlot.setTitle("正弦与余弦波形")
# 重绘图表
self.customPlot.replot()
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = PlotWindow()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
```
#### 三、核心功能详解
1. **图表类型支持**
- 折线图:`addGraph()`
- 散点图:`setScatterStyle(QCPScatterStyle(QCPScatterStyle.ssCircle))`
- 柱状图:使用`QCPBars`
```python
from qcustomplot_pyqt import QCPBars
bars = QCPBars(self.customPlot.xAxis, self.customPlot.yAxis)
bars.setData([1,2,3,4], [8,6,4,5])
```
2. **动态数据更新**
```python
def update_data(self):
new_x = [i/10.0 for i in range(100)]
new_y = [math.sin(val + time.time()/10) for val in new_x]
self.graph1.setData(new_x, new_y)
self.customPlot.replot()
# 使用定时器实现动态更新
self.timer = QTimer()
self.timer.timeout.connect(self.update_data)
self.timer.start(100) # 每100ms更新一次
```
3. **样式定制**
```python
# 曲线样式
self.graph1.setPen(QPen(QColor(255,100,0), 2, Qt.DashLine))
# 坐标轴样式
self.customPlot.xAxis.grid().setPen(QPen(QColor(200,200,200), 1, Qt.DotLine))
# 背景色
self.customPlot.setBackground(QColor(240, 240, 240))
# 图例
self.customPlot.legend.setVisible(True)
self.graph1.setName("正弦波")
self.graph2.setName("余弦波")
```
4. **交互功能**
```python
# 添加点选功能
self.customPlot.setSelectionTolerance(10) # 选择容差
# 连接选择信号
self.customPlot.selectionChangedByUser.connect(self.handle_selection)
def handle_selection(self):
if self.graph1.selected():
print("正弦曲线被选中")
```
#### 四、高级应用技巧
1. **多轴系统**
```python
# 创建右侧Y轴
self.customPlot.yAxis2.setVisible(True)
self.graph2.setValueAxis(self.customPlot.yAxis2)
self.customPlot.yAxis2.setLabel("右侧Y轴")
```
2. **实时数据可视化**
```python
# 使用环形缓冲区
self.data_buffer = collections.deque(maxlen=1000)
def add_data_point(self, value):
self.data_buffer.append((time.time(), value))
self.update_plot()
def update_plot(self):
x, y = zip(*self.data_buffer)
self.graph.setData(list(x), list(y))
self.customPlot.rescaleAxes()
self.customPlot.replot()
```
3. **导出图像**
```python
# 保存为PNG
self.customPlot.savePng("plot.png", 800, 600)
# 保存为PDF
self.customPlot.savePdf("plot.pdf")
```
#### 五、性能优化建议
1. 大数据集时启用OpenGL加速:
```python
self.customPlot.setOpenGl(True) # 需要系统支持OpenGL
```
2. 使用`setData`的`QVector`版本替代Python列表:
```python
from PyQt5.QtCore import QVector
x_vec = QVector([x for x in range(100)])
y_vec = QVector([math.sin(x) for x in range(100)])
self.graph.setData(x_vec, y_vec)
```
3. 禁用自动重绘,批量更新:
```python
self.customPlot.setAutoReplot(False)
# ...执行多次数据更新...
self.customPlot.replot()
```
#### 六、资源推荐
1. [官方示例代码库](https://github.com/nixgnauhcuy/QCustomPlot_Pyqt_Study) [^3]
2. [QCustomPlot文档](https://www.qcustomplot.com/documentation/)
3. 交互式学习工具:
```python
# 在图表上显示坐标值
self.customPlot.mouseMove.connect(self.show_coordinates)
def show_coordinates(self, event):
x = self.customPlot.xAxis.pixelToCoord(event.x())
y = self.customPlot.yAxis.pixelToCoord(event.y())
self.statusBar().showMessage(f"X: {x:.2f}, Y: {y:.2f}")
```
> **提示**:QCustomPlot在PyQt5中的使用与C++版本高度一致,遇到问题时参考C++文档通常也能解决[^1][^3]。
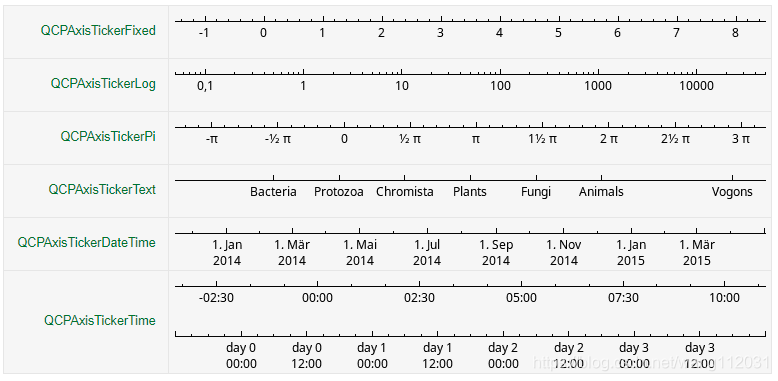





 本文介绍如何使用QCustomPlot库中的QCPAxisTickerDateTime类进行实时时序数据的绘图,包括设置时间刻度格式、调整刻度显示策略及实现数据的实时更新。
本文介绍如何使用QCustomPlot库中的QCPAxisTickerDateTime类进行实时时序数据的绘图,包括设置时间刻度格式、调整刻度显示策略及实现数据的实时更新。
















 616
616

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








