1. Mybatis简介
1.1 Mybatis特性
- 是一个基于Java的持久层框架
- MyBatis是支持定制化SQL、存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架
- MyBatis避免了几乎所有的JDBC代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集
- MyBatis可以使用简单的XML或注解用于配置和原始映射,将接口和Java的POJO(Plain Old Java Objects,普通的Java对象)映射成数据库中的记录
- MyBatis 是一个半自动的ORM(Object Relation Mapping)框架
1.2 和其它持久化层技术对比
- JDBC
- SQL夹杂在Java代码中耦合度高,导致硬编码内伤
- 维护不易且实际开发需求中SQL有变化,频繁修改的情况多见
- 代码冗长,开发效率低
- Hibernate和JPA
- 操作简便,开发效率高
- 程序中的长难复杂SQL需要绕过框架
- 内部自动生产的SQL,不容易做特殊优化
- 基于全映射的全自动框架,大量字段的POJO进行部分映射时比较困难。
- 反射操作太多,导致数据库性能下降
- MyBatis
- 轻量级,性能出色
- SQL和Java编码分开,功能边界清晰。Java代码专注业务、SQL语句专注数据
- 开发效率稍逊于HIbernate,但是完全能够接受
2. 搭建Mybatis
2.1 开发环境
- IDE:idea2021.3
- 构建工具:maven3.8.4
- MySQL版本:MySQL8.0.28
- MyBatis版本:MyBatis3.5.9
2.2 创建maven工程
- 打包方式:jar包
- 引入依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- Mybatis核心 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.9</version>
</dependency>
<!-- junit测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.28</version>
</dependency>
<!-- log4j日志 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.3 创建Mybatis的核心配置文件
- 习惯上命名为mybatis-config.xml,这个文件名仅仅只是建议,并非强制要求。存放的位置是src/main/resources目录下。将来整合Spring之后,这个配置文件可以省略,所以大家操作时可以直接复制、粘贴。核心配置文件主要用于配置连接数据库的环境以及MyBatis的全局配置信息
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!--
Mybatis核心配置文件中,标签的顺序有要求,不遵循会报错:
properties?,settings?,typeAliases?,typeHandlers?,objectFactory?,objectWrapperFactory?,
reflectorFactory?,plugins?,environments?,databaseIdProvider?,mappers?
-->
<!--引入properties文件,此时就可以${属性名}的方式访问属性值-->
<properties resource="jdbc.properties"/>
<!--设置类型别名(alias)-->
<typeAliases>
<!--
typeAlias:设置某个具体的类型的别名
属性:
type:需要设置别名的类型的全类名
alias:设置此类型的别名,若不设置此属性,该类型拥有默认的别名,即类名且不区分大小写
-->
<typeAlias type="com.atguigu.mybatis.pojo.User" alias="User"/>
<!--
以包为单位,设置该包下所有的类型都拥有默认的别名,即类名且不区分大小写
-->
<package name="com.atguigu.mybatis.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
<!--
environments:配置多个连接数据库的环境
属性default:来设置默认使用的环境的id,可以通过设置default的值来决定使用哪个环境
-->
<environments default="development">
<!--
environment:配置某个具体的连接数据库的环境
属性id:表示连接数据库的环境的唯一标识,不能重复
-->
<environment id="development">
<!--
transactionManager:事务管理器
属性type:设置事务的管理方式,其值有两种:JDBC/MANAGED
JDBC:表示当前环境中,执行SQL时,使用的是JDBC中原生的事务管理方式,事务的提交或回滚需要手动处理
MANAGED:设置事务被管理,例如spring
dataSource:配置数据源
属性type:设置数据源的类型,其值有三种:POOLED/UNPOOLED/JNDI
POOLED:表示使用数据库连接池缓存数据库连接,下次使用可以从缓存中直接获取,不需要重新创建
UNPOOLED:表示不使用数据库连接池
JNDI:表示使用上下文中的数据源
-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!--设置连接数据库的驱动、连接地址、用户名、密码-->
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="abc123"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
<environment id="test">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!--引入映射文件-->
<mappers>
<!--引入单个-->
<!--<mapper resource="mappers/UserMapper.xml"/>-->
<!--
以包为单位引入映射文件
要求:
1.mapper接口所在的包要和映射文件所在的包一致
2.mapper接口要和映射文件的名字一致
3.resource中创建包的方式:创建directory,命名方式用 "/" 隔开
-->
<package name="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
2.4 创建Mapper接口
- MyBatis中的mapper接口相当于以前的dao。但是区别在于,mapper仅仅是接口,我们不需要提供实现类。
public interface UserMapper {
/**
* Mybatis面向接口编程的两个一致:
* 1.映射文件的namespace要和mapper接口的全类名保持一致
* 2.映射文件中sql语句的id要和Mapper接口中的方法名一致
* 对应关系:
* 表 - 实体类 - mapper接口 - 映射文件
*/
/**
* 添加用户信息
*/
int insertUser();
/**
* 修改用户信息
*/
void updateUser();
/**
* 查询单个用户信息
*/
User selectUser();
/**
* 查询多个用户信息
*/
List<User> selectUsers();
/**
* 删除用户信息
*/
void deleteUser();
}
2.5 创建Mybatis的映射文件
- ORM:对象关系映射
- 对象:java的实体类对象
- 关系:关系型数据库
- 映射:二者之间的对应关系
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper">
<!--int insertUser();-->
<insert id="insertUser">
insert into t_user values(null,'admin','123456',23,'男','12345@qq.com')
</insert>
<!--void updateUser();-->
<update id="updateUser">
update t_user set username = '张三' where id = 3
</update>
<!--void deleteUser();-->
<delete id="deleteUser">
delete from t_user where id = 4
</delete>
<!--User selectUser();-->
<!--
查询功能的标签必须设置resultType或resultMap
resultType:设置的是默认的映射关系(要求表的字段名和java实体类的属性名一致,然后就可以自动创建映射关系,把查询出来的字段名为相对应的属性赋值)
resultMap:设置的是自定义的映射关系()
-->
<select id="selectUser" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.pojo.User">
select * from t_user where id = 2
</select>
<!--List<User> selectUsers();-->
<select id="selectUsers" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.pojo.User">
select * from t_user
</select>
</mapper>
2.6 通过junit测试功能
public class MybatisTest {
/**
* sqlSession默认不自动提交事务,需要使用sqlSession.commit()手动提交事务
* 若需要自动提交事务,可以使用qlSessionFactory.openSession(true)
*/
@Test
public void testMybatis() throws IOException {
//获取SQLSession:代表Java程序和数据库之间的会话。(HttpSession是Java程序和浏览器之间的会话)
//1.加载核心配置文件,读取配置文件,获取对应的字节输入流
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
//2.获取SQLSessionFactoryBuilder(是一个提供SQLSession的一个工厂对象的一个构件对象)对象
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
//3.获取SQLSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(is);
//4.获取Mybatis操作数据库的一个会话对象:SqlSession对象,此时通过SqlSession对象所操作的sql都会自动提交
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
//通过代理模式创建UserMapper接口的代理实现类对象
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
//测试功能
int result = userMapper.insertUser();
System.out.println("result:"+result);
//提交事务,使用sqlSessionFactory.openSession()获取sqlSession时,需要手动提交事务;
//使用sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true)获取sqlSession时,代表自动提交事务;
//sqlSession.commit();
}
}
2.7 加入log4j日志功能
###################加入依赖
<!-- log4j日志 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
###################加入log4j的配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE log4j:configuration SYSTEM "log4j.dtd">
<log4j:configuration xmlns:log4j="http://jakarta.apache.org/log4j/">
<appender name="STDOUT" class="org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender">
<param name="Encoding" value="UTF-8"/>
<layout class="org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout">
<param name="ConversionPattern" value="%-5p %d{MM-dd HH:mm:ss,SSS}%m (%F:%L) \n"/>
</layout>
</appender>
<logger name="java.sql">
<level value="debug"/>
</logger>
<logger name="org.apache.ibatis">
<level value="info"/>
</logger>
<root>
<level value="debug"/>
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
</root>
</log4j:configuration>
3. 核心配置文件详解
- 核心配置文件中的标签必须按照固定的顺序,否则会报错:
- properties?,settings?,typeAliases?,typeHandlers?,objectFactory?,objectWrapperFactory?,reflectorFactory?,plugins?,environments?,databaseIdProvider?,mappers?
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//MyBatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://MyBatis.org/dtd/MyBatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!--引入properties文件,此时就可以${属性名}的方式访问属性值-->
<properties resource="jdbc.properties"></properties>
<settings>
<!--将表中字段的下划线自动转换为驼峰-->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
<!--开启延迟加载-->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
<typeAliases>
<!--
typeAlias:设置某个具体的类型的别名
属性:
type:需要设置别名的类型的全类名
alias:设置此类型的别名,若不设置此属性,该类型拥有默认的别名,即类名且不区分大小写
若设置此属性,此时该类型的别名只能使用alias所设置的值
-->
<!--<typeAlias type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.User"></typeAlias>-->
<!--<typeAlias type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.User" alias="abc"></typeAlias>-->
<!--以包为单位,设置改包下所有的类型都拥有默认的别名,即类名且不区分大小写-->
<package name="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean"/>
</typeAliases>
<!--
environments:设置多个连接数据库的环境
属性default:设置默认使用的环境的id
-->
<environments default="mysql_test">
<!--
environment:设置具体的连接数据库的环境信息
属性id:设置环境的唯一标识,可通过environments标签中的default设置某一个环境的id,表示默认使用的环境
-->
<environment id="mysql_test">
<!--
transactionManager:设置事务管理方式
属性type:设置事务管理方式,type="JDBC|MANAGED"
type="JDBC":设置当前环境的事务管理都必须手动处理
type="MANAGED":设置事务被管理,例如spring中的AOP
-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!--
dataSource:设置数据源
属性type:设置数据源的类型,type="POOLED|UNPOOLED|JNDI"
type="POOLED":使用数据库连接池,即会将创建的连接进行缓存,下次使用可以从缓存中直接获取,不需要重新创建
type="UNPOOLED":不使用数据库连接池,即每次使用连接都需要重新创建
type="JNDI":调用上下文中的数据源
-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!--设置驱动类的全类名-->
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<!--设置连接数据库的连接地址-->
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<!--设置连接数据库的用户名-->
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<!--设置连接数据库的密码-->
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!--引入映射文件-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="UserMapper.xml"/>
<!--
以包为单位,将包下所有的映射文件引入核心配置文件
注意:此方式必须保证mapper接口和mapper映射文件必须在相同的包下
-->
<package name="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
4. Mybatis的增删改查
##########添加################
<!--int insertUser();-->
<insert id="insertUser">
insert into t_user values(null,'admin','123456',23,'男','12345@qq.com')
</insert>
##########修改################
<!--void updateUser();-->
<update id="updateUser">
update t_user set username = '张三' where id = 3
</update>
##########删除################
<!--void deleteUser();-->
<delete id="deleteUser">
delete from t_user where id = 4
</delete>
##########查询一个实体类对象################
<!--User selectUser();-->
<!--
查询功能的标签必须设置resultType或resultMap
resultType:设置的是默认的映射关系(要求表的字段名和java实体类的属性名一致,然后就可以自动创建映射关系,把查询出来的字段名为相对应的属性赋值)
resultMap:设置的是自定义的映射关系()
-->
<select id="selectUser" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.pojo.User">
select * from t_user where id = 2
</select>
##########查询集合################
<!--
当查询的数据为多条时,不能使用实体类作为返回值,只能使用集合,否则会抛出异常TooManyResultsException;
但是若查询的数据只有一条,可以使用实体类或集合作为返回值
-->
<!--List<User> selectUsers();-->
<select id="selectUsers" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.pojo.User">
select * from t_user
</select>
5. Mybatis获取参数值的两种方式(重点)
- Mybatis获取参数值的两种方式:${}和#{}
- ${}的本质是字符串拼接,可能会造成sql注入,' '需要手动拼接
- #{}的本质是占位符赋值,只需要把需要获取的值放在相对应的位置上
- ${}使用字符串拼接的方式拼接sql,若为字符串类型或日期类型的字段进行赋值,需要手动加单引号;但是#{}使用占位符赋值的方式拼接sql,此时为字符串类型或日期类型的字段进行赋值时,可以自动添加单引号
5.1 单个字面量类型的参数
- 若mapper接口中的方法参数为单个的字面量类型,此时可以使用${}和#{}以任意的名称获取参数的值,注意${}需要手动加单引号
public interface ParameterMapper {
/**
* 根据用户名查询用户信息
*/
User getUserByUserName(String username);
}
ParameterMapper.xml
<!--User getUserByUserName(String username);-->
<select id="getUserByUserName" resultType="User">
<!--select * from t_user where username = #{username}-->
select * from t_user where username = '${username}'
</select>
5.2 多个字面量类型的参数
- 若mapper接口中的方法参数为多个时,此时MyBatis会自动将这些参数放在一个map集合中,以arg0,arg1...为键,以参数为值;以param1,param2...为键,以参数为值;因此只需要通过${}和#{}访问map集合的键就可以获取相对应的值,注意${}需要手动加单引号
public interface ParameterMapper{
/**
* 通过用户名和密码进行验证登录
*/
User checkLogin(String username,String password);
}
ParameterMapper.xml
<!--User checkLogin(String username,String password);-->
<select id="checkLogin" resultType="User">
<!--select * from t_user where username = #{arg0} and password = #{arg1}-->
select * from t_user where username = '${arg0}' and password = '${arg1}'
</select>
5.3 map集合类型的参数
- 若mapper接口中的方法需要参数为多个时,可以手动创建map集合,将这些数据放在map中只需要通过${}和#{}访问map集合的键就可以获取相对应的值,注意${}需要手动加单引号
public interface ParameterMapper {
/**
* 通过用户名和密码进行验证登录(参数为map)
*/
User checkLoginByMap(Map<String,Object> map);
}
ParameterMapper.xml
<!--User checkLoginByMap(Map<String,Object> map);-->
<select id="checkLoginByMap" resultType="User">
select * from t_user where username = #{username} and password = #{password}
</select>
5.4 实体类类型的参数
- 若mapper接口中的方法参数为实体类对象时,此时可以使用${}和#{},通过访问实体类对象中的属性名获取属性值,注意${}需要手动加单引号
public interface ParameterMapper {
/**
* 添加一个用户信息
*/
int insertUser(User user);
}
ParameterMapper.xml
<!--int insertUser(User user);-->
<insert id="insertUser">
insert into t_user values(null,#{username},#{password},#{age},#{sex},#{email})
</insert>
5.5 使用@Param标识参数
- 可以通过@Param注解标识mapper接口中的方法参数,此时,会将这些参数放在map集合中,以@Param注解的value属性值为键,以参数为值;以param1,param2...为键,以参数为值;只需要通过${}和#{}访问map集合的键就可以获取相对应的值,注意${}需要手动加单引号
public interface ParameterMapper {
/**
* 验证登录(使用@param)
*/
User checkLoginByParam(@Param("username") String username, @Param("password") String password);
}
ParameterMapper.xml
<!--User checkLoginByParam(@Param("username") String username, @Param("password") String password);-->
<select id="checkLoginByParam" resultType="User">
select * from t_user where username = #{username} and password = #{password}
</select>
6. Mybatis的各种查询功能
6.1 查询一个实体类对象
/**
* 根据用户id查询用户信息
*/
User getUserById(@Param("id") Integer id);
<!--User getUserById(@Param("id") Integer id);-->
<select id="getUserById" resultType="User">
select * from t_user where id = #{id}
</select>
6.2 查询一个List集合
/**
* 查询所有的用户的信息
*/
List<User> getAllUser();
<!--List<User> getAllUser();-->
<select id="getAllUser" resultType="User">
select * from t_user
</select>
6.3 查询单个数据
/**
* 查询用户信息的总记录数
* 在Mybatis中,对于Java中常用的类型都设置了类型别名
* java.lang.Integer --> int|integer
* int --> _int|_integer
* Map --> map
* List --> list
*/
Integer getCount();
<!--Integer getCount();-->
<select id="getCount" resultType="java.lang.Integer">
select count(*) from t_user
</select>
6.4 查询一条数据为map集合
/**
* 根据id查询用户信息为一个map集合
*/
Map<String,Object> getUserByIdToMap(@Param("id") Integer id);
<!--Map<String,Object> getUserByIdToMap(@Param("id") Integer id);-->
<select id="getUserByIdToMap" resultType="map">
select * from t_user where id = #{id}
</select>
<!--结果:{password=123456, sex=男, id=1, age=23, username=admin}-->
6.5 查询多条数据为map集合
/**
* 查询所有用户信息为一个map集合
* 将表中的数据以map集合的方式查询,一条数据对应一个map;
* 若有多条数据,就会产生多个map集合,此时可以将这些map放在一个list集合中获取
*/
方式1:
List<Map<String,Object>> getAllUserToMap();
<!--List<Map<String,Object>> getAllUserToMap();-->
<select id="getAllUserToMap" resultType="map">
select * from t_user
</select>
/**
* 查询所有用户信息为一个map集合
* 将表中的数据以map集合的方式查询,一条数据对应一个map;
* 若有多条数据,就会产生多个map集合,并且最终要以一个map的方式返回数据
* 此时需要通过@MapKey注解设置Map集合的键,值是每条数据所对应的map集合
*/
方式2:
@MapKey("id")
Map<String,Object> getAllUserToMap();
<!--Map<String, Object> getAllUserToMap();-->
<select id="getAllUserToMap" resultType="map">
select * from t_user
</select>
结果:
<!--
{
1={password=123456, sex=男, id=1, age=23, username=admin},
2={password=123456, sex=男, id=2, age=23, username=张三},
3={password=123456, sex=男, id=3, age=23, username=张三}
}
-->
7. 特殊SQL的执行
7.1 模糊查询
/**
* 根据用户名模糊查询用户信息
*/
List<User> getUserByLike(@Param("username") String username);
<!--List<User> getUserByLike(@Param("username") String username);-->
<select id="getUserByLike" resultType="User">
<!--select * from t_user where username like '%${username}%'-->
<!--select * from t_user where username like concat('%',#{username},'%')-->
select * from t_user where username like "%"#{username}"%"
</select>
7.2 批量删除
/**
* 批量删除
*/
int deleteMore(@Param("ids") String ids);
<!--int deleteMore(@Param("ids") String ids);-->
<delete id="deleteMore">
delete from t_user where id in (${ids})
</delete>
7.3 动态设置表名
/**
* 查询指定表中的数据
*/
List<User> getUserByTableName(@Param("tableName") String tableName);
<!--List<User> getUserByTableName(@Param("tableName") String tableName);-->
<select id="getUserByTableName" resultType="User">
select * from ${tableName}
</select>
7.4 添加功能获取自增的主键
/**
* 添加用户信息
* useGeneratedKeys:设置使用自增的主键
* keyProperty:因为增删改有统一的返回值是受影响的行数
* 因此只能将获取的自增的主键放在传输的参数user对象的某个属性中
*/
int insertUser(User user);
<!--
int insertUser(User user);
useGeneratedKeys:设置当前标签中的sql使用了自增的主键(id)
keyProperty:将自增的主键(id)的值赋值给传输到映射文件中参数的某个属性
-->
<insert id="insertUser" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into t_user values(null,#{username},#{password},#{age},#{sex},#{email})
</insert>
8. 自定义映射resultMap
8.1 resultMap处理字段和属性的映射关系
- 若字段名和实体类中的属性名不一致,则可以通过resultMap设置自定义映射
<!--
resultMap:设置自定义映射
属性:
id:表示自定义映射的唯一标识
type:查询的数据要映射的实体类的类型
子标签:
id:设置主键的映射关系
result:设置普通字段的映射关系
association:设置多对一的映射关系
collection:设置一对多的映射关系
属性:
property:设置映射关系中实体类中的属性名
column:设置映射关系中表中的字段名
-->
<resultMap id="userMap" type="User">
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<result property="userName" column="user_name"></result>
<result property="password" column="password"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
</resultMap>
<!--List<User> testMohu(@Param("mohu") String mohu);-->
<select id="testMohu" resultMap="userMap">
<!--select * from t_user where username like '%${mohu}%'-->
select id,user_name,password,age,sex from t_user where user_name like concat('%',#{mohu},'%')
</select>
8.2 多对一映射处理
- 查询员工信息以及员工所对应的部门信息
8.2.1 实体类Emp和Dept
public class Dept {
private Integer did;
private String deptName;
private List<Emp> empList;//一对多
}
public class Emp implements Serializable {
private Integer eid;
private String empName;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
private String email;
private Dept dept;//多对一
}
8.2.2 级联方式处理映射关系
<resultMap id="empDeptMap" type="Emp">
<id column="eid" property="eid"></id>
<result column="ename" property="ename"></result>
<result column="age" property="age"></result>
<result column="sex" property="sex"></result>
<result column="did" property="dept.did"></result>
<result column="dname" property="dept.dname"></result>
</resultMap>
<!--Emp getEmpAndDeptByEid(@Param("eid") int eid);-->
<select id="getEmpAndDeptByEid" resultMap="empDeptMap">
select emp.*,dept.* from t_emp emp left join t_dept dept on emp.did = dept.did where emp.eid = #{eid}
</select>
8.2.3 使用association处理映射关系
<resultMap id="empAndDeptResultMap" type="Emp">
<id property="eid" column="eid"/>
<result property="empName" column="emp_name"/>
<result property="age" column="age"/>
<result property="sex" column="sex"/>
<result property="email" column="email"/>
<!--association:处理多对一的映射关系,property是实体类的属性,javaType是属性对应的实体类-->
<association property="dept" javaType="Dept">
<id property="did" column="did"/>
<result property="deptName" column="dept_name"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<!--Emp getEmpAndDeptById(@Param("eid") Integer eid); -->
<select id="getEmpAndDeptById" resultMap="empAndDeptResultMap">
select * from t_emp emp left join t_dept dept on emp.did = dept.did where emp.eid = #{eid}
</select>
8.2.4 分步查询
1>查询员工信息
/**
* 通过分步查询查询员工信息
*/
Emp getEmpByStep(@Param("eid") int eid);
<resultMap id="empDeptStepMap" type="Emp">
<id column="eid" property="eid"></id>
<result column="ename" property="ename"></result>
<result column="age" property="age"></result>
<result column="sex" property="sex"></result>
<!--
select:设置分步查询,查询某个属性的值的sql的标识(namespace.sqlId)
column:将sql以及查询结果中的某个字段设置为分步查询的条件
-->
<association property="dept" select="com.atguigu.MyBatis.mapper.DeptMapper.getEmpDeptByStep" column="did"></association>
</resultMap>
<!--Emp getEmpByStep(@Param("eid") int eid);-->
<select id="getEmpByStep" resultMap="empDeptStepMap">
select * from t_emp where eid = #{eid}
</select>
2>根据员工所对应的部门id查询部门信息
/**
* 分步查询的第二步:根据员工所对应的did查询部门信息
*/
Dept getEmpDeptByStep(@Param("did") int did);
<!--Dept getEmpDeptByStep(@Param("did") int did);-->
<select id="getEmpDeptByStep" resultType="Dept">
select * from t_dept where did = #{did}
</select>
8.3 一对多映射处理
8.3.1 使用collection处理映射关系
/**
* 根据部门id查新部门以及部门中的员工信息
*/
Dept getDeptEmpByDid(@Param("did") int did);
<resultMap id="deptEmpMap" type="Dept">
<id property="did" column="did"></id>
<result property="dname" column="dname"></result>
<!--
ofType:设置collection标签所处理的集合属性中存储数据的类型
-->
<collection property="emps" ofType="Emp">
<id property="eid" column="eid"></id>
<result property="ename" column="ename"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<!--Dept getDeptEmpByDid(@Param("did") int did);-->
<select id="getDeptEmpByDid" resultMap="deptEmpMap">
select dept.*,emp.* from t_dept dept left join t_emp emp on dept.did = emp.did where dept.did = #{did}
</select>
8.3.2 分步查询
1>查询部门信息
/**
* 分步查询部门和部门中的员工
*/
Dept getDeptByStep(@Param("did") int did);
<resultMap id="deptEmpStep" type="Dept">
<id property="did" column="did"></id>
<result property="dname" column="dname"></result>
<collection property="emps" fetchType="eager" select="com.atguigu.MyBatis.mapper.EmpMapper.getEmpListByDid" column="did"></collection>
</resultMap>
<!--Dept getDeptByStep(@Param("did") int did);-->
<select id="getDeptByStep" resultMap="deptEmpStep">
select * from t_dept where did = #{did}
</select>
2>查询员工信息
/**
* 根据部门id查询员工信息
*/
List<Emp> getEmpListByDid(@Param("did") int did);
<!--List<Emp> getEmpListByDid(@Param("did") int did);-->
<select id="getEmpListByDid" resultType="Emp">
select * from t_emp where did = #{did}
</select>
8.4 分步查询的优点
- 可以实现延迟加载,但是必须在核心配置文件中设置全局配置信息
- lazyLoadingEnabled:延迟加载的全局开关。当开启时,所有关联对象都会延迟加载
- aggressiveLazyLoading:当开启时,任何方法的调用都会加载该对象的所有属性。 否则,每个属性会按需加载
- 此时就可以实现按需加载,获取的数据是什么,就只会执行相应的sql。此时可通过association和collection中的fetchType属性设置当前的分步查询是否使用延迟加载,fetchType="lazy(延迟加载)|eager(立即加载)"
9. 动态SQL
- Mybatis框架的动态SQL技术是一种根据特定条件动态拼装SQL语句的功能,它存在的意义是为了解决拼接SQL语句字符串时的痛点问题。
9.1 if
- if标签可通过test属性的表达式进行判断,若表达式的结果为true,则标签中的内容会执行;反之标签中的内容不会执行
- SQL语句:select * from t_emp where 1=1中,where 1=1 是为了避免where 关键字后面的第一个词直接就是 “and”而导致语法错误。 因为table中根本就没有名称为1的字段,所以该SQL等效于select * from t_emp
<!--List<Emp> getEmpListByMoreTJ(Emp emp);-->
<select id="getEmpListByMoreTJ" resultType="Emp">
select * from t_emp where 1=1
<if test="empName != '' and empName != null">
and emp_name = #{empName}
</if>
<if test="age != '' and age != null">
and age = #{age}
</if>
<if test="sex != '' and sex != null">
and sex = #{sex}
</if>
<if test="email != '' and email != null">
and email = #{email}
</if>
</select>
9.2 where
- where和if一般结合使用:
- 若where标签中的if条件都不满足,则where标签没有任何功能,即不会添加where关键字
- 若where标签中的if条件满足,则where标签会自动添加where关键字,并将条件最前方多余的and去掉
- 注意:where标签不能去掉条件最后多余的and
<select id="getEmpListByMoreTJ2" resultType="Emp">
select * from t_emp
<where>
<if test="empName != '' and empName != null">
emp_name = #{empName}
</if>
<if test="age != '' and age != null">
and age = #{age}
</if>
<if test="sex != '' and sex != null">
and sex = #{sex}
</if>
<if test="email != '' and email != null">
and email = #{email}
</if>
</where>
</select>
9.3 trim
- trim用于去掉或添加标签中的内容
- 常用属性:
- prefix:在trim标签中的内容的前面添加某些内容
- prefixOverrides:在trim标签中的内容的前面去掉某些内容
- suffix:在trim标签中的内容的后面添加某些内容
- suffixOverrides:在trim标签中的内容的后面去掉某些内容
<select id="getEmpListByMoreTJ" resultType="Emp">
select * from t_emp
<trim prefix="where" suffixOverrides="and|or">
<if test="empName != '' and empName != null">
emp_name = #{empName} and
</if>
<if test="age != '' and age != null">
age = #{age} or
</if>
<if test="sex != '' and sex != null">
sex = #{sex} and
</if>
<if test="email != '' and email != null">
email = #{email} and
</if>
</trim>
</select>
9.4 choose、when、otherwise
- choose、when、otherwise相当于if...else if..else
<!--List<Emp> getEmpByChoose(Emp emp);-->
<select id="getEmpByChoose" resultType="Emp">
select * from t_emp
<where>
<choose>
<when test="empName != '' and empName != null">
emp_name = #{empName}
</when>
<when test="age != '' and age != null">
age = #{age}
</when>
<when test="sex != '' and sex != null">
sex = #{sex}
</when>
<when test="email != '' and email != null">
email = #{email}
</when>
<otherwise>
did = 1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
9.5 foreach
- 属性:
- collection:设置要循环的数组或集合
- item:表示集合或数组中的每一个数据
- separator:设置循环体之间的分隔符
- open:设置foreach标签中的内容的开始符
- close:设置foreach标签中的内容的结束符
<!--int insertMoreByList(@Param("emps") List<Emp> emps);-->
<insert id="insertMoreByList">
insert into t_emp values
<foreach collection="emps" item="emp" separator=",">
(null,#{emp.empName},#{emp.age},#{emp.sex},#{emp.email},null)
</foreach>
</insert>
<!--int deleteMoreByArray(@Param("eids") Integer[] eids);-->
<delete id="deleteMoreByArray">
delete from t_emp where
<foreach collection="eids" item="eid" separator="or">
eid = #{eid}
</foreach>
</delete>
<!--int deleteMoreByArray(int[] eids);-->
<delete id="deleteMoreByArray">
delete from t_emp where eid in
<foreach collection="eids" item="eid" separator="," open="(" close=")">
#{eid}
</foreach>
</delete>
9.6 SQL片段
- sql片段,可以记录一段公共sql片段,在使用的地方通过include标签进行引入
<sql id="empColumns">
eid,ename,age,sex,did
</sql>
select <include refid="empColumns"></include> from t_emp
10. Mybatis的缓存
10.1 Mybatis的一级缓存
- 一级缓存是SqlSession级别的,通过同一个SqlSession查询的数据会被缓存,下次查询相同的数据,就会从缓存中直接获取,不会从数据库重新访问
- 使一级缓存失效的四种情况:
- 不同的SqlSession对应不同的一级缓存
- 同一个SqlSession但是查询条件不同
- 同一个SqlSession两次查询期间执行了任何一次增删改操作
- 同一个SqlSession两次查询期间手动清空了缓存
10.2 Mybatis的二级缓存
- 二级缓存是SqlSessionFactory级别,通过同一个SqlSessionFactory创建的SqlSession查询的结果会被缓存;此后若再次执行相同的查询语句,结果就会从缓存中获取
- 二级缓存开启的条件:
- 在核心配置文件中,设置全局配置属性cacheEnabled="true",默认为true,不需要设置
- 在映射文件中设置标签:<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"/>
- 二级缓存必须在SqlSession关闭或提交之后有效
- 查询的数据所转换的实体类类型必须实现序列化的接口
- 使二级缓存失效的情况:
- 两次查询之间执行了任意的增删改,会使一级和二级缓存同时失效
10.3 二级缓存的相关配置
- 在mapper配置文件中添加的cache标签可以设置一些属性:
- eviction属性:缓存回收策略
- LRU(Least Recently Used) – 最近最少使用的:移除最长时间不被使用的对象。
- FIFO(First in First out) – 先进先出:按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。
- SOFT – 软引用:移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象。
- WEAK – 弱引用:更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象。
- 默认的是 LRU。
- flushInterval属性:刷新间隔,单位毫秒
- 默认情况是不设置,也就是没有刷新间隔,缓存仅仅调用语句时刷新
- size属性:引用数目,正整数
- 代表缓存最多可以存储多少个对象,太大容易导致内存溢出
- readOnly属性:只读,true/false
- true:只读缓存;会给所有调用者返回缓存对象的相同实例。因此这些对象不能被修改。这提供了很重要的性能优势。
- false:读写缓存;会返回缓存对象的拷贝(通过序列化)。这会慢一些,但是安全,因此默认是false。
- eviction属性:缓存回收策略
10.4 MyBatis缓存查询的顺序
- 先查询二级缓存,因为二级缓存中可能会有其他程序已经查出来的数据,可以拿来直接使用。
- 如果二级缓存没有命中,再查询一级缓存
- 如果一级缓存也没有命中,则查询数据库
- SqlSession关闭之后,一级缓存中的数据会写入二级缓存
10.5 整合第三方缓存EHCache
10.5.1 添加依赖
<!-- Mybatis EHCache整合包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.caches</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>1.2.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- slf4j日志门面的一个具体实现 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
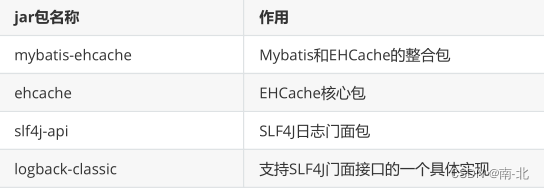
10.5.2 各jar包功能
10.5.3 创建EHCache的配置文件ehcache.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="../config/ehcache.xsd">
<!-- 磁盘保存路径 -->
<diskStore path="D:\atguigu\ehcache"/>
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="1000"
maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="true"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
</defaultCache>
</ehcache>
10.5.4 在CacheMapper.xml映射文件中设置二级缓存的类型
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"/>
10.5.5 加入logback日志
- 存在SLF4j时,作为简易日志的log4j将失效,此时我们需要借助SLF4j的具体实现logback来打印日志。创建logback的配置文件logback.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration debug="true">
<!-- 指定日志输出的位置 -->
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<!-- 日志输出的格式 -->
<!-- 按照顺序分别是:时间、日志级别、线程名称、打印日志的类、日志主体内容、换行 -->
<pattern>[%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS}] [%-5level] [%thread] [%logger] [%msg]%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!--设置全局日志级别。日志级别按顺序分别是:DEBUG、INFO、WARN、ERROR -->
<!-- 指定任何一个日志级别都只打印当前级别和后面级别的日志。 -->
<root level="DEBUG">
<!-- 指定打印日志的appender,这里通过“STDOUT”引用了前面配置的appender -->
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
</root>
<!-- 根据特殊需求指定局部日志级别 -->
<logger name="com.atguigu.crowd.mapper" level="DEBUG"/>
</configuration>
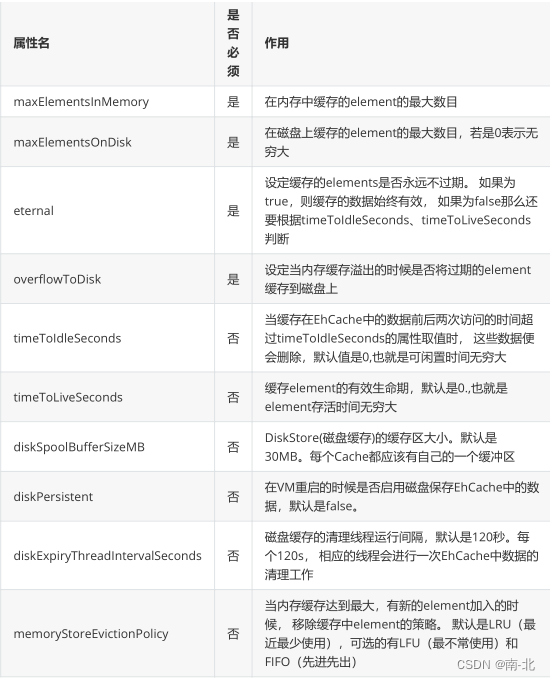
10.5.6 EHCache配置文件说明
11. Mybatis的逆向工程
- 正向工程:先创建java实体类,由框架负责根据实体类生成数据库表,Hibernate是支持正向工程的
- 逆向工程:先创建数据库表,由框架负责根据数据库表,反向生成如下资源:
- java实体类
- Mapper接口
- Mapper映射文件
11.1 创建逆向工程的步骤
①.添加依赖和插件
<dependencies>
<!-- Mybatis核心 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.9</version>
</dependency>
<!-- junit测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.28</version>
</dependency>
<!-- log4j日志 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!-- 控制Maven在构建过程中相关配置 -->
<build>
<!-- 构建过程中用到的插件 -->
<plugins>
<!-- 具体插件,逆向工程的操作是以构建过程中插件形式出现的 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generator</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.3.0</version>
<!-- 插件的依赖 -->
<dependencies>
<!-- 逆向工程的核心依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generator</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator-core</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据库连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mchange</groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0</artifactId>
<version>0.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.28</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
②.创建Mybatis的核心配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<properties resource="jdbc.properties"/>
<typeAliases>
<package name=""/>
</typeAliases>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<package name=""/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
③.创建逆向工程的配置文件,文件名必须是:generatorConfig.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE generatorConfiguration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD MyBatis Generator Configuration 1.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-generator-config_1_0.dtd">
<generatorConfiguration>
<!--
targetRuntime: 用于选择执行生成的逆向工程的版本
MyBatis3Simple: 生成基本的CRUD(清新简洁版)
MyBatis3: 生成带条件的CRUD(奢华尊享版)
-->
<context id="DB2Tables" targetRuntime="MyBatis3">
<!-- 数据库的连接信息 -->
<jdbcConnection driverClass="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"
connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC"
userId="root"
password="abc123">
</jdbcConnection>
<!--
javaBean(实体类)的生成策略
targetPackage:包名;
targetProject:包的位置
-->
<javaModelGenerator targetPackage="com.atguigu.mybatis.pojo" targetProject=".\src\main\java">
<!--enableSubPackages:是否能够使用子包;trimStrings:去掉字符串前后的空格-->
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="true" />
<property name="trimStrings" value="true" />
</javaModelGenerator>
<!-- SQL映射文件的生成策略 -->
<sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper" targetProject=".\src\main\resources">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="true" />
</sqlMapGenerator>
<!-- Mapper接口的生成策略 -->
<javaClientGenerator type="XMLMAPPER" targetPackage="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper" targetProject=".\src\main\java">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="true" />
</javaClientGenerator>
<!-- 逆向分析的表 -->
<!-- tableName设置为*号,可以对应所有表,此时不写domainObjectName -->
<!-- domainObjectName属性指定生成出来的实体类的类名 -->
<table tableName="t_emp" domainObjectName="Emp"/>
<table tableName="t_dept" domainObjectName="Dept"/>
</context>
</generatorConfiguration>
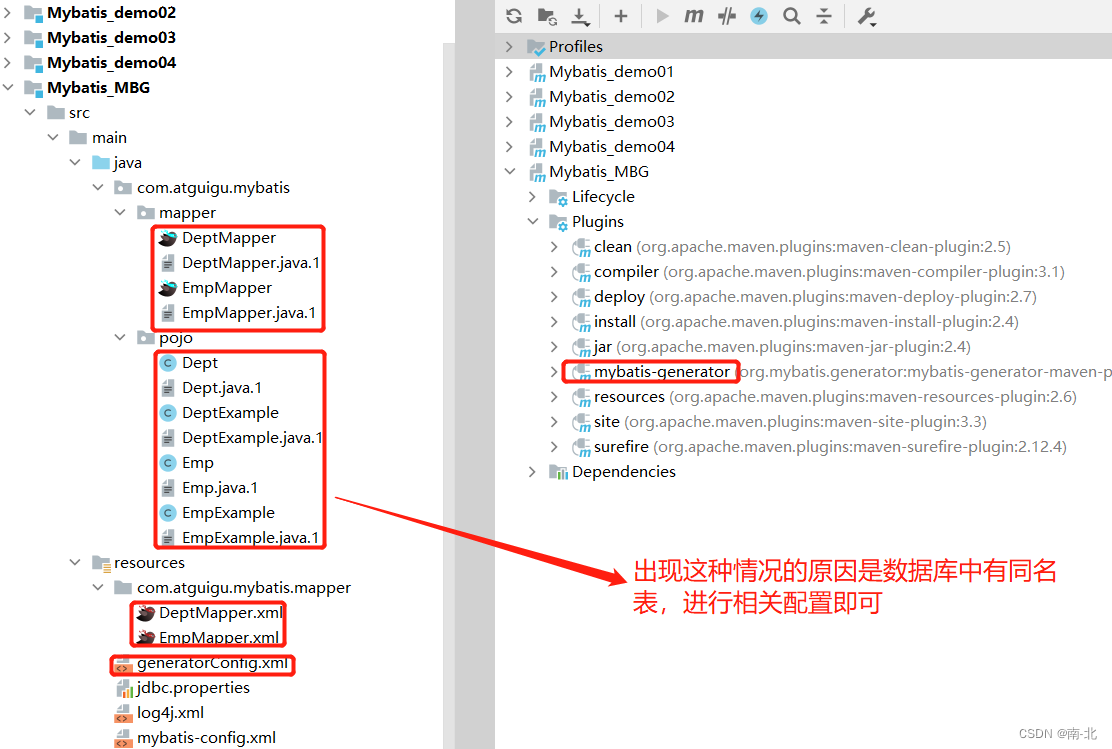
④.执行MBG插件的generate目标
11.2 QBC查询
@Test
public void testMBG() throws IOException {
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSession sqlSession = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is).openSession(true);
EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class);
EmpExample empExample = new EmpExample();
//创建条件对象,通过andXXX方法为SQL添加查询添加,每个条件之间是and关系
empExample.createCriteria().andEnameLike("a").andAgeGreaterThan(20).andDidIsNotNull();
//将之前添加的条件通过or拼接其他条件
empExample.or().andSexEqualTo("男");
List<Emp> list = mapper.selectByExample(empExample);
for (Emp emp : list) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
12. 分页插件
12.1 添加依赖,并配置分页插件
<!--分页插件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId>
<version>5.2.0</version>
</dependency>
###################在Mybatis的核心配置文件中配置插件
<plugins>
<!--设置分页插件-->
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"/>
</plugins>
12.2 分页插件的使用
- 在查询功能之前使用PageHelper.startPage(int pageNum, int pageSize)开启分页功能
- pageNum:当前页的页码
- pageSize:每页显示的条数
- 在查询获取list集合之后,使用PageInfo<T> pageInfo = new PageInfo<>(List<T> list, int navigatePages)获取分页相关数据
- list:分页之后的数据
- navigatePages:导航分页的页码数
public class PageHelperTest {
/**
* sql分页:
* limit index,pageSize
* index:当前页的起始索引
* pageSize:每页显示的条数
* pageNum:当前页的页码
* index=(pageNum-1)*pageSize
*
* 使用Mybatis的分页插件实现分页功能:
* 1.在查询功能之前开启分页:PageHelper.startPage(int pageNum, int pageSize)开启分页功能
* pageNum:当前页的页码
* pageSize:每页显示的条数
* 2.在查询获取list集合之后,使用PageInfo<T> pageInfo = new PageInfo<>(List<T> list, int navigatePages)获取分页相关信息
* list:表示分页数据
* navigatePages:表示当前导航分页的数量
*/
@Test
public void testPageHelper(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();
EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class);
//查询功能之前开启分页功能
PageHelper.startPage(2, 3);
List<Emp> emps = mapper.getEmps();
emps.forEach(System.out::println);
//在查询获取list集合之后,使用PageInfo<T> pageInfo = new PageInfo<>(List<T> list, int navigatePages)获取分页相关数据
//list:分页之后的数据
//navigatePages:导航分页的页码数
PageInfo<Emp> pageInfo = new PageInfo<>(emps,3);
System.out.println(pageInfo);
}
}
 MyBatis框架详解与实践
MyBatis框架详解与实践




















 5万+
5万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








