什么是 Server-Sent Events?
Server-Sent Events(SSE)是一种允许服务器向客户端实时推送数据的 Web 技术。与传统的轮询或长轮询相比,SSE 提供了更高效、更简单的服务器到客户端的单向通信机制。
SSE 的核心特点
- 单向通信:服务器 → 客户端。
- 基于 HTTP:使用标准 HTTP 协议,无需特殊协议。
- 自动重连:内置连接断开自动重连机制。
- 简单易用:浏览器原生支持,API 简洁。
- 文本数据传输:适合传输文本格式的数据。
SSE 与 WebSocket 的对比
| 特性 | SSE | WebSocket |
|---|---|---|
| 通信方向 | 单向(服务器→客户端) | 双向 |
| 协议 | HTTP | 自定义协议(ws://) |
| 复杂度 | 简单 | 相对复杂 |
| 重连机制 | 内置自动重连 | 需要手动实现 |
| 数据传输 | 文本数据 | 文本和二进制数据 |
| 浏览器支持 | 大部分现代浏览器 | 广泛支持 |
SSE 协议详解
事件流格式
SSE 使用简单的文本格式传输数据:
event: message
data: 这是一条普通消息
event: update
data: {"type": "status", "value": "online"}
id: 123
retry: 5000
: 这是一条注释
字段说明
data:必需字段,消息内容(可多行)。event:可选,事件类型(默认:message)。。id:可选,事件ID,用于重连时指定最后接收的事件。retry:可选,重连时间(毫秒)。。::注释行,会被客户端忽略。
客户端实现
基本用法
// 创建 EventSource 连接
const eventSource = new EventSource('/events');
// 监听消息事件(默认事件类型)
eventSource.onmessage = function(event) {
console.log('收到消息:', event.data);
};
// 监听自定义事件
eventSource.addEventListener('customEvent', function(event) {
const data = JSON.parse(event.data);
console.log('自定义事件:', data);
});
// 监听连接打开
eventSource.onopen = function() {
console.log('连接已建立');
};
// 监听错误
eventSource.onerror = function() {
console.log('连接错误');
};
服务器端实现
Node.js + Express 示例
import express from "express";
import cors from "cors";
const app = express();
const PORT = 8090;
// 中间件
app.use(cors({
origin: '*',
methods: 'GET,HEAD,PUT,PATCH,POST,DELETE',
preflightContinue: false,
optionsSuccessStatus: 200,
credentials: true,
}));
app.use(express.json());
// EventSource 路由
app.get('/events', async (req, res) => {
const convId = Date.now();
// 设置 SSE 头
res.writeHead(200, {
'Content-Type': 'text/event-stream',
});
// 发送初始连接消息
res.write(`data:${JSON.stringify({type: "text", data: `你好:${req.body.msg},你的幸运数字为:`,convId})}\n\n`);
await Promise.all(Array.from({length: 10}, async () => {
const randomValue = Math.floor(Math.random() * 1000);
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, randomValue));
res.write(`data:${JSON.stringify({id: Date.now(), type: "text", data: randomValue, convId})}\n\n`);
}))
res.write(`data:${JSON.stringify({id: Date.now(), type: "text", data: "end", convId})}\n\n`);
// 客户端断开连接时清理
req.on('close', () => {
console.log('客户端断开连接');
});
});
// 启动服务器
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`EventSource 服务器运行在 http://localhost:${PORT}`);
});
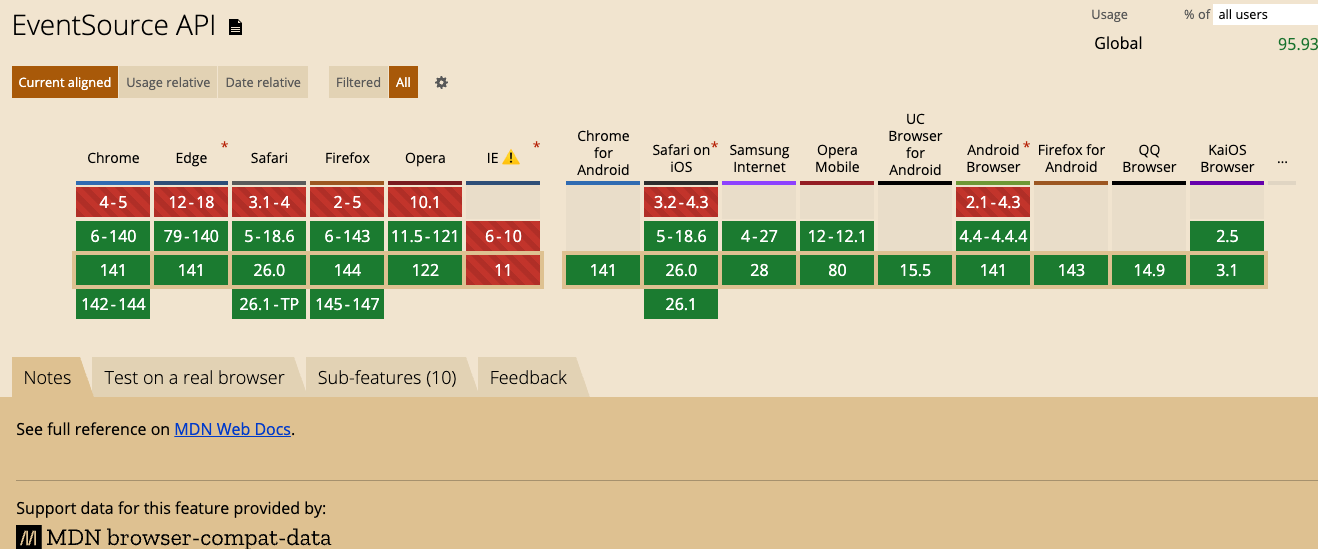
浏览器兼容性
SSE 在现代浏览器中得到了很好的支持:
- Chrome 6+
- Firefox 6+
- Safari 5+
- Edge 79+
POST 请求兼容
EventSource 默认不支持 POST 请求请求。设计目标是简化从服务器接收实时更新的过程。其工作方式和限制包括:
- 设计初衷:HTML5 中的
EventSource接口主要用于让网页能自动获取来自服务器的更新。在客户端,你通过一个 URL 实例化EventSource对象来建立连接。 - 单向通信:SSE 本质上是服务器到客户端的单向通信。客户端通过
EventSource发起连接后,服务器便可以随时通过这个连接向客户端推送数据。这种模式使得 GET 请求成为自然的选择,因为它通常用于从服务器获取数据。 - API 限制:标准的
EventSource构造函数只接受 URL 和可选的配置对象(如withCredentials),但不允许你指定请求方法或自定义请求头。这也是你不能用它直接发送 POST 请求的原因之一。
如果你确实需要使用 POST 方法,网上其实有很多方案,比如使用 @microsoft/fetch-event-source 库,小伙伴们自己去尝试一下。
我们换个方式,尝试从 EventSource 源码来支持下 POST 请求,以及修改 Header 参数等其它的一些定制需求。
方式一:修改 EventSource 源码
直接找一份 EventSourcePollyfill 的源码:https://github.com/EventSource/eventsource
我们换一个名字叫 MEventSource.js:
import {createParser} from './Parser'
import {ErrorEvent, flattenError, syntaxError} from './errors.js'
/**
* An `EventSource` instance opens a persistent connection to an HTTP server, which sends events
* in `text/event-stream` format. The connection remains open until closed by calling `.close()`.
*
* @public
* @example
* ```js
* const eventSource = new EventSource('https://example.com/stream')
* eventSource.addEventListener('error', (error) => {
* console.error(error)
* })
* eventSource.addEventListener('message', (event) => {
* console.log('Received message:', event.data)
* })
* ```
*/
export class MEventSource extends EventTarget {
/**
* ReadyState representing an EventSource currently trying to connect
*
* @public
*/
/**
* ReadyState representing an EventSource currently trying to connect
*
* @public
*/
static CONNECTING = 0;
/**
* ReadyState representing an EventSource connection that is open (eg connected)
*
* @public
*/
static OPEN = 1;
/**
* ReadyState representing an EventSource connection that is closed (eg disconnected)
*
* @public
*/
static CLOSED = 2;
/**
* Returns the state of this EventSource object's connection. It can have the values described below.
*
* [MDN Reference](https://developer.mozilla.org/docs/Web/API/EventSource/readyState)
*
* Note: typed as `number` instead of `0 | 1 | 2` for compatibility with the `EventSource` interface,
* defined in the TypeScript `dom` library.
*
* @public
*/
get readyState() {
return this.#readyState
}
/**
* Returns the URL providing the event stream.
*
* [MDN Reference](https://developer.mozilla.org/docs/Web/API/EventSource/url)
*
* @public
*/
get url() {
return this.#url.href
}
/**
* Returns true if the credentials mode for connection requests to the URL providing the event stream is set to "include", and false otherwise.
*
* [MDN Reference](https://developer.mozilla.org/docs/Web/API/EventSource/withCredentials)
*/
get withCredentials() {
return this.#withCredentials
}
/** [MDN Reference](https://developer.mozilla.org/docs/Web/API/EventSource/error_event) */
get onerror() {
return this.#onError
}
set onerror(value) {
this.#onError = value
}
/** [MDN Reference](https://developer.mozilla.org/docs/Web/API/EventSource/message_event) */
get onmessage() {
return this.#onMessage
}
set onmessage(value) {
this.#onMessage = value
}
/** [MDN Reference](https://developer.mozilla.org/docs/Web/API/EventSource/open_event) */
get onopen() {
return this.#onOpen
}
set onopen(value) {
this.#onOpen = value
}
addEventListener(
type,
listener,
options) {
super.addEventListener(type, listener, options)
}
removeEventListener(
type,
listener,
options) {
super.removeEventListener(type, listener, options)
}
constructor(url, eventSourceInitDict, requestOptions) {
super()
try {
if(url instanceof URL) {
this.#url = url
} else if(typeof url === 'string') {
this.#url = new URL(url, getBaseURL())
} else {
throw new Error('Invalid URL')
}
} catch (err) {
throw syntaxError('An invalid or illegal string was specified')
}
this.#parser = createParser({
onEvent: this.#onEvent,
onRetry: this.#onRetryChange,
})
this.#readyState = MEventSource.CONNECTING
this.#reconnectInterval = 3000
this.#fetch = eventSourceInitDict?.fetch ?? window.fetch
this.#withCredentials = eventSourceInitDict?.withCredentials ?? false
this.requestOptions = requestOptions
this.#connect()
}
/**
* Aborts any instances of the fetch algorithm started for this EventSource object, and sets the readyState attribute to CLOSED.
*
* [MDN Reference](https://developer.mozilla.org/docs/Web/API/EventSource/close)
*
* @public
*/
close() {
if(this.#reconnectTimer) clearTimeout(this.#reconnectTimer)
if(this.#readyState === MEventSource.CLOSED) return
if(this.#controller) this.#controller.abort()
this.#readyState = MEventSource.CLOSED
this.#controller = undefined
}
// PRIVATES FOLLOW
/**
* Current connection state
*
* @internal
*/
#readyState;
/**
* Original URL used to connect.
*
* Note that this will stay the same even after a redirect.
*
* @internal
*/
#url;
/**
* The destination URL after a redirect. Is reset on reconnection.
*
* @internal
*/
#redirectUrl;
/**
* Whether to include credentials in the request
*
* @internal
*/
#withCredentials;
/**
* The fetch implementation to use
*
* @internal
*/
#fetch;
/**
* The reconnection time in milliseconds
*
* @internal
*/
#reconnectInterval;
/**
* Reference to an ongoing reconnect attempt, if any
*
* @internal
*/
#reconnectTimer;
/**
* The last event ID seen by the EventSource, which will be sent as `Last-Event-ID` in the
* request headers on a reconnection attempt.
*
* @internal
*/
#lastEventId;
/**
* The AbortController instance used to abort the fetch request
*
* @internal
*/
#controller;
/**
* Instance of an EventSource parser (`eventsource-parser` npm module)
*
* @internal
*/
#parser;
/**
* Holds the current error handler, attached through `onerror` property directly.
* Note that `addEventListener('error', …)` will not be stored here.
*
* @internal
*/
#onError;
/**
* Holds the current message handler, attached through `onmessage` property directly.
* Note that `addEventListener('message', …)` will not be stored here.
*
* @internal
*/
#onMessage;
/**
* Holds the current open handler, attached through `onopen` property directly.
* Note that `addEventListener('open', …)` will not be stored here.
*
* @internal
*/
#onOpen;
/**
* Connect to the given URL and start receiving events
*
* @internal
*/
#connect() {
this.#readyState = MEventSource.CONNECTING
this.#controller = new AbortController()
// Browser tests are failing if we directly call `this.#fetch()`, thus the indirection.
const fetch = this.#fetch
fetch(this.#url, this.getRequestOptions())
.then(this.#onFetchResponse)
.catch(this.#onFetchError)
}
/**
* Handles the fetch response
*
* @param response - The Fetch(ish) response
* @internal
*/
#onFetchResponse = async (response) => {
this.#parser.reset()
const {body, redirected, status, headers} = response
// [spec] a client can be told to stop reconnecting using the HTTP 204 No Content response code.
if(status === 204) {
// We still need to emit an error event - this mirrors the browser behavior,
// and without it there is no way to tell the user that the connection was closed.
this.failConnection('Server sent HTTP 204, not reconnecting', 204)
this.close()
return
}
// [spec] …Event stream requests can be redirected using HTTP 301 and 307 redirects as with
// [spec] normal HTTP requests.
// Spec does not say anything about other redirect codes (302, 308), but this seems an
// unintended omission, rather than a feature. Browsers will happily redirect on other 3xxs's.
if(redirected) {
this.#redirectUrl = new URL(response.url)
} else {
this.#redirectUrl = undefined
}
// [spec] if res's status is not 200, …, then fail the connection.
if(status !== 200) {
this.failConnection(`Non-200 status code (${status})`, status)
return
}
// [spec] …or if res's `Content-Type` is not `text/event-stream`, then fail the connection.
const contentType = headers.get('content-type') || ''
if(!contentType.startsWith('text/event-stream')) {
this.failConnection('Invalid content type, expected "text/event-stream"', status)
return
}
// [spec] …if the readyState attribute is set to a value other than CLOSED…
if(this.#readyState === MEventSource.CLOSED) {
return
}
// [spec] …sets the readyState attribute to OPEN and fires an event
// [spec] …named open at the EventSource object.
this.#readyState = MEventSource.OPEN
const openEvent = new Event('open')
this.#onOpen?.(openEvent)
this.dispatchEvent(openEvent)
// Ensure that the response stream is a web stream
if(typeof body !== 'object' || !body || !('getReader' in body)) {
this.failConnection('Invalid response body, expected a web ReadableStream', status)
this.close() // This should only happen if `fetch` provided is "faulty" - don't reconnect
return
}
const decoder = new TextDecoder()
const reader = body.getReader()
let open = true
do {
const {done, value} = await reader.read()
if(value) {
this.#parser.feed(decoder.decode(value, {stream: !done}))
}
if(!done) {
continue
}
open = false
this.#parser.reset()
this.scheduleReconnect()
} while (open)
}
/**
* Handles rejected requests for the EventSource endpoint
*
* @param err - The error from `fetch()`
* @internal
*/
#onFetchError = (err) => {
this.#controller = undefined
// We expect abort errors when the user manually calls `close()` - ignore those
if(err.name === 'AbortError' || err.type === 'aborted') {
return
}
this.scheduleReconnect(flattenError(err))
}
/**
* Get request options for the `fetch()` request
*
* @returns The request options
* @internal
*/
getRequestOptions() {
const lastEvent = this.#lastEventId ? {'Last-Event-ID': this.#lastEventId} : undefined
let init = {
// [spec] Let `corsAttributeState` be `Anonymous`…
// [spec] …will have their mode set to "cors"…
mode: 'cors',
redirect: 'follow',
headers: {Accept: 'text/event-stream', ...lastEvent},
cache: 'no-store',
signal: this.#controller?.signal,
}
// Some environments crash if attempting to set `credentials` where it is not supported,
// eg on Cloudflare Workers. To avoid this, we only set it in browser-like environments.
if('window' in window) {
// [spec] …and their credentials mode set to "same-origin"
// [spec] …if the `withCredentials` attribute is `true`, set the credentials mode to "include"…
init.credentials = this.withCredentials ? 'include' : 'same-origin'
}
const requestOptions = this.requestOptions
if(requestOptions) {
init = {...init, ...requestOptions}
if(init.headers) {
init.headers = {...init.headers, Accept: 'text/event-stream', ...lastEvent};
}
}
return init
}
/**
* Called by EventSourceParser instance when an event has successfully been parsed
* and is ready to be processed.
*
* @param event - The parsed event
* @internal
*/
#onEvent = (event) => {
if(typeof event.id === 'string') {
this.#lastEventId = event.id
}
const messageEvent = new MessageEvent(event.event || 'message', {
data: event.data,
origin: this.#redirectUrl ? this.#redirectUrl.origin : this.#url.origin,
lastEventId: event.id || '',
})
// The `onmessage` property of the EventSource instance only triggers on messages without an
// `event` field, or ones that explicitly set `message`.
if(this.#onMessage && (!event.event || event.event === 'message')) {
this.#onMessage(messageEvent)
}
this.dispatchEvent(messageEvent)
}
/**
* Called by EventSourceParser instance when a new reconnection interval is received
* from the EventSource endpoint.
*
* @param value - The new reconnection interval in milliseconds
* @internal
*/
#onRetryChange = (value) => {
this.#reconnectInterval = value
}
/**
* Handles the process referred to in the EventSource specification as "failing a connection".
*
* @param message - The error causing the connection to fail
* @param code - The HTTP status code, if available
* @internal
*/
failConnection(message, code) {
// [spec] …if the readyState attribute is set to a value other than CLOSED,
// [spec] sets the readyState attribute to CLOSED…
if(this.#readyState !== MEventSource.CLOSED) {
this.#readyState = MEventSource.CLOSED
}
// [spec] …and fires an event named `error` at the `EventSource` object.
// [spec] Once the user agent has failed the connection, it does not attempt to reconnect.
// [spec] > Implementations are especially encouraged to report detailed information
// [spec] > to their development consoles whenever an error event is fired, since little
// [spec] > to no information can be made available in the events themselves.
// Printing to console is not very programatically helpful, though, so we emit a custom event.
const errorEvent = new ErrorEvent('error', {code, message})
this.#onError?.(errorEvent)
this.dispatchEvent(errorEvent)
}
/**
* Schedules a reconnection attempt against the EventSource endpoint.
*
* @param message - The error causing the connection to fail
* @param code - The HTTP status code, if available
* @internal
*/
scheduleReconnect(message, code) {
// [spec] If the readyState attribute is set to CLOSED, abort the task.
if(this.#readyState === MEventSource.CLOSED) {
return
}
// [spec] Set the readyState attribute to CONNECTING.
this.#readyState = MEventSource.CONNECTING
// [spec] Fire an event named `error` at the EventSource object.
const errorEvent = new ErrorEvent('error', {code, message})
this.#onError?.(errorEvent)
this.dispatchEvent(errorEvent)
// [spec] Wait a delay equal to the reconnection time of the event source.
this.#reconnectTimer = setTimeout(this.#reconnect, this.#reconnectInterval)
}
/**
* Reconnects to the EventSource endpoint after a disconnect/failure
*
* @internal
*/
#reconnect = () => {
this.#reconnectTimer = undefined
// [spec] If the EventSource's readyState attribute is not set to CONNECTING, then return.
if(this.#readyState !== MEventSource.CONNECTING) {
return
}
this.#connect()
}
}
/**
* According to spec, when constructing a URL:
* > 1. Let baseURL be environment's base URL, if environment is a Document object
* > 2. Return the result of applying the URL parser to url, with baseURL.
*
* Thus we should use `document.baseURI` if available, since it can be set through a base tag.
*
* @returns The base URL, if available - otherwise `undefined`
* @internal
*/
function getBaseURL() {
const doc = 'document' in window ? window.document : undefined
return doc && typeof doc === 'object' && 'baseURI' in doc && typeof doc.baseURI === 'string'
? doc.baseURI
: undefined
}
源码其实很好看懂,我就不一一解析了。
相比之前源码,我们对 getRequestOptions 方法做了一点小小的修改:
constructor(url, eventSourceInitDict, requestOptions) {
//...
// 支持构造函数传入 requestOptions 参数
this.requestOptions = requestOptions
this.#connect()
}
//...
getRequestOptions() {
//...
// 支持可以传入 requestOptions 参数
const requestOptions = this.requestOptions
if(requestOptions) {
// 替换之前的 request 参数
init = {...init, ...requestOptions}
if(init.headers) {
init.headers = {...init.headers, Accept: 'text/event-stream', ...lastEvent};
}
}
return init
}
这样我们就可以自定义请求参数了。
方式二:自定义 fetch
当然,你也可以不用修改 polyfill 的源码,直接在创建 polyfill 的 EventSource 构造函数中传入一个自定义的 fetch 就可以达到改造默认请求的目的了,比如:
const es = new EventSource('https://my-server.com/sse', {
fetch: (input, init) =>
fetch(input, {
...init,
headers: {
...init.headers,
Authorization: 'Bearer myToken',
},
}),
})
fetch 兼容
可以看到即使我们用了 polyfill 来支持 EventSource 了,但是从 polyfill 源码中可以看到,EventSource 内部请求默认使用的是 window.fetch:
constructor(url, eventSourceInitDict, requestOptions) {
//...
// 默认使用 window.fetch 请求
this.#fetch = eventSourceInitDict?.fetch ?? window.fetch
this.#withCredentials = eventSourceInitDict?.withCredentials ?? false
this.requestOptions = requestOptions
this.#connect()
}
那么如果浏览器连 fetch 也不支持的话怎么办呢?有小伙伴要说了,那我们也搞一个 fetch-polyfill 就好了呀~ 是的!
fetch-polyfill 大家第一印象就会想到 whatwg-fetch:https://github.com/JakeChampion/fetch。
但是 whatwg-fetch 默认不支持 ReadableStream 类型的 Response 的,所以我们还得改造一下 whatwg-fetch 的源码:
/* eslint-disable no-prototype-builtins */
var g =
(typeof globalThis !== 'undefined' && globalThis) ||
(typeof self !== 'undefined' && self) ||
// eslint-disable-next-line no-undef
(typeof global !== 'undefined' && global) ||
{}
var support = {
searchParams: 'URLSearchParams' in g,
iterable: 'Symbol' in g && 'iterator' in Symbol,
blob:
'FileReader' in g &&
'Blob' in g &&
(function() {
try {
new Blob()
return true
} catch (e) {
return false
}
})(),
formData: 'FormData' in g,
arrayBuffer: 'ArrayBuffer' in g
}
function isDataView(obj) {
return obj && DataView.prototype.isPrototypeOf(obj)
}
if (support.arrayBuffer) {
var viewClasses = [
'[object Int8Array]',
'[object Uint8Array]',
'[object Uint8ClampedArray]',
'[object Int16Array]',
'[object Uint16Array]',
'[object Int32Array]',
'[object Uint32Array]',
'[object Float32Array]',
'[object Float64Array]'
]
var isArrayBufferView =
ArrayBuffer.isView ||
function(obj) {
return obj && viewClasses.indexOf(Object.prototype.toString.call(obj)) > -1
}
}
function normalizeName(name) {
if (typeof name !== 'string') {
name = String(name)
}
if (/[^a-z0-9\-#$%&'*+.^_`|~!]/i.test(name) || name === '') {
throw new TypeError('Invalid character in header field name: "' + name + '"')
}
return name.toLowerCase()
}
function normalizeValue(value) {
if (typeof value !== 'string') {
value = String(value)
}
return value
}
// Build a destructive iterator for the value list
function iteratorFor(items) {
var iterator = {
next: function() {
var value = items.shift()
return {done: value === undefined, value: value}
}
}
if (support.iterable) {
iterator[Symbol.iterator] = function() {
return iterator
}
}
return iterator
}
export function Headers(headers) {
this.map = {}
if (headers instanceof Headers) {
headers.forEach(function(value, name) {
this.append(name, value)
}, this)
} else if (Array.isArray(headers)) {
headers.forEach(function(header) {
if (header.length != 2) {
throw new TypeError('Headers constructor: expected name/value pair to be length 2, found' + header.length)
}
this.append(header[0], header[1])
}, this)
} else if (headers) {
Object.getOwnPropertyNames(headers).forEach(function(name) {
this.append(name, headers[name])
}, this)
}
}
Headers.prototype.append = function(name, value) {
name = normalizeName(name)
value = normalizeValue(value)
var oldValue = this.map[name]
this.map[name] = oldValue ? oldValue + ', ' + value : value
}
Headers.prototype['delete'] = function(name) {
delete this.map[normalizeName(name)]
}
Headers.prototype.get = function(name) {
name = normalizeName(name)
return this.has(name) ? this.map[name] : null
}
Headers.prototype.has = function(name) {
return this.map.hasOwnProperty(normalizeName(name))
}
Headers.prototype.set = function(name, value) {
this.map[normalizeName(name)] = normalizeValue(value)
}
Headers.prototype.forEach = function(callback, thisArg) {
for (var name in this.map) {
if (this.map.hasOwnProperty(name)) {
callback.call(thisArg, this.map[name], name, this)
}
}
}
Headers.prototype.keys = function() {
var items = []
this.forEach(function(value, name) {
items.push(name)
})
return iteratorFor(items)
}
Headers.prototype.values = function() {
var items = []
this.forEach(function(value) {
items.push(value)
})
return iteratorFor(items)
}
Headers.prototype.entries = function() {
var items = []
this.forEach(function(value, name) {
items.push([name, value])
})
return iteratorFor(items)
}
if (support.iterable) {
Headers.prototype[Symbol.iterator] = Headers.prototype.entries
}
function consumed(body) {
if (body._noBody) return
if (body.bodyUsed) {
return Promise.reject(new TypeError('Already read'))
}
body.bodyUsed = true
}
function fileReaderReady(reader) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
reader.onload = function() {
resolve(reader.result)
}
reader.onerror = function() {
reject(reader.error)
}
})
}
function readBlobAsArrayBuffer(blob) {
var reader = new FileReader()
var promise = fileReaderReady(reader)
reader.readAsArrayBuffer(blob)
return promise
}
function readBlobAsText(blob) {
var reader = new FileReader()
var promise = fileReaderReady(reader)
var match = /charset=([A-Za-z0-9_-]+)/.exec(blob.type)
var encoding = match ? match[1] : 'utf-8'
reader.readAsText(blob, encoding)
return promise
}
function readArrayBufferAsText(buf) {
var view = new Uint8Array(buf)
var chars = new Array(view.length)
for (var i = 0; i < view.length; i++) {
chars[i] = String.fromCharCode(view[i])
}
return chars.join('')
}
function bufferClone(buf) {
if (buf.slice) {
return buf.slice(0)
} else {
var view = new Uint8Array(buf.byteLength)
view.set(new Uint8Array(buf))
return view.buffer
}
}
function Body() {
this.bodyUsed = false
this._initBody = function(body) {
/*
fetch-mock wraps the Response object in an ES6 Proxy to
provide useful test harness features such as flush. However, on
ES5 browsers without fetch or Proxy support pollyfills must be used;
the proxy-pollyfill is unable to proxy an attribute unless it exists
on the object before the Proxy is created. This change ensures
Response.bodyUsed exists on the instance, while maintaining the
semantic of setting Request.bodyUsed in the constructor before
_initBody is called.
*/
// eslint-disable-next-line no-self-assign
this.bodyUsed = this.bodyUsed
// 设置 _bodyInit 字段
this._bodyInit = body
// 让其支持 ReadableStream
if(body && body.stream){
this.body = body.stream();
}
// 添加 body 参数
this.body = this.body || body;
if (!body) {
this._noBody = true;
this._bodyText = ''
} else if (typeof body === 'string') {
this._bodyText = body
} else if (support.blob && Blob.prototype.isPrototypeOf(body)) {
this._bodyBlob = body
} else if (support.formData && FormData.prototype.isPrototypeOf(body)) {
this._bodyFormData = body
} else if (support.searchParams && URLSearchParams.prototype.isPrototypeOf(body)) {
this._bodyText = body.toString()
} else if (support.arrayBuffer && support.blob && isDataView(body)) {
this._bodyArrayBuffer = bufferClone(body.buffer)
// IE 10-11 can't handle a DataView body.
this._bodyInit = new Blob([this._bodyArrayBuffer])
} else if (support.arrayBuffer && (ArrayBuffer.prototype.isPrototypeOf(body) || isArrayBufferView(body))) {
this._bodyArrayBuffer = bufferClone(body)
} else {
this._bodyText = body = Object.prototype.toString.call(body)
}
if (!this.headers.get('content-type')) {
if (typeof body === 'string') {
this.headers.set('content-type', 'text/plain;charset=UTF-8')
} else if (this._bodyBlob && this._bodyBlob.type) {
this.headers.set('content-type', this._bodyBlob.type)
} else if (support.searchParams && URLSearchParams.prototype.isPrototypeOf(body)) {
this.headers.set('content-type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8')
}
}
}
if (support.blob) {
this.blob = function() {
var rejected = consumed(this)
if (rejected) {
return rejected
}
if (this._bodyBlob) {
return Promise.resolve(this._bodyBlob)
} else if (this._bodyArrayBuffer) {
return Promise.resolve(new Blob([this._bodyArrayBuffer]))
} else if (this._bodyFormData) {
throw new Error('could not read FormData body as blob')
} else {
return Promise.resolve(new Blob([this._bodyText]))
}
}
}
this.arrayBuffer = function() {
if (this._bodyArrayBuffer) {
var isConsumed = consumed(this)
if (isConsumed) {
return isConsumed
} else if (ArrayBuffer.isView(this._bodyArrayBuffer)) {
return Promise.resolve(
this._bodyArrayBuffer.buffer.slice(
this._bodyArrayBuffer.byteOffset,
this._bodyArrayBuffer.byteOffset + this._bodyArrayBuffer.byteLength
)
)
} else {
return Promise.resolve(this._bodyArrayBuffer)
}
} else if (support.blob) {
return this.blob().then(readBlobAsArrayBuffer)
} else {
throw new Error('could not read as ArrayBuffer')
}
}
this.text = function() {
var rejected = consumed(this)
if (rejected) {
return rejected
}
if (this._bodyBlob) {
return readBlobAsText(this._bodyBlob)
} else if (this._bodyArrayBuffer) {
return Promise.resolve(readArrayBufferAsText(this._bodyArrayBuffer))
} else if (this._bodyFormData) {
throw new Error('could not read FormData body as text')
} else {
return Promise.resolve(this._bodyText)
}
}
if (support.formData) {
this.formData = function() {
return this.text().then(decode)
}
}
this.json = function() {
return this.text().then(JSON.parse)
}
return this
}
// HTTP methods whose capitalization should be normalized
var methods = ['CONNECT', 'DELETE', 'GET', 'HEAD', 'OPTIONS', 'PATCH', 'POST', 'PUT', 'TRACE']
function normalizeMethod(method) {
var upcased = method.toUpperCase()
return methods.indexOf(upcased) > -1 ? upcased : method
}
export function Request(input, options) {
if (!(this instanceof Request)) {
throw new TypeError('Please use the "new" operator, this DOM object constructor cannot be called as a function.')
}
options = options || {}
var body = options.body
if (input instanceof Request) {
if (input.bodyUsed) {
throw new TypeError('Already read')
}
this.url = input.url
this.credentials = input.credentials
if (!options.headers) {
this.headers = new Headers(input.headers)
}
this.method = input.method
this.mode = input.mode
this.signal = input.signal
if (!body && input._bodyInit != null) {
body = input._bodyInit
input.bodyUsed = true
}
} else {
this.url = String(input)
}
this.credentials = options.credentials || this.credentials || 'same-origin'
if (options.headers || !this.headers) {
this.headers = new Headers(options.headers)
}
this.method = normalizeMethod(options.method || this.method || 'GET')
this.mode = options.mode || this.mode || null
this.signal = options.signal || this.signal || (function () {
if ('AbortController' in g) {
var ctrl = new AbortController();
return ctrl.signal;
}
}());
this.referrer = null
if ((this.method === 'GET' || this.method === 'HEAD') && body) {
throw new TypeError('Body not allowed for GET or HEAD requests')
}
this._initBody(body)
if (this.method === 'GET' || this.method === 'HEAD') {
if (options.cache === 'no-store' || options.cache === 'no-cache') {
// Search for a '_' parameter in the query string
var reParamSearch = /([?&])_=[^&]*/
if (reParamSearch.test(this.url)) {
// If it already exists then set the value with the current time
this.url = this.url.replace(reParamSearch, '$1_=' + new Date().getTime())
} else {
// Otherwise add a new '_' parameter to the end with the current time
var reQueryString = /\?/
this.url += (reQueryString.test(this.url) ? '&' : '?') + '_=' + new Date().getTime()
}
}
}
}
Request.prototype.clone = function() {
return new Request(this, {body: this._bodyInit})
}
function decode(body) {
var form = new FormData()
body
.trim()
.split('&')
.forEach(function(bytes) {
if (bytes) {
var split = bytes.split('=')
var name = split.shift().replace(/\+/g, ' ')
var value = split.join('=').replace(/\+/g, ' ')
form.append(decodeURIComponent(name), decodeURIComponent(value))
}
})
return form
}
function parseHeaders(rawHeaders) {
var headers = new Headers()
// Replace instances of \r\n and \n followed by at least one space or horizontal tab with a space
// https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7230#section-3.2
var preProcessedHeaders = rawHeaders.replace(/\r?\n[\t ]+/g, ' ')
// Avoiding split via regex to work around a common IE11 bug with the core-js 3.6.0 regex polyfill
// https://github.com/github/fetch/issues/748
// https://github.com/zloirock/core-js/issues/751
preProcessedHeaders
.split('\r')
.map(function(header) {
return header.indexOf('\n') === 0 ? header.substr(1, header.length) : header
})
.forEach(function(line) {
var parts = line.split(':')
var key = parts.shift().trim()
if (key) {
var value = parts.join(':').trim()
try {
headers.append(key, value)
} catch (error) {
console.warn('Response ' + error.message)
}
}
})
return headers
}
Body.call(Request.prototype)
export function Response(bodyInit, options) {
if (!(this instanceof Response)) {
throw new TypeError('Please use the "new" operator, this DOM object constructor cannot be called as a function.')
}
if (!options) {
options = {}
}
this.type = 'default'
this.status = options.status === undefined ? 200 : options.status
if (this.status < 200 || this.status > 599) {
throw new RangeError("Failed to construct 'Response': The status provided (0) is outside the range [200, 599].")
}
this.ok = this.status >= 200 && this.status < 300
this.statusText = options.statusText === undefined ? '' : '' + options.statusText
this.headers = new Headers(options.headers)
this.url = options.url || ''
this._initBody(bodyInit)
}
Body.call(Response.prototype)
Response.prototype.clone = function() {
return new Response(this._bodyInit, {
status: this.status,
statusText: this.statusText,
headers: new Headers(this.headers),
url: this.url
})
}
Response.error = function() {
var response = new Response(null, {status: 200, statusText: ''})
response.ok = false
response.status = 0
response.type = 'error'
return response
}
var redirectStatuses = [301, 302, 303, 307, 308]
Response.redirect = function(url, status) {
if (redirectStatuses.indexOf(status) === -1) {
throw new RangeError('Invalid status code')
}
return new Response(null, {status: status, headers: {location: url}})
}
export var DOMException = g.DOMException
try {
new DOMException()
} catch (err) {
DOMException = function(message, name) {
this.message = message
this.name = name
var error = Error(message)
this.stack = error.stack
}
DOMException.prototype = Object.create(Error.prototype)
DOMException.prototype.constructor = DOMException
}
export function fetch(input, init) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
var request = new Request(input, init)
if (request.signal && request.signal.aborted) {
return reject(new DOMException('Aborted', 'AbortError'))
}
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
function abortXhr() {
xhr.abort()
}
xhr.onload = function() {
var options = {
statusText: xhr.statusText,
headers: parseHeaders(xhr.getAllResponseHeaders() || '')
}
// This check if specifically for when a user fetches a file locally from the file system
// Only if the status is out of a normal range
if (request.url.indexOf('file://') === 0 && (xhr.status < 200 || xhr.status > 599)) {
options.status = 200;
} else {
options.status = xhr.status;
}
options.url = 'responseURL' in xhr ? xhr.responseURL : options.headers.get('X-Request-URL')
var body = 'response' in xhr ? xhr.response : xhr.responseText
setTimeout(function() {
resolve(new Response(body, options))
}, 0)
}
xhr.onerror = function() {
setTimeout(function() {
reject(new TypeError('Network request failed'))
}, 0)
}
xhr.ontimeout = function() {
setTimeout(function() {
reject(new TypeError('Network request timed out'))
}, 0)
}
xhr.onabort = function() {
setTimeout(function() {
reject(new DOMException('Aborted', 'AbortError'))
}, 0)
}
function fixUrl(url) {
try {
return url === '' && g.location.href ? g.location.href : url
} catch (e) {
return url
}
}
xhr.open(request.method, fixUrl(request.url), true)
if (request.credentials === 'include') {
xhr.withCredentials = true
} else if (request.credentials === 'omit') {
xhr.withCredentials = false
}
if ('responseType' in xhr) {
if (support.blob) {
xhr.responseType = 'blob'
} else if (
support.arrayBuffer
) {
xhr.responseType = 'arraybuffer'
}
}
if (init && typeof init.headers === 'object' && !(init.headers instanceof Headers || (g.Headers && init.headers instanceof g.Headers))) {
var names = [];
Object.getOwnPropertyNames(init.headers).forEach(function(name) {
names.push(normalizeName(name))
xhr.setRequestHeader(name, normalizeValue(init.headers[name]))
})
request.headers.forEach(function(value, name) {
if (names.indexOf(name) === -1) {
xhr.setRequestHeader(name, value)
}
})
} else {
request.headers.forEach(function(value, name) {
xhr.setRequestHeader(name, value)
})
}
if (request.signal) {
request.signal.addEventListener('abort', abortXhr)
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
// DONE (success or failure)
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
request.signal.removeEventListener('abort', abortXhr)
}
}
}
xhr.send(typeof request._bodyInit === 'undefined' ? null : request._bodyInit)
})
}
fetch.polyfill = true
if (!g.fetch) {
g.fetch = fetch
g.Headers = Headers
g.Request = Request
g.Response = Response
}
我们也是做了一些小改动:
function Body() {
this.bodyUsed = false
this._initBody = function(body) {
// ...
// 设置 _bodyInit 字段
this._bodyInit = body
// 让其支持 ReadableStream
if(body && body.stream){
this.body = body.stream();
}
// 添加 body 参数
this.body = this.body || body;
ok,这样我们的 fetch-polyfill 也算是改造完成了。
当然,实际项目中大家也没必要花那么大功夫去兼容原生的 EventSource,它在现代浏览器的兼容性还是非常可以的,本文也只是带着学习源码的目的去针对性修改的(除非后端一定要用 POST 请求,并且加些SSE非标准的一些操作,那没辙了,只能改源码了!!!)。
运行效果
POST + 自定义 fetch + 自定义 EventSource:

总结
Server-Sent Events 是一个简单而强大的实时通信技术,特别适合以下场景:
- ✅ 服务器向客户端的单向数据推送。
- ✅ 实时通知和提醒。
- ✅ 实时数据监控和仪表盘。
- ✅ 新闻推送、股票行情等。
- ✅ 简单的聊天应用(只需要接收消息)。
它的主要优势在于:
- 使用简单,浏览器原生支持
- 自动处理重连机制
- 基于 HTTP,易于调试和集成
- 对服务器资源消耗相对较小
虽然 SSE 不支持双向通信,但在很多实际应用场景中,这种简单的服务器推送模式已经足够满足需求,而且比 WebSocket 更易于实现和维护。
最后附上一下 demo 的源码地址:https://github.com/913453448/sse-demo




















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








