2022年2月21日
学习CSS属性书写顺序
页面布局整体思路
定位:静态定位、相对定位、绝对定位、固定定位
定位的扩展知识
元素的隐藏与显示:display、visibility、overflow
今日学习内容:
1 CSS属性书写顺序

2 页面布局整体思路

3 定位
3.1 定位的作用

3.2 定位组成

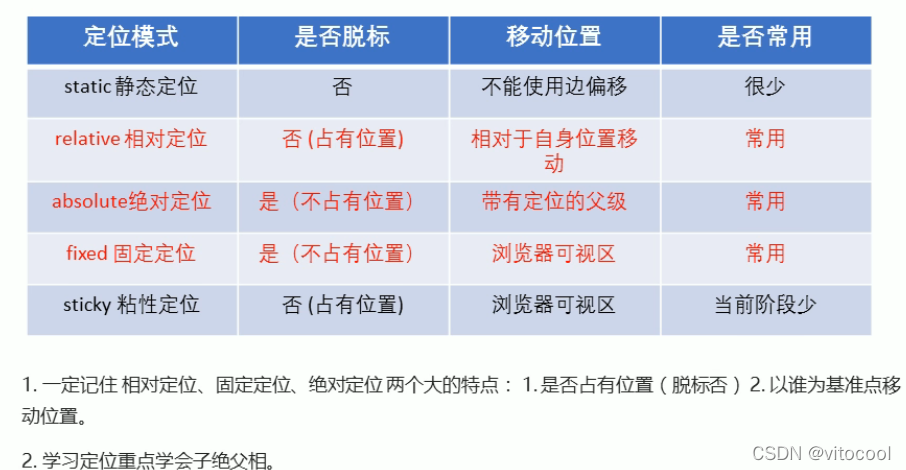
3.2.1 定位模式
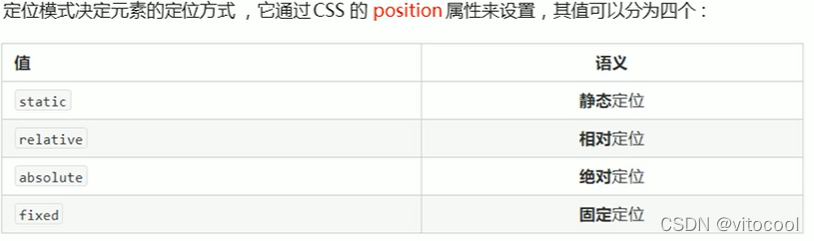
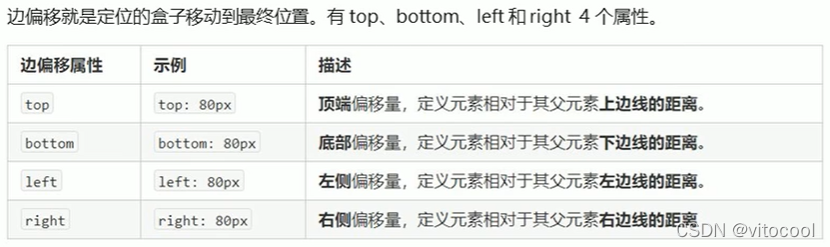
3.2.2 边偏移
3.3 静态定位 static

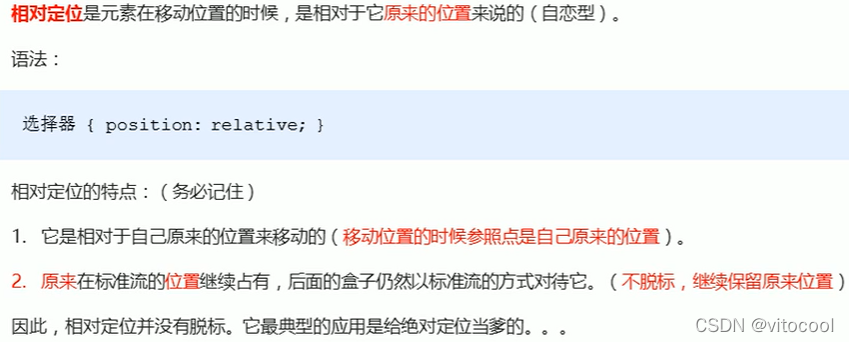
3.4 相对定位 relative
<head>
<style type="text/css">
.div1 {
position: static;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
color: black;
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
}
.div2 {
position: relative;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: black;
color: white;
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>相对定位</h3>
<div class="div2">相对定位</div>
<div class="div1">静态定位</div>
</body>
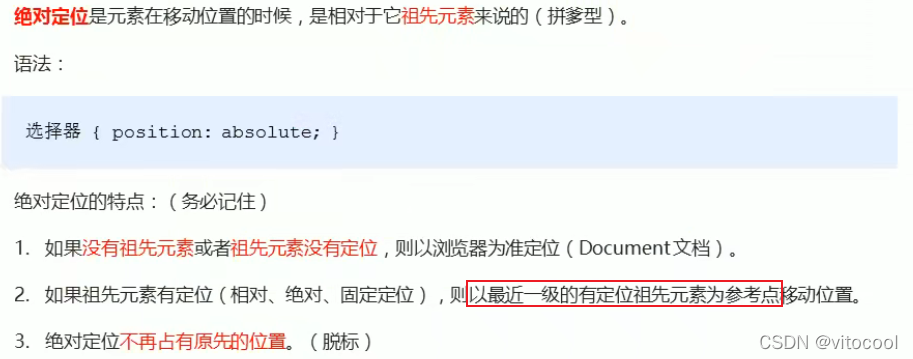
3.5 绝对定位 absolute
<head>
<style type="text/css">
.div1 {
position: static;
width: 120px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
color: black;
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
}
.div2 {
position: relative;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
width: 120px;
height: 100px;
background-color: black;
color: white;
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
}
.div3 {
position: absolute;
top: 500px;
left: 120px;
width: 120px;
height: 100px;
background-color: black;
color: white;
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
}
.div4 {
position: absolute;
top: 10px;
left: 120px;
width: 120px;
height: 100px;
background-color: black;
color: white;
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>绝对定位</h3>
<div class="div1">
父元素静态定位
<div class="div3">子元素绝对定位</div>
</div>
<div class="div2">
父元素相对定位
<div class="div4">子元素绝对定位</div>
</div>
</body>
3.6 子绝父相

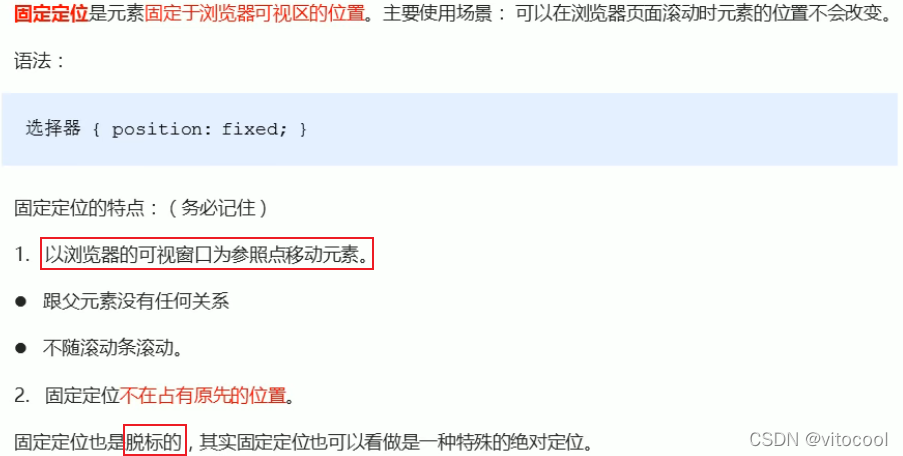
3.7 固定定位 fixed
<head>
<style type="text/css">
.div5 {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 50px;
background-color: black;
color: white;
line-height: 50px;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>固定定位</h3>
<div class="div5">
固定定位
</div>
</body>
3.7.1 固定定位到版心右侧

3.8 粘性定位 sticky

3.9 定位总结
3.10 定位的叠放顺序 z-index

<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
.div2 {
position: relative;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
width: 120px;
height: 100px;
background-color: black;
color: white;
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
z-index: 10;
}
.div7 {
position: relative;
top: -10px;
left: 100px;
width: 120px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
color: white;
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
z-index: -1;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>定位叠放次序</h3>
<div class="div2">
在上
</div>
<div class="div7">
在下
</div>
</body>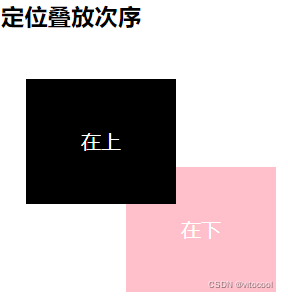
3.11 绝对定位的盒子居中算法

但是相对定位可以通过margin:0 auto实现水平居中,因为相对定位不脱标
<head>
<style>
.div8 {
position: relative;
height: 200px;
width: 100%;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.div9 {
position: absolute;
/*水平居中*/
left: 50%;
margin-left: -50px;
/*垂直居中*/
top: 50%;
margin-top: -50px;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>绝对定位的盒子居中算法</h3>
<div class="div8">
<div class="div9"></div>
</div>
</body>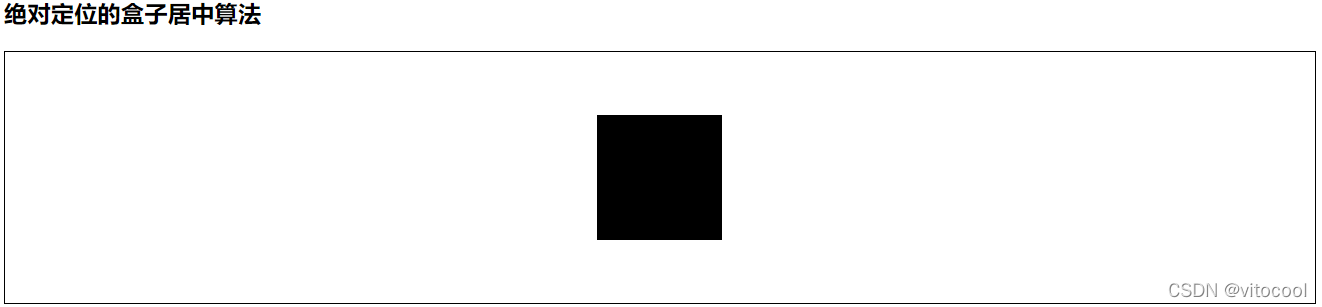
3.12 定位特殊特性

浮动具有行内块元素特性 https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/vitocool/article/details/122617577?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/vitocool/article/details/122617577?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
3.13 脱标的盒子不会触发外边距塌陷
![]()
嵌套块元素垂直外边距的塌陷 https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/vitocool/article/details/122573558?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/vitocool/article/details/122573558?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
3.14 绝对定位(固定定位)会压住下面所有标准流内容

<head>
<style>
.div11 {
position: absolute;
left: 10px;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>绝对定位(固定定位)会完全压住盒子</h3>
<div class="div11"></div>
<p>绝对定位(固定定位)会完全压住盒子</p>
</body>
浮动的元素不会压住下面标准流的文字 https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/vitocool/article/details/122617577
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/vitocool/article/details/122617577
4 网页布局总结

竖用标准,横用浮动,自由移动用定位
5 元素的显示与隐藏
![]()
5.1 display

<head>
<style>
.div12, .div13 {
/*隐藏*/
display: none;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: black;
color: white;
}
.div13 {
/*显示*/
display: block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>display</h3>
<div class="div12">隐藏</div>
<div class="div13">显示</div>
</body>
5.2 visibility 可见性

<head>
<style type="text/css">
.div14, .div15 {
/*隐藏*/
visibility: hidden;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: black;
color: white;
}
.div15 {
/*显示*/
visibility: visible;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>visibility</h3>
<div class="div14">隐藏</div>
<div class="div15">显示</div>
</body>
5.3 overflow溢出

<head>
<style>
.div16, .div17, .div18, .div19 {
/*显示*/
overflow: visible;
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
background-color: pink;
color: black;
}
.div17 {
/*隐藏溢出*/
overflow: hidden;
}
.div18 {
/*以滚动条的形式显示溢出*/
overflow: scroll;
}
.div19 {
/*只有溢出时才用滚动条显示*/
overflow: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>overflow</h3>
<div class="div16">
显<br>示<br>溢<br>出<br>
</div>
<br><br><br>
<div class="div17">
隐<br>藏<br>溢<br>出<br>
</div>
<br>
<div class="div18">
滚<br>动<br>显<br>示<br>
</div>
<br>
<div class="div19">
在需要时<br>滚<br>动<br>显<br>示<br>
</div>
</body>
6 总结
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
.div1 {
position: static;
width: 120px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
color: black;
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
}
.div2 {
position: relative;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
width: 120px;
height: 100px;
background-color: black;
color: white;
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
z-index: 10;
}
.div3 {
position: absolute;
top: 500px;
left: 120px;
width: 120px;
height: 100px;
background-color: black;
color: white;
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
}
.div4 {
position: absolute;
top: 10px;
left: 120px;
width: 120px;
height: 100px;
background-color: black;
color: white;
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
}
.div5 {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 50px;
background-color: black;
color: white;
line-height: 50px;
text-align: center;
}
.div6 {
position: sticky;
top: 0;
width: 120px;
height: 100px;
background-color: black;
color: white;
line-height: 50px;
text-align: center;
}
.div7 {
position: relative;
top: -10px;
left: 100px;
width: 120px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
color: white;
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
z-index: -1;
}
.div8 {
position: relative;
height: 200px;
width: 100%;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.div9 {
position: absolute;
/*水平居中*/
left: 50%;
margin-left: -50px;
/*垂直居中*/
top: 50%;
margin-top: -50px;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: black;
}
.div10 {
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: black;
}
.div11 {
position: absolute;
left: 10px;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #000;
}
.div12, .div13 {
/*隐藏*/
display: none;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: black;
color: white;
}
.div13 {
/*显示*/
display: block;
}
.div14, .div15 {
/*隐藏*/
visibility: hidden;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: black;
color: white;
}
.div15 {
/*显示*/
visibility: visible;
}
.div16, .div17, .div18, .div19 {
/*显示*/
overflow: visible;
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
background-color: pink;
color: black;
}
.div17 {
/*隐藏溢出*/
overflow: hidden;
}
.div18 {
/*以滚动条的形式显示溢出*/
overflow: scroll;
}
.div19 {
/*只有溢出时才用滚动条显示*/
overflow: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>静态定位</h3>
<div class="div1"></div>
<h3>相对定位</h3>
<div class="div2">相对定位</div>
<div class="div1">静态定位</div>
<h3>绝对定位</h3>
<div class="div1">
父元素静态定位
<div class="div3">子元素绝对定位</div>
</div>
<div class="div2">
父元素相对定位
<div class="div4">子元素绝对定位</div>
</div>
<h3>固定定位</h3>
<div class="div5">
固定定位
</div>
<h3>粘性定位</h3>
<div class="div6">粘性定位</div>
<h3>定位叠放次序</h3>
<div class="div2">
在上
</div>
<div class="div7">
在下
</div>
<h3>绝对定位的盒子居中算法</h3>
<div class="div8">
<div class="div9"></div>
</div>
<h3>浮动的元素不会压住下面标准流的文字</h3>
<div class="div10"></div>
<p>浮动的元素不会压住下面标准流的文字</p>
<br><br><br>
<h3>绝对定位(固定定位)会完全压住盒子</h3>
<div class="div11"></div>
<p>绝对定位(固定定位)会完全压住盒子</p>
<br><br><br>
<h3>display</h3>
<div class="div12">隐藏</div>
<div class="div13">显示</div>
<h3>visibility</h3>
<div class="div14">隐藏</div>
<div class="div15">显示</div>
<h3>overflow</h3>
<div class="div16">
显<br>示<br>溢<br>出<br>
</div>
<br><br><br>
<div class="div17">
隐<br>藏<br>溢<br>出<br>
</div>
<br>
<div class="div18">
滚<br>动<br>显<br>示<br>
</div>
<br>
<div class="div19">
在需要时<br>滚<br>动<br>显<br>示<br>
</div>
</body>
</html>



















 359
359

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








