原题
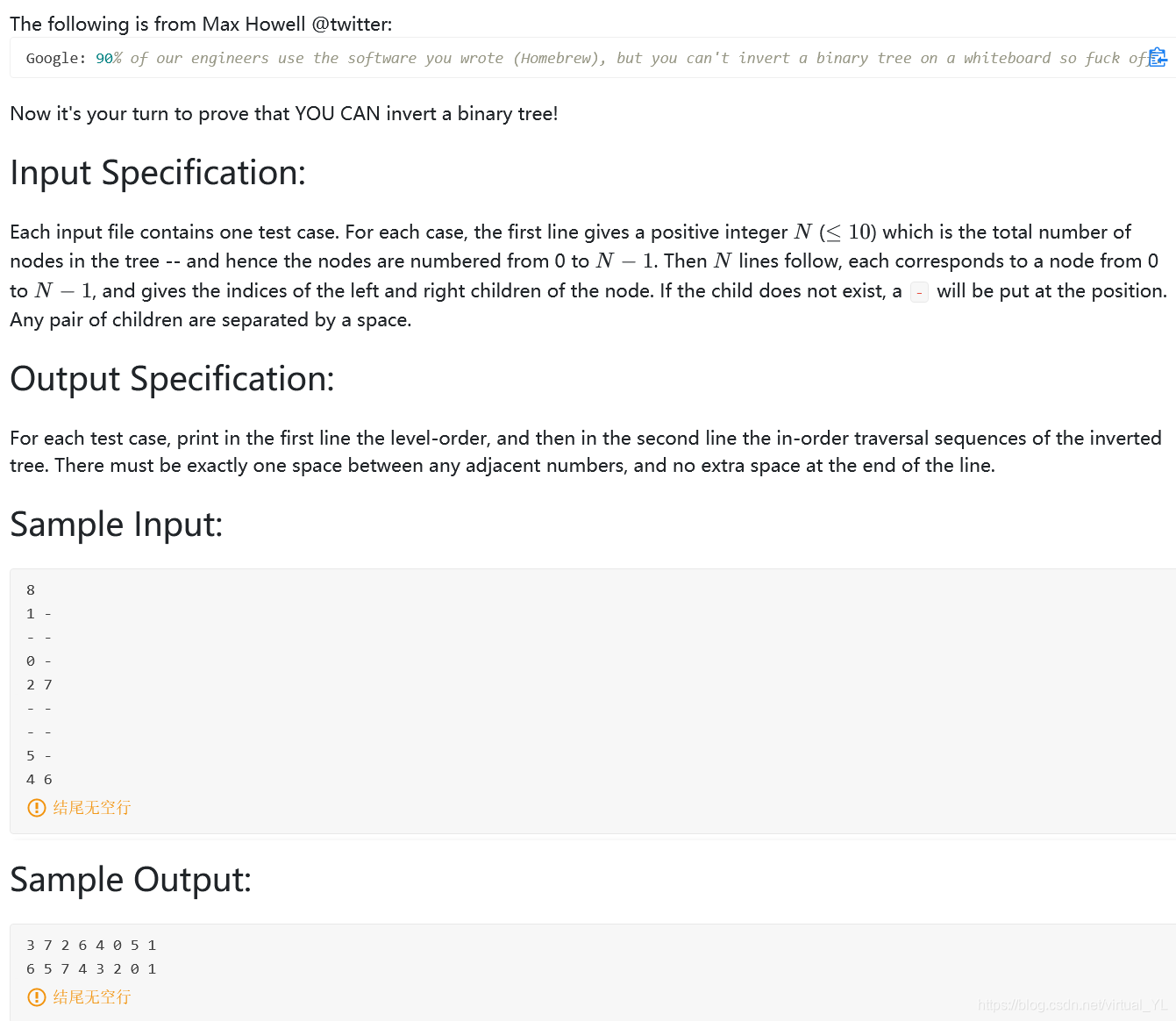
题目大意及思路
通过给了每个节点的左右孩子,输出翻转后的层序遍历序列和中序遍历。(其实翻转很简单,在输出的时候就交换左右孩子或者之后遍历顺序换一下就可以)
在最开始定义所有结点的父亲结点为-1;
在输入时,存下将左右孩子结点的父节点改为自己。
遍历一遍后父亲结点仍为-1的结点就是根节点。
再分别通过队列和递归(BFS和DFS)对树进行遍历,就可以得到相应序列。
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int father,invrc,invlc;
};
vector<node> tree;
vector<int> level,inord;
void levelorder(int rootindex){
queue<int> pre;
pre.push(rootindex);
while(!pre.empty()){
int top=pre.front();
level.push_back(top);
pre.pop();
if(tree[top].invlc!=-1) pre.push(tree[top].invlc);
if(tree[top].invrc!=-1) pre.push(tree[top].invrc);
}
return;
}
int n;
int number=0;
void inorder(int rootindex){
if(rootindex==-1) return;
number++;
inorder(tree[rootindex].invlc);
inord.push_back(rootindex);
inorder(tree[rootindex].invrc);
return;
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
tree.resize(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) tree[i].father=-1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
char lc,rc;
cin>>rc>>lc;
if(lc!='-'){
tree[i].invlc=lc-48;
tree[lc-48].father=i;
}
else tree[i].invlc=-1;
if(rc!='-'){
tree[i].invrc=rc-48;
tree[rc-48].father=i;
}
else tree[i].invrc=-1;
}
int rootindex=0;
for(;tree[rootindex].father!=-1;rootindex=tree[rootindex].father) ;
levelorder(rootindex);
inorder(rootindex);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) printf("%d%s",level[i],i==n-1?"\n":" ");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) printf("%d%s",inord[i],i==n-1?"":" ");
return 0;
}
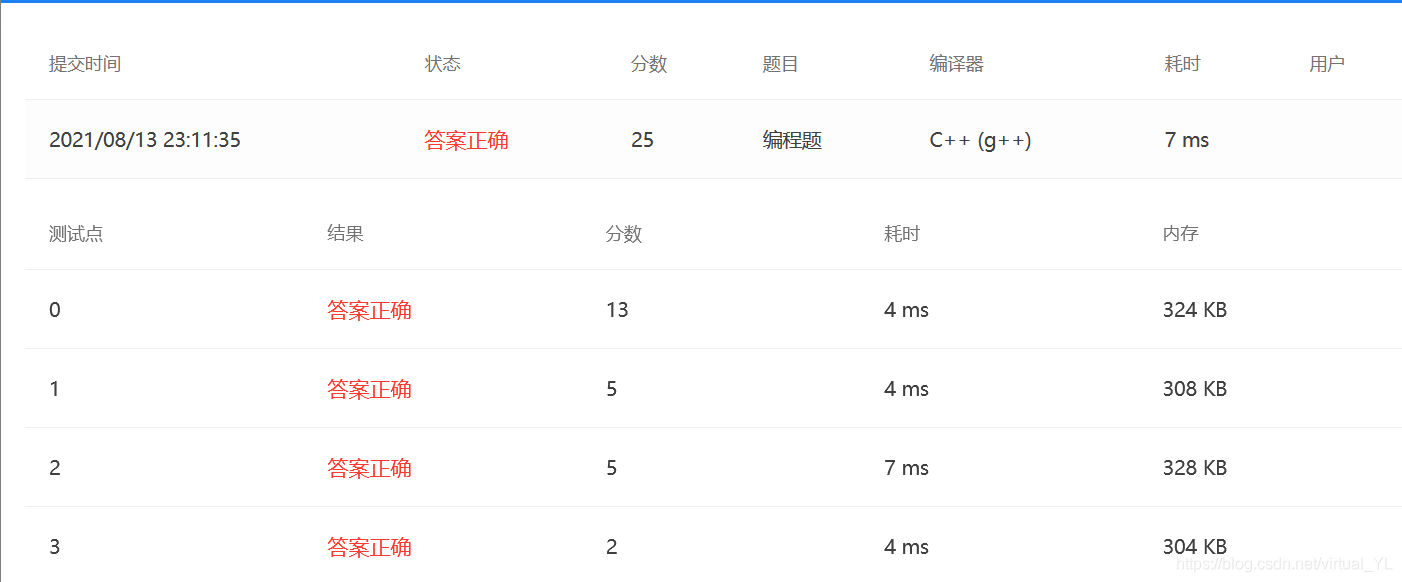
运行截图
收获
刚开始在遍历的过程中输出结点,但有一个测试样例因格式错误无法通过,之后便尝试存入数组中统一输出,便全部正确了。
其实暂时也没太搞懂究竟是哪个环节出了问题(测试了一下特殊边界值都没有问题),但在之后的编写代码的过程中争取吸收错误经验,编写更严谨的代码!





 这篇博客主要介绍了如何通过给定的节点左右孩子信息,实现二叉树的翻转,并输出翻转后的层序遍历和中序遍历序列。作者首先定义每个节点的父节点为-1,然后在输入时更新左右孩子节点的父节点。遍历找到根节点后,使用BFS和DFS分别进行遍历得到序列。通过调整输出方式,解决了某个测试样例的格式问题,提高了代码的严谨性。
这篇博客主要介绍了如何通过给定的节点左右孩子信息,实现二叉树的翻转,并输出翻转后的层序遍历和中序遍历序列。作者首先定义每个节点的父节点为-1,然后在输入时更新左右孩子节点的父节点。遍历找到根节点后,使用BFS和DFS分别进行遍历得到序列。通过调整输出方式,解决了某个测试样例的格式问题,提高了代码的严谨性。
















 891
891

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








