States
State 的实例封装了owner在指定时刻下的条件和行为。. 一个 State 是又methods, arbitrary data, events, guards, substates, 和 transition expressions的集合组成。
一个owner通常拥有多个 States, 并且指向其中一个作为 current state, 在current state中owner会表现出相应的方法和行为。通过行为来触发 transition使得由一个状态转变为另外一个状态。
Object model
State objects are modeled by a set of relational references that define three distinct dimensions or “axes”.状态对象是由一组定义三个不同的维度或“轴”关系的参考蓝本。
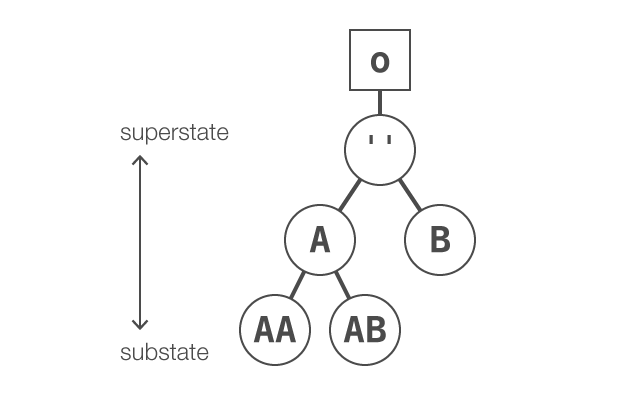
从根本上来说,State 模型是分层次的,从 owner 拥有着唯一的root state开始,每个state都作为 superstate被 substates 继承
一个 State 可能从零个或者多个 parastates继承,提供了定义成分的关系,通过C3线性多重继承实现的一种手段。 providing a means to define compositional relations, implemented via C3 linearized multiple inheritance.
如果owner的state树是由其他owner的prototypal继承而来 ,继承的owner将可以view their prototype’s States as protostates from which their own epistates inherit.
var p = {};
state( p, {
A: state,
B: state({
BA: state,
BB: state
})
});
var o = Object.create( p );
state( o, {
A: state({
AA: state.extend('X, Y')
}),
X: state,
Y: state
});
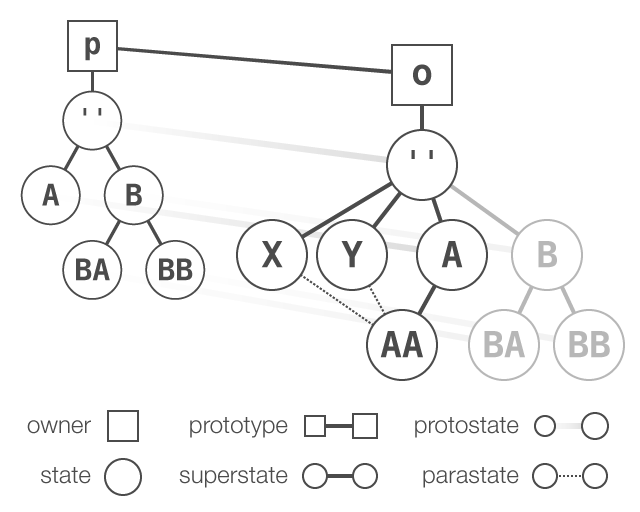
State S 的继承顺序如下 relation precedence:
- S的protostate继承链
- S的parastates,按照声明的先后顺序
- S的superstate
其中parastate和superstate线性加载, or “parastate–superstate chain”, protostate则按照顺序加载
The root state
所有被 State 影响的 owner 都要单独的 root state. root state的名称为唯一的空字符串 ''.
owner.state().root === owner.state(''); // >>> true (invariant)
owner.state('->');
owner.state(); // >>> State ''
默认的owner’s 初始current state被设置为 root state — 除非 root state 被标记为 abstract attribute, 或者另外一个 State 被标记为 initial attribute.
root state 还可以用来存储 methods 并且可以被owner的 States重写。这些方法被替换至root state。如果没有被重写,则会调用默认的方法。
Superstates and substates
owner 表现得行为由 substates 决定 ,这些substates 由 superstates 生成
var o = {};
state( o, {
A: state({
AA: state,
AB: state
}),
B: state
});
var root = o.state(''); // >>> RootState
o.state() === root; // >>> true
o.state('-> AA');
o.state() === o.state('AA'); // >>> true
o.state().superstate === o.state('A'); // >>> true
o.state().superstate.superstate === root; // >>> true
Parastates and composition
除了通过 superstates 继承,State 模型还支持通过 parastate 关系实现多继承。
The lone exception to this is a
RootState, which bears neither relation.
Parastates 通过 state.extend 函数声明, which takes a string of one or more paths to parastates, along with optional parameters attributes and expression, and returns a StateExpression that can be used to produce a State with the named parastates.
var o = {};
state( o, {
A: state({
AA: state.extend('X, Y')
}),
X: state,
Y: state
});
State
AAinherits conventionally from superstateA, but not before inheriting compositionally from parastatesXandY.
Linearization, inheriting precedence, and monotonicity
The resolution order by which a State inherits from its lineage of parastate and superstate ancestors is guaranteed to be unambiguous. It is also guaranteed to be monotonic relative to the resolution order for any descendants of the State:
-
Given
StateS with ancestorStates A and B (either parastates or superstates), where A precedes B in the resolution order of S; -
A
StateT, to which S is related as either a parastate or superstate of T, is guaranteed to encounter A before B in its own resolution order.
These assertions are enforced by an implementation of the C3 linearization algorithm (Dylan, Perl, Python) — with the State–specific stipulations that:
-
A
State’s “parents” are defined and ordered by its immediate parastates, in declared order, followed by its immediate superstate. -
A
RootStateby rule cannot inherit from parastates, and by definition does not inherit from a superstate.
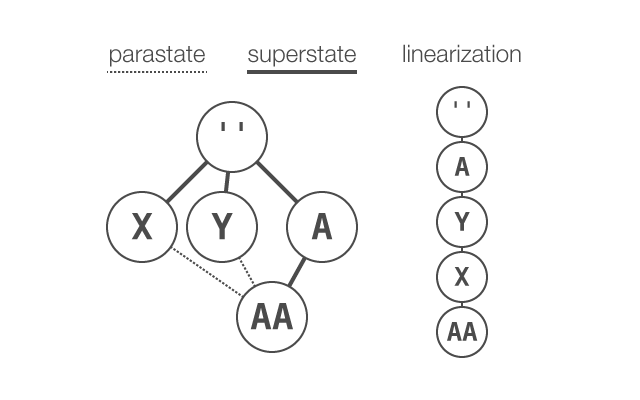
Parastate–superstate graph and linearization — from the example code above, parastates
XandYofStateAAare depicted to the left of its superstateA, indicating the superstate’s intrinsic position as the “final parent” of aState. The linearization ofAAdetermines the precedence, or resolution order, by which theStatewill inherit methods, data, and events defined in its ancestors.
Attempting to implement an expression that produces a State graph which does not conform to the C3 restrictions will throw a TypeError.
Prototypal flattening
In the State model, a State and its parastates must share a common owner. However, parastate declarations may include paths that resolve to States belonging to a prototype of the owner. In such a case these “proto-parastates” are automatically flattened onto the owner’s state tree:
-
Given
StateS withownerO, which has prototype P, where P bears aStateA whose path is'A', and given that S declares path'A'as a parastate relation; -
As O contains no
Statewith path'A', the protostate A belonging to P will be automaticallyvirtualized andrealized — effectively flattening it — into the state tree of O as an epistate Aʹ, with path'A', such that S may inherit from parastate Aʹ.
Miscellanea
-
The progression of a transition is conceptually orthogonal to the parastate relation, and traversal proceeds only over the state tree defined by the superstate–substate relations.
-
Parastates provide for compositional reuse of only their own or inherited methods, data, and custom events. Built-in events, guards, substates, transitions, and attributes are not heritable via parastate.








 本文深入探讨了状态模式的核心概念,包括状态(State)实例如何封装对象在特定时刻的状态与行为,以及状态之间的转换机制。此外,文章详细介绍了状态模型的层次结构、状态间的继承关系及其线性化过程,并解释了如何通过状态的parastate和superstate关系实现多继承。
本文深入探讨了状态模式的核心概念,包括状态(State)实例如何封装对象在特定时刻的状态与行为,以及状态之间的转换机制。此外,文章详细介绍了状态模型的层次结构、状态间的继承关系及其线性化过程,并解释了如何通过状态的parastate和superstate关系实现多继承。
















 5190
5190

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








