原型模式(Prototype Pattern)
定义
原型模式是一种创建型设计模式,通过复制现有对象(原型)来创建新对象,避免重复执行耗时的初始化操作。核心思想是以复制代替构造,特别适用于创建成本高的对象。
UML 类图
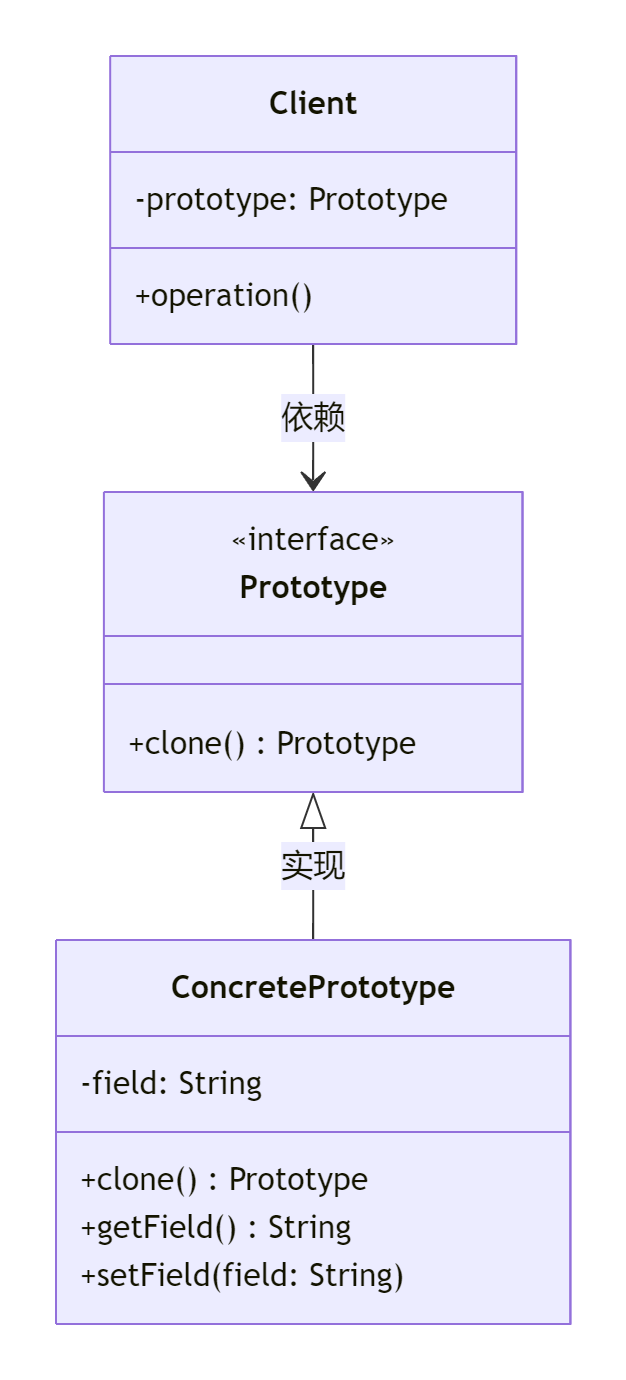
核心角色
- Prototype:抽象原型接口,声明克隆方法(如 clone())。
- ConcretePrototype:具体原型类,实现克隆逻辑(支持深拷贝或浅拷贝)。
- Client:客户端,通过复制原型对象创建新实例。
优点
- 性能优化:避免重复执行耗时的初始化代码(如数据库连接、复杂计算)。
- 动态创建对象:运行时通过克隆生成新对象,无需依赖具体类。
- 简化对象创建:隐藏对象创建细节,客户端仅需调用 clone()。
- 支持状态保存与恢复:可通过克隆快速生成对象的历史状态副本。
缺点
- 深拷贝复杂度高:若对象包含嵌套引用,需递归处理所有层级,增加实现复杂度。
- 需实现克隆方法:每个类需重写 clone(),可能违反开闭原则(需修改已有类)。
- 循环引用问题:若对象间存在循环引用,深拷贝可能导致栈溢出或逻辑错误。
适用场景
创建成本高的对象
- 数据库连接对象(避免重复建立连接)。
- 复杂计算结果的缓存副本(如机器学习模型参数)。
## 动态生成对象 - 游戏中的敌人复制(快速生成相同属性的敌人)。
- 图形编辑器中的图形元素复制(如复制一个已配置的按钮)。
## 状态保存与回滚 - 文本编辑器的撤销操作(克隆并保存文档状态)。
- 事务操作的回滚点(克隆并暂存数据库状态)。
## 替代继承的扩展方式 - 通过组合原型对象动态配置新对象,避免子类爆炸。
浅拷贝实现
深拷贝实现
原型管理器(扩展)
总结:原型模式是优化对象创建性能的有效手段,尤其适用于需要频繁创建复杂对象的场景,但需谨慎处理深拷贝问题。





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








