目录
4种帮助命令
1、man
man+命令名 (我这里用的是ls}

下面是man的快捷键

2、info
info与man的用途其实差不多,都是用来查询命令的用法或者是文件的格式。但是与man page不同的 是,info page则是将文件数据拆成一个一个的段落,每个段落用自己的页面来撰写, 并且在各个页面中 还有类似网页的『超链接』来跳到各不同的页面中,每个独立的页面也被称为一个节点(node)。 不过你要查询的目标数据的说明文件必须要以info的格式来写成才能够使用info的特殊功能(例如超链 接)。 而这个支持info命令的文件默认是放置在/usr/share/info/这个目录当中的。

下面是info的快捷键

3、help
命令+help
help只能获取shell内置命令,当不知道你要查询的命令是内部还是外部,可以用 type+命令 来看是否为内部
4、--help
命令 + --help
查看目录下的文件:ls
英文 简写
instrument -l 以长格形式显示文件和目录的详细信息,ls命令默认只显示名称的短格式。
dictionary -d 显示指定目录本身的信息,而不显示目录下的各个文件和子目录的信息。
concept -c 按文件的修改时间排序后,予以显示。
hard -h 以更人性化的方式显示出目录或文件的大小,默认的大小单位为字节,使用-h 选项 后将显示为 K 、M等单位。此选项需要和-l选项结合使用才能体现出结 果。
Recursion -R 以递归的方式显示指定目录及其子目录中的所有内容。
--directory -a 显示所有子目录和文件的信息,包括名称以“.”开头的隐藏目录和隐藏文件。--almost-all -A 与-a选项的作用类似,但不显示表示当前目录的“.”和表示父目录的“..”。 inode -i 显示文件索引节点号(inode)。一个索引节点代表一个文件,在linux中保 存在磁盘分区中的文件都给它分配一个编号,称为索引节点号inode。
sequence -s 按照文件大小排序
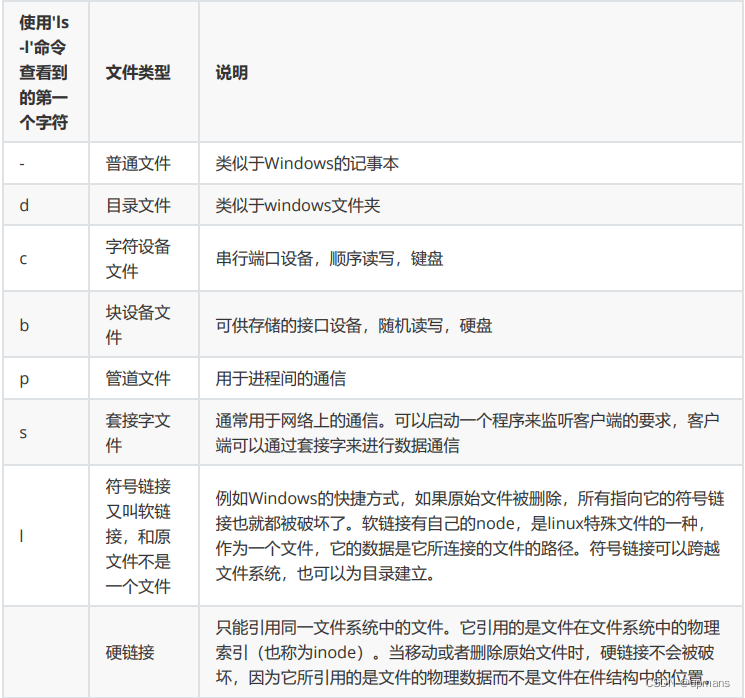
date
%Y 完整年份(例如:2020)
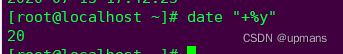
%m 月份(1~12)
![]()
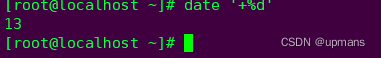
%d 本月中的第几天
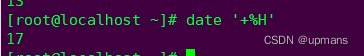
%H 小时(00~23)
%M 分钟(00~59)
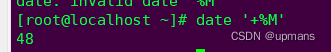
%j 今年中的第几天
![]()
date看查看当前时间
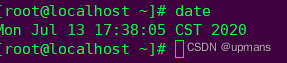
这些命令可以组合使用
比如:按年-月-日 时-分-秒
![]()
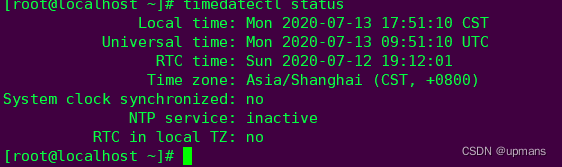
timedatectl命令
timedatectl命令用于设置系统的时间,英文全称为:“time date control”,语法格式为: timedatectl [OPTIONS...] COMMAND ...
status 显示状态信息
list-timezones 列出已知时区
set-timezone 设置生效时区
![]()
set-time 设置系统时间
![]()
file和stat命令的使用
stat
stat命令用于显示文件或文件系统的详细信息。在显示文件信息时,比ls命令更加详细
%a access rights in octal (note '#' and '0' printf flags)
%A access rights in human readable form
%b number of blocks allocated (see %B)
%B the size in bytes of each block reported by %b
%C SELinux security context string
%d device number in decimal
%D device number in hex
%f raw mode in hex
%F file type
%g group ID of owner
%G group name of owner
%h number of hard links
%i inode number
%m mount point
%n file name
%N quoted file name with dereference if symbolic link
%o optimal I/O transfer size hint
%s total size, in bytes
%t major device type in hex, for character/block device special files
%T minor device type in hex, for character/block device special files
%u user ID of owner
%U user name of owner
%w time of file birth, human-readable; - if unknown
%W time of file birth, seconds since Epoch; 0 if unknown
%x time of last access, human-readable
%X time of last access, seconds since Epoch
%y time of last data modification, human-readable
%Y time of last data modification, seconds since Epoch
%z time of last status change, human-readable
%Z time of last status change, seconds since Epoch
Valid format sequences for file systems:
%a free blocks available to non-superuser
%b total data blocks in file system
%c total file nodes in file system
%d free file nodes in file system
%f free blocks in file system
%i file system ID in hex
%l maximum length of filenames
%n file name
%s block size (for faster transfers)
%S fundamental block size (for block counts)
%t file system type in hex
%T file system type in human readable form
file
-v, --version output version information and exit
-m, --magic-file LIST use LIST as a colon-separated list of magic
number files
-z, --uncompress try to look inside compressed files
-Z, --uncompress-noreport only print the contents of compressed files
-b, --brief do not prepend filenames to output lines
-c, --checking-printout print the parsed form of the magic file, use in
conjunction with -m to debug a new magic file
before installing it
-e, --exclude TEST exclude TEST from the list of test to be
performed for file. Valid tests are:
apptype, ascii, cdf, compress, elf, encoding,
soft, tar, text, tokens
-f, --files-from FILE read the filenames to be examined from FILE
-F, --separator STRING use string as separator instead of `:'
-i, --mime output MIME type strings (--mime-type and
--mime-encoding)
--apple output the Apple CREATOR/TYPE
--extension output a slash-separated list of extensions
--mime-type output the MIME type
--mime-encoding output the MIME encoding
-k, --keep-going don't stop at the first match
-l, --list list magic strength
-L, --dereference follow symlinks
-h, --no-dereference don't follow symlinks (default)
-n, --no-buffer do not buffer output
-N, --no-pad do not pad output
-0, --print0 terminate filenames with ASCII NUL
-p, --preserve-date preserve access times on files
-P, --parameter set file engine parameter limits
indir 15 recursion limit for indirection
name 30 use limit for name/use magic
elf_notes 256 max ELF notes processed
elf_phnum 128 max ELF prog sections processed
elf_shnum 32768 max ELF sections processed
-r, --raw don't translate unprintable chars to \ooo
-s, --special-files treat special (block/char devices) files as
ordinary ones
-C, --compile compile file specified by -m
-d, --debug print debugging messages




 本文介绍了Linux系统中的四个常用命令:man、info、help和--help,提供了ls命令的详细使用,包括不同参数的解释,如-l、-d等。还讲解了date命令的时间格式,并提到了timedatectl命令。此外,深入讨论了file和stat命令,展示了它们在查看文件详细信息时的不同应用。
本文介绍了Linux系统中的四个常用命令:man、info、help和--help,提供了ls命令的详细使用,包括不同参数的解释,如-l、-d等。还讲解了date命令的时间格式,并提到了timedatectl命令。此外,深入讨论了file和stat命令,展示了它们在查看文件详细信息时的不同应用。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








