基于王道机试指南的保研机试笔记(C语言翻译版)
技巧
C语言哈希表用法
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define HASHSIZE 100000
typedef char* ElemType,*KeyType;
typedef struct node{
KeyType key; // 关键字
ElemType data; // 值
struct node *next;
} node, *LinkList;
typedef LinkList HashTable[HASHSIZE];
void init(HashTable H);
bool insert(HashTable H,KeyType key,ElemType value);
ElemType get(HashTable H,KeyType key);
bool delete(HashTable H,KeyType key);
int hash(KeyType key,int mod);
bool equal(KeyType str1,KeyType str2);
void init(HashTable H){
LinkList T;
for(int i=0;i<HASHSIZE;i++){
//创建头节点,方便操作
T=(LinkList)malloc(sizeof(node));
T->key=NULL;
T->data=NULL;
T->next = NULL;
H[i] = T;
}
}
bool insert(HashTable H,KeyType key,ElemType value){
int index;
LinkList L,T,P;
index = hash(key,HASHSIZE);
P = H[index];
L = H[index]->next;
while(L!=NULL){
if(equal(L->key,key)){
L->data = value;
return true;
}
P = L;
L=L->next;
}
T=(LinkList)malloc(sizeof(node));
T->key=key;
T->data=value;
T->next = NULL;
P->next = T;
return true;
}
ElemType get(HashTable H,KeyType key){
int index;
LinkList L;
index = hash(key,HASHSIZE);
L = H[index]->next;
while(L!=NULL){
if(equal(L->key,key)){
return L->data;
}
L=L->next;
}
return NULL;
}
bool delete(HashTable H,KeyType key){
int index;
LinkList L,P;
index = hash(key,HASHSIZE);
P = H[index];
L = H[index]->next;
while(L!=NULL){
if(equal(L->key,key)){
P->next = L->next;
free(L);
return true;
}
P = L;
L = L->next;
}
return false;
}
int hash(KeyType key,int mod)
{
unsigned long h=0;
while(*key)
{
h += *key++;
}
return h % mod;
}
bool equal(KeyType str1,KeyType str2){
return 0==strcmp(str1,str2);
}
int main(){
HashTable h;
init(h);
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
char *name = (char *) malloc(sizeof(char) * 20); // 必须用这种方式分配内存,不能用char name[20],否则分配的是同一块
char *number = (char *) malloc(sizeof(char) * 20);
scanf("%s %s", name, number);
insert(h, name, number);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
char name[20];
scanf("%s", name);
char *number = get(h, name);
if(number == NULL)
printf("Not Found\n");
else
printf("%s\n", number);
}
delete(h, "bob");
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
char name[20];
scanf("%s", name);
char *number = get(h, name);
if(number == NULL)
printf("Not Found\n");
else
printf("%s\n", number);
}
}
C语言string.h函数
字符串长度
char a[] = "ABC";
int l = strlen(a); // 返回3,不包含'\0'的长度
int l = sizeof(a) / sizeof(char); // 返回4,包含'\0'的长度
字符串切割
char buf[] = "abckd$kdf%kdlfk";
char *p = strtok(buf, "%$"); // 以$或,将字符串buf切割,即遇到$或,都会切割,并将第一个子串返回给p
while(p != NULL) // strtok会一直切割,直到返回NULL,切割完成
{
printf("%s\n", p);
p = strtok(NULL, "%$"); // 获取第二个子串时,strtok的第一个参数写NULL即可
}
字符串复制
char src[] = "source";
char dest[10];
strcpy(dest, src);
printf("%s\n", dest); // 输出source
// 也可以用于切割
strncpy(dest, src, 2);
dest[2] = '\0';
printf("%s\n", dest); // 输出so
字符串拼接
strcat
char a[] = "aaa";
char b[] = "bbb";
strcat(a, b); // 将b拼接到a上
printf("%s\n", a); // 输出aaabbb
字符串比较
char b[] = "bbb";
char b2[] = "bbb";
char a[] = "aaa";
char c[] = "ccc";
printf("b cmp b2 is %d\n", strcmp(b, b2)); // b = b2返回0
printf("b cmp a is %d\n", strcmp(b, a)); // b > a 返回1
printf("b cmp c is %d\n", strcmp(b, c)); // b < c 返回-1
char a1[] = "aaabbb";
char a2[] = "aaaccc";
printf("a1 cmp a2 in first 3 * sizeof(char) is %d\n", strncmp(a1, a2, 3 * sizeof(char))); // 只比较前三个字节,返回0
printf("a1 cmp a2 in first 4 * sizeof(char) is %d\n", strncmp(a1, a2, 4 * sizeof(char))); // 比较前四个字节,返回-1
字符串查找
char* p1 = "abcdefgh";
char* p2 = "def";
char* ret = strstr(p1, p2);//把返回的字符串首地址赋给ret
if (ret == NULL){
printf("子串不存在\n");//当返回的字符串首地址为空,ret为一个空指针,代表不存在该子串
}
else{
printf("%s\n", ret);//当返回的字符串首地址不为空,则会从字符串首地址开始打印,到‘\0’停止
}
C语言math.h函数
- 取绝对值
double fabs(double a); 对a取绝对值
2.取整与取余
int ceil (double a); 取上整(里面可以填整数也能填小数,整数返回自己,小数向上取整)
int floor (double a); 取下整(同上)
double modf (double a, double ip); 将参数的整数部分通过指针回传, 返回小数部分,整数部分保存在ip中
double fmod (double a, double b); 返回两参数相除a/b的余数,符号与a相同。如果b为0,则结果与具体的额实现有关
- 三角函数
double sin (double a); a的正弦值
double cos (double a); a的余弦值
double tan (double a); a的正切值
- 反三角函数
double asin (double a); 结果介于[-PI/2, PI/2],a值域为[-1,1]
double acos (double a); 结果介于[0, PI],a值域为[-1,1]
double atan (double a); 反正切(主值), 结果介于[-PI/2, PI/2]
double atan2 (double b, double a); 反正切(整圆值), 结果介于[-PI, PI]
- 指数与对数
double exp (double a); 幂函数ea
double pow (double a, double b); ab,如果a=0且b<=0,或者a<0且b不是整型数,将产生定义域错误
double sqrt (double a); a的平方根,其中a>=0
double log (double a); 以e为底的对数,自然对数,a>0
double log10 (double a); 以10为底的对数,a>0
- 双曲三角函数
double sinh (double a); a的双曲正弦值
double cosh (double a); a的双曲余弦值
double tanh (double a); a的双曲正切值
- 标准化浮点数
double frexp (double a, int exp); 标准化浮点数, a = f * 2^exp, 已知a求f, exp ( a介于[0.5, 1] )并返回f值
double ldexp (double a, int eap); 与frexp相反, 已知a, exp求a2exp
数据结构
链表
基本实现
struct node{
int data;
struct node* next;
};
struct node* head;
反转链表
原地反转
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
if(head == NULL) return NULL;
struct ListNode* curr = head->next;
struct ListNode* prev = head;
struct ListNode* temp;
head->next = NULL;
while(curr != NULL){
temp = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = temp;
}
return prev;
}
头插法
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
if(head == NULL) return NULL;
struct ListNode* pre = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
pre->val = head->val;
pre->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* cur1 = head->next;
struct ListNode* cur2 = pre;
while(cur1 != NULL){
cur2 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
cur2->val = cur1->val;
cur2->next = pre;
cur1 = cur1->next;
pre = cur2;
}
return cur2;
}
栈
基本实现
struct stack{
int stack_list[MAXSIZE];
int top;
};
void initStack(struct stack* s){
s->top = -1;
}
bool isEmpty(struct stack* s){
return s->top == -1;
}
bool isFull(struct stack* s){
return s->top == MAXSIZE - 1;
}
bool pushStack(struct stack* s, int elem){
if(isFull(s)) return false;
s->stack_list[++s->top] = elem;
return true;
}
bool popStack(struct stack* s){
if(isEmpty(s)) return false;
s->top--;
return true;
}
int topStack(struct stack* s){
return s->stack_list[s->top];
}
// 简易版
int stack[MAXN];
int top = -1;
// 入栈
stack[++top] = x;
// 出栈
int x = stack[top--];
// 是否为空
if(top == -1)
括号匹配
如果是左括号,入栈,如果是右括号,从栈顶出栈一个元素,如果正好与当前元素匹配,匹配成功,否则匹配失败。
所有元素匹配完成后,如果栈为空,匹配成功,否则匹配失败。
表达式求值
如果遇到数字,push进数字栈
如果遇到操作符,比较栈顶操作符a和当前操作符b的优先级关系,如果a>=b,先计算a,push结果,再push b,否则直接push(注意如果先计算a,有可能a下面的c也>=b,因此要把所有>=b的栈顶元素都计算完,才能push b,见69行)
如果遇到左括号,直接push,如果遇到右括号,不断pop并计算直到找到左括号,将最终结果push进栈中
int num_stack[1000000];
int num_top = -1;
char op_stack[1000000];
int op_top = -1;
int getNum(char *s, int* point){
int ret = 0;
int len = strlen(s);
while(*point < len && s[*point] >= '0' && s[*point] <= '9'){
ret = ret * 10 + (s[*point] - '0'); // 必须加括号,否则很大的数加上s[*point]的ASCII码可能超出int范围
(*point) = (*point) + 1;
}
return ret;
}
int judge_type(char a){
if(a >= '0' && a <= '9')
return 1;
else if(a == '+' || a == '-' || a == '*' || a == '/')
return 2;
else if(a == '(')
return 3;
else if(a == ')')
return 4;
else
return 5;
}
bool judge_privilege(char a, char b){
int aa = -1, bb = -1;
if(a == '+' || a == '-') aa = 1;
if(a == '*' || a == '/') aa = 2;
if(b == '+' || b == '-') bb = 1;
if(b == '*' || b == '/') bb = 2;
if(aa < bb) return true; // 栈顶操作符a比当前操作符优先级低,则放入即可;如果高或相等,则需要计算
return false; // 相等也要算出来,否则1-1+1这种顺序就变了,会变成1-(1+1)
}
int calculate_result(){
int b = num_stack[num_top--];
int a = num_stack[num_top--];
char op = op_stack[op_top--];
if(op == '+') return a + b;
if(op == '-') return a - b;
if(op == '*') return a * b;
if(op == '/') return a / b;
return -1;
}
int calculate(char * s){
memset(num_stack, 0, sizeof(num_stack));
memset(op_stack, 0, sizeof(op_stack));
num_top = -1;
op_top = -1;
int len = strlen(s);
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
int temp_judge_type = judge_type(s[i]);
if(temp_judge_type == 1){
// 是数字
int temp_point = i;
int temp_value = getNum(s, &temp_point);
i = temp_point - 1;
num_stack[++num_top] = temp_value;
}
else if(temp_judge_type == 2){
// 是字符
if(op_top == -1 || judge_privilege(op_stack[op_top], s[i])){
op_stack[++op_top] = s[i];
}
else{
int result = calculate_result();
num_stack[++num_top] = result;
i--; // 当前只计算不push,直到栈顶元素优先级比s[i]小或相等才push进去
}
}
else if(temp_judge_type == 3){
// 是左括号,直接push进去
op_stack[++op_top] = s[i];
}
else if(temp_judge_type == 4){
// 是右括号
while(1){
char temp_op = op_stack[op_top];
if(temp_op == '('){
op_top--;
break;
}
int result = calculate_result();
num_stack[++num_top] = result;
}
}
}
while(op_top != -1){
int result = calculate_result();
num_stack[++num_top] = result;
}
return num_stack[num_top];
}
队列
基本实现
struct queue{
struct position q_list[MAXN];
int front, rear, len;
};
void initQ(struct queue *q){
q->front = 0;
q->rear = 0;
q->len = 0;
}
bool isQEmpty(struct queue *q){
// front与rear相等即队列为空
if(q->front == q->rear) return true;
else return false;
}
bool isQFull(struct queue *q){
if(q->rear == MAXN) return true;
else return false;
}
bool pushQ(struct queue *q, struct position x){
if(!isQFull(q)){
q->q_list[q->rear++] = x;
q->len++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
struct position popQ(struct queue* q){
if(!isQEmpty(q)){
q->len--;
return q->q_list[q->front++];
}
}
约瑟夫问题
用队列的思路是:对于不该死的人从队首pop出去后(报数后)再push进队尾(还活着等待下一轮报数),对于该死的人,不需要再push进入
int n, m, p; // n是所有人数,m是报数到m的人死亡,p是报数起始人数
queue<int> life;
// 从报数起始人p开始入队
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
life.push((p + i) % n);
while(!life.empty()){
// m-1个不死的人,pop出去后再加回队尾,以实现循环链表的功能【1】
for(int i = 1; i < m; i++){
life.push(life.front());
life.pop();
}
// 报数报到m的人死去
life.pop();
}
队列模拟可能会超时,数学公式递归得结果f(n, m) = (f(n−1, m) + m) % n
// f(n, m) = (f(n−1, m) + m) % n
int f(int n, int m){
if(n == 1) return 0;
return (f(n-1, m) + m) % n;
}
int lastRemaining(int n, int m){
return f(n, m);
}
查找
二分查找
查找的前提是数组有序
int BinarySearch(int *array, int len, int key){
int left, right, middle;
left = 0;
right = len - 1;
while (left <= right){
middle = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(array[middle] > key){
right = middle - 1;
} else if(array[middle] < key){
left = middle + 1;
} else{
printf("The index is ");
break;
}
}
if(left > right) return -1;
else return middle;
}
排序
qsort
ElemType *array = (ElemType*)malloc(sizeof(ElemType) * n);
qsort(array, n, sizeof(ElemType), compare);
// qsort函数第一个参数是数组指针,第二个参数是数组中元素个数,第三个参数是数组中单个元素的大小,第四个参数是自定义比较函数
int compare(const void *a, const void *b){
ElemType *aa = (ElemType *)a;
ElemType *bb = (ElemType *)b;
if(aa->length > bb->length) return 1;
else return 0;
}
各种排序写法
冒泡排序
冒泡排序思路:第i轮遍历从[i, n-1]中挑出一个最小的,通过逐个交换使其浮到最左侧i处
void BubbleSort(int *array, int n){
bool flag;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ // 第i轮遍历
flag = false;
for(int j = n - 1; j > i; j--){ // 第i轮遍历从[i, n-1]中挑出一个最小的通过交换使其浮到最左侧i处
if(array[j] < array[j - 1]){ // 升序为<,降序为>
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j - 1];
array[j - 1] = temp;
flag = true;
}
}
if(!flag) return;
}
}
选择排序
选择排序思路:第i轮遍历从[i, n-1]中挑出一个最小的,直接使其与i处元素交换
void selectSort(int* array, int n){
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++){
// 从i到n-1中挑出一个最小的
int min_pos = i;
for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j++){
if(array[min_pos] > array[j]){
min_pos = j;
}
}
// 交换min_pos和i的位置
if(min_pos != i){
int temp = array[min_pos];
array[min_pos] = array[i];
array[i] = temp;
}
}
}
插入排序
每轮排序将待排序序列的第一个元素插入已排序序列的对应位置
void insertSort(int *array, int n){
int temp;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){ // 已排序序列为array[0]
temp = array[i]; // 待排序元素为array[i](i从下标1开始)
int j;
// 对于从0到i-1的已排序序列,如果待排序元素temp小于他们,将他们后移一个位置
for(j = i - 1; j >= 0 && temp < array[j]; j--){
array[j + 1] = array[j];
}
// 直到大于temp的元素全部后移完成,空出来的位置j+1存放temp
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
快速排序
分治法思想:找到一个元素,将比它小的都放在左边,比它大的都放在右边,这样就确定了该元素应该放置的位置,然后分别再对其左右执行相同操作
void swap(int *a, int *b){
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
void quickSort(int *array, int left, int right){
if(left < right){
int key = array[left];
int i = left, j = right + 1;
while(1){
// 找到key左边第一个比key大的元素
while(array[++i] < key && i != right);
// 找到key右边第一个比key小的元素
while(array[--j] > key && j != left);
// 如果i < j互换位置,否则本轮排序完成
if(i < j) swap(&array[i], &array[j]);
else break;
}
// j为排序元素key该在的位置
swap(&array[left], &array[j]);
// 分治
quickSort(array, left, j - 1);
quickSort(array, j + 1, right);
}
}
int array[5] = {5, 3, 6, 2, 8};
quickSort(array, 0, 4);
归并排序
将左右两个子序列排序完成,然后使用merge函数将其合并
void mergeSort(int *array, int n){
int *temp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
mSort(array, temp, 0, n - 1);
}
void mSort(int *array, int *temp, int left, int right){
int middle;
if(left < right){
middle = left + (right - left) / 2;
mSort(array, temp, left, middle);
mSort(array, temp, middle + 1, right);
merge(array, temp, left, middle, right);
}
}
void merge(int *array, iny *temp, int left, int leftend, int rightend){
int i = left, j = leftend + 1, k = left;
while(i <= leftend && j <= rightend){
if(array[i] <= array[j]){
temp[k++] = array[i++];
}
else
temp[k++] = array[j++];
}
while(i <= leftend)
temp[k++] = array[i++];
while(j <= rightend)
temp[k++] = array[j++];
for(int i = left; i <= right; i++)
array[i] = temp[i];
}
字符串
KMP算法
// 求next数组,即求最长匹配前后缀
int* getNextTable(char* pattern) {
int m = strlen(pattern);
int *next = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (m + 4));
int i = -1; // i是最长匹配前缀的最后一个字符的下标,初始化为-1(同时也是前后缀匹配长度)
int j = 0; // j是最长匹配后缀的最后一个字符的下标,初始化为0
next[0] = i;
while(j < m){
if(i == -1 || pattern[i] == pattern[j]){
// 如果两个前后缀的下一个字符仍然匹配,直接加一即可
i++;
j++;
next[j] = i; // j处的next值为前后缀长度i
}
else
i = next[i];
// 如果下一个字符不匹配,将i回退回nextTable[i]处继续寻找前后缀
}
return next;
}
// KMP算法寻找text中第一个匹配pattern的位置
int KMP(char *text, char *pattern){
int n = strlen(text);
int m = strlen(pattern);
int *next = getNextTable(pattern);
int i = 0; // text中的指针
int j = 0; // pattern中的指针
while(i < n && j < m){
if(j == -1 || text[i] == pattern[j]){
// 如果当前字符匹配成功,继续匹配下一个字符
i++;
j++;
}
else{
// 如果当前字符匹配不成功,pattern指针改到nextTable[j]处,i指针不用变,继续匹配text[i]的字符
j = next[j];
}
}
// 如果pattern指针移动到了最后,说明pattern全串匹配成功,i为匹配到的子串的末尾位置,i-j+1即为匹配到的子串的起始位置
if(j == m)
return i - j;
else
return -1;
// 否则匹配不成功
return -1;
}
// KMP算法寻找text中匹配pattern的数量
int KMP2(char *text, char *pattern){
int n = strlen(text);
int m = strlen(pattern);
int *next = getNextTable(pattern);
int i = 0; // text中的指针
int j = 0; // pattern中的指针
int count = 0;
while(i < n){
if(j == -1 || text[i] == pattern[j]){
// 如果当前字符匹配成功,继续匹配下一个字符
i++;
j++;
}
else{
// 如果当前字符匹配不成功,pattern指针改到nextTable[j]处,i指针不用变,继续匹配text[i]的字符
j = next[j];
}
if(j == m){
count++;
j = next[j];
}
}
return count;
}
树
基本存储
struct TreeNode{
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
};
struct TreeNode *root;
遍历
前中后
// 遍历并存入数组order中
void middleOrder(struct TreeNode* root, int *order, int *returnSize){
if(root != NULL){
middleOrder(root->left, order, returnSize);
order[(*returnSize)++] = root->val;
middleOrder(root->right, order, returnSize);
}
}
// 前序preOrder、后序只是三行代码顺序区别
层次
void levelOrder(TreeNodePoint root){
queue<TreeNodePoint> node_queue;
TreeNodePoint temp;
node_queue.push(root);
while(!node_queue.empty()){
temp = node_queue.front();
node_queue.pop();
visit(temp);
if(temp->lchild != NULL)
node_queue.push(temp->lchild);
if(temp->rchild != NULL)
node_queue.push(temp->rchild);
}
}
将每层存在一个数组里,例如:
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:[[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
方法:内外两层遍历,外层遍历遍历树的层数,内层遍历遍历一整层的节点
int** levelOrder(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
if(root == NULL){
*returnSize = 0;
return NULL;
}
struct queue Q;
initQ(&Q);
int level = 0;
int *length = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * MAXN);
int **ret = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * MAXN);
memset(length, 0, sizeof(length));
pushQ(&Q, root);
while(!isQEmpty(&Q)){
int re = Q.rear; // 从此时的front到re是当前一整层的所有节点
int len = 0;
ret[level] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * MAXN);
while(Q.front < re){ // 遍历当前层
struct TreeNode *temp = popQ(&Q);
ret[level][len++] = temp->val;
if(temp->left != NULL){
pushQ(&Q, temp->left);
}
if(temp->right != NULL){
pushQ(&Q, temp->right);
}
}
length[level] = len;
level++;// 层数+
}
*returnSize = level;
*returnColumnSizes = length;
return ret;
}
DFS(用DFS递归得到树的高度)
int DFS(struct TreeNode* head){
if(head == NULL) return 0;
int h = 0;
visited[head->val] = 1;
h = max(h, DFS(head->left)); // 左子树高度
h = max(h, DFS(head->right)); // 右子树高度
return h + 1; // 左右子树高度最大值加根节点
}
由遍历序列得到树
前序+中序得到树
struct TreeNode *buildTree(int *preorder, int preorderSize, int *inorder, int inorderSize){
if(preorderSize == 0) return NULL;
struct TreeNode *root = (struct TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
root->val = preorder[0];
int pos;
for(int i = 0; i < inorderSize; i++)
if(inorder[i] == preorder[0]){
pos = i;
break;
}
root->left = buildTree(preorder + 1, pos, inorder, pos);
root->right = buildT(preorder + 1 + pos, preorderSize - pos - 1, inorder + pos + 1, inorderSize - pos - 1);
return root;
}
int main(){
int preorder[5] = {3,9,20,15,7}, inorder[5] = {9,3,15,20,7}
struct TreeNode *root = buildTree(preorder, 5, inorder, 5);
}
二叉排序树
二叉排序树的性质:中序遍历序列是升序序列
完全二叉排序树:
可以算出h=log2n(n为节点数目,向下取整)
除最后一排的叶节点外,其他节点共2h-1
最后一排共n-(2h-1)个节点
平衡二叉排序树:升序序列中点做根节点
判断是否是二叉排序树
进行中序遍历,判断是否是一个递增序列(是否比前一个值大)
long long pre = LONG_MIN;
bool inOrder(TreeNode* root){
if(root == NULL) return true;
bool l = inOrder(root->left);
if(root->val <= pre) return false;
pre = root->val;
bool r = inOrder(root->right);
return l && r;
}
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
return inOrder(root);
}
按照定义判断:
左子树上的每一个元素都比根节点小,右子树上的每一个元素都比根节点大。
且左子树、右子树也是一个二叉排序树。
bool judge_left(struct TreeNode* left, int root_val){
if(left->val >= root_val) return false;
if(left->left != NULL){
if(!judge_left(left->left, root_val)) return false;
}
if(left->right != NULL){
if(!judge_left(left->right, root_val)) return false;
}
return true;
}
bool judge_right(struct TreeNode* right, int root_val){
if(right->val <= root_val) return false;
if(right->left != NULL){
if(!judge_right(right->left, root_val)) return false;
}
if(right->right != NULL){
if(!judge_right(right->right, root_val)) return false;
}
return true;
}
bool judge(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root->left != NULL){
if(!judge_left(root->left, root->val)) return false;
if(!judge(root->left)) return false;
}
if(root->right != NULL){
if(!judge_right(root->right, root->val)) return false;
if(!judge(root->right)) return false;
}
return true;
}
bool isValidBST(struct TreeNode* root){
return judge(root);
}
平衡二叉树AVL
首先平衡二叉树是一个二叉搜索树,另外它还满足左右子树高度差不大于1

#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define null 0
typedef struct TreeNode* AVLTree;
struct TreeNode{
int elem;
AVLTree left;
AVLTree right;
int height;
};
int max(int a,int b){ return a > b ? a : b; }
int getHeight(AVLTree T){
if(T == null) return -1;
else return T->height;
}
AVLTree singleLeftRotation(AVLTree T){
//左单旋:破坏点在左子树的左子树上
AVLTree B = T->left;
T->left = B->right;
B->right = T;
//更新T,B的树高
T->height = max(getHeight(T->left), getHeight(T->right)) + 1;
B->height = max(getHeight(B->left), getHeight(B->right)) + 1;
return B;
}
AVLTree singleRightRotation(AVLTree T){
//右单旋:破坏点在右子树的右子树上
AVLTree B = T->right;
T->right = B->left;
B->left = T;
//更新T,B的树高
T->height = max(getHeight(T->left), getHeight(T->right)) + 1;
B->height = max(getHeight(B->left), getHeight(B->right)) + 1;
return B;
}
AVLTree doubleLeftRightRotation(AVLTree T){
//左右双旋:破坏点在左子树的右子树上
T->left = singleRightRotation(T->left);
return singleLeftRotation(T);
}
AVLTree doubleRightLeftRotation(AVLTree T){
//右左双旋:破坏点在右子树的左子树上
T->right = singleLeftRotation(T->right);
return singleRightRotation(T);
}
AVLTree AVLInsert(AVLTree T, int n){
//插入过程一定会访问被插结点的所有祖宗结点,更新所有祖宗的树高
//在AVL上插入一个数,并返回树根
if(T == null){
T = (AVLTree)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
T->elem = n;
T->left = T->right = null;
T->height = 0;
}
else{
if(n > T->elem){
T->right = AVLInsert(T->right, n);
if(getHeight(T->right) - getHeight(T->left) == 2){
if(n < T->right->elem){
//破坏点在右子树的左子树上
T = doubleRightLeftRotation(T);
}
else//破坏点在右子树的右子树上
T = singleRightRotation(T);
}
}
if(n < T->elem){
T->left = AVLInsert(T->left, n);
if(getHeight(T->left) - getHeight(T->right) == 2){
if(n > T->left->elem){
//破坏点在左子树的右子树上
T = doubleLeftRightRotation(T);
}
else//破坏点在左子树的左子树上
T = singleLeftRotation(T);
}
}
}
T->height = max(getHeight(T->left), getHeight(T->right)) + 1;
return T;
}
AVLTree makeAVL(int N){
AVLTree T = null;
int e;
while(N--){
scanf("%d",&e);
T = AVLInsert(T,e);
}
return T;
}
void printAVLTree(AVLTree T){
if(T != NULL){
printf("%d ", T->elem);
printAVLTree(T->left);
printAVLTree(T->right);
}
}
void freeTree(AVLTree T){
if(T->left) freeTree(T->left);
if(T->right) freeTree(T->right);
free(T);
}
int main(){
int N;
if(scanf("%d\n",&N)){
AVLTree T = makeAVL(N);
printAVLTree(T);
printf("\nroot is %d\n", T->elem);
freeTree(T);
}
return 0;
}
哈夫曼树
struct BTreeNode* CreateHuffman(ElemType a[], int n)
{
int i, j;
struct BTreeNode **b, *q;
b = malloc(n*sizeof(struct BTreeNode));
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) //初始化b指针数组,使每个指针元素指向a数组中对应的元素结点
{
b[i] = malloc(sizeof(struct BTreeNode));
b[i]->data = a[i];
b[i]->left = b[i]->right = NULL;
}
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)//进行 n-1 次循环建立哈夫曼树
{
//k1表示森林中具有最小权值的树根结点的下标,k2为次最小的下标
int k1 = -1, k2;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)//让k1初始指向森林中第一棵树,k2指向第二棵
{
if (b[j] != NULL && k1 == -1)
{
k1 = j;
continue;
}
if (b[j] != NULL)
{
k2 = j;
break;
}
}
for (j = k2; j < n; j++)//从当前森林中求出最小权值树和次最小
{
if (b[j] != NULL)
{
if (b[j]->data < b[k1]->data)
{
k2 = k1;
k1 = j;
}
else if (b[j]->data < b[k2]->data)
k2 = j;
}
}
//由最小权值树和次最小权值树建立一棵新树,q指向树根结点
q = malloc(sizeof(struct BTreeNode));
q->data = b[k1]->data + b[k2]->data;
q->left = b[k1];
q->right = b[k2];
b[k1] = q;//将指向新树的指针赋给b指针数组中k1位置
b[k2] = NULL;//k2位置为空
}
free(b); //删除动态建立的数组b
return q; //返回整个哈夫曼树的树根指针
}
堆(优先队列)
堆排序是从后到前排,对于升序排列,首先将堆调整为一个大顶堆,则根节点即为最大元素,将其与末尾元素互换位置,继续调整,找到第二大元素,将第二大元素放在倒数第二个位置上。
因此升序序列需要用max,降序序列需要用min。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
void Swap(int* array, int i, int j)
{
assert(array);
int tmp;
tmp = array[j];
array[j] = array[i];
array[i] = tmp;
}
/*大根堆调整*/
void MaxHeapify(int* array, int heapSize, int currentNode)
{
int leftChild, rightChild, largest; // 在根节点currentNode、左孩子leftChild、右孩子rightChild之中找到最大的
leftChild = 2*currentNode + 1;
rightChild = 2*currentNode + 2;
if(leftChild < heapSize && array[leftChild] > array[currentNode])
largest = leftChild;
else
largest = currentNode;
if(rightChild < heapSize && array[rightChild] > array[largest])
largest = rightChild;
if(largest != currentNode)
{
Swap(array, largest, currentNode); // 将三个中最大的调整到根节点
MaxHeapify(array, heapSize, largest); // 重新调整原来的largest对应
}
}
/*构建大根堆*/
void MaxHeapCreate(int* array, int heapSize)
{
int i;
for(i = heapSize/2; i >= 0; i--)
{
MaxHeapify(array, heapSize, i);
}
}
/*小根堆调整*/
void MinHeapify(int* array, int heapSize, int currentNode)
{
int leftChild, rightChild, minimum;
leftChild = 2*currentNode + 1;
rightChild = 2*currentNode + 2;
if(leftChild < heapSize && array[leftChild] < array[currentNode])
minimum = leftChild;
else
minimum = currentNode;
if(rightChild < heapSize && array[rightChild] < array[minimum])
minimum = rightChild;
if(minimum != currentNode)
{
Swap(array, minimum, currentNode);
MinHeapify(array, heapSize, minimum);
}
}
/*构建小根堆*/
void MinHeapCreate(int* array, int heapSize)
{
int i;
for(i = heapSize/2; i >= 0; i--)
{
MinHeapify(array, heapSize, i);
}
}
/*升序堆排序*/
void HeapSort(int* array, int heapSize)
{
MaxHeapCreate(array, heapSize); // 第一步构建大根堆,堆顶元素为最大元素
while (heapSize > 0)
{
Swap(array, 0, heapSize - 1); // 将堆顶元素移动到最后面
heapSize = heapSize - 1; // 堆顶元素排序完毕
MaxHeapify(array, heapSize, 0); // 重新调整剩余大根堆
}
}
/*降序堆排序*/
void HeapSort2(int* array, int heapSize)
{
MinHeapCreate(array, heapSize); //第一步建堆
while (heapSize > 0) //第二部排序
{
Swap(array, 0, heapSize - 1);
heapSize = heapSize - 1;
MinHeapify(array, heapSize, 0);
}
}
int main()
{
int array[5] = {3, 5, 2, 1, 7};
int heapSize = 5;
/*构建小根堆并输出*/
MinHeapCreate(array, heapSize);
for(int i = 0; i < heapSize; i++) {
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
/*构建大根堆并输出*/
MaxHeapCreate(array, heapSize);
for(int i = 0; i < heapSize; i++) {
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
/*升序堆排序*/
HeapSort(array, heapSize);
for(int i = 0; i < heapSize; i++) {
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
/*降序堆排序*/
HeapSort2(array, heapSize);
for(int i = 0; i < heapSize; i++) {
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
}
// 向堆中插入一个元素x
void heap_insert(int* array, int heapSize, int x){
array[heapSize++] = x;
//i的父节点是i/2,如果父节点小于子节点,不符合大顶堆要求,互换父节点和子节点
for(int i = heapSize - 1; i > 0 && array[i/2] < array[i]; i /= 2){
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[i/2];
array[i/2] = temp;
}
}
// 删除堆的根节点(最大或最小元素)
void heap_delete(int* array, int num){
array[0] = array[num - 1]; // 删掉0处元素,将末尾调整到根
num--;
max_heapify(a, num, 0); // 重新调整堆
}
找第k大元素,用升序序列排序
/*第k大元素*/
int HeapSort(int* array, int heapSize, int k)
{
int num = heapSize;
MaxHeapCreate(array, heapSize); //第一步建堆
while (heapSize > 0) //第二步排序
{
Swap(array, 0, heapSize - 1);
heapSize = heapSize - 1;
if(heapSize == num - k){ // 当heapSize==num - k时,恰好找到第k大元素,可以break
break;
}
MaxHeapify(array, heapSize, 0);
}
return array[heapSize];
}
图
遍历算法
BFS(可以用来判断图是否连通、连通分量的个数,还可以用于无权图的最短路径问题)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXN 50005
struct position{
int pos, dis;
};
struct queue{
struct position q_list[MAXN];
int front, rear, len;
};
void initQ(struct queue *q){
q->front = 0;
q->rear = 0;
q->len = 0;
}
bool isQEmpty(struct queue *q){
// front与rear相等即队列为空
if(q->front == q->rear) return true;
else return false;
}
bool isQFull(struct queue *q){
if(q->rear == MAXN) return true;
else return false;
}
bool pushQ(struct queue *q, struct position x){
if(!isQFull(q)){
q->q_list[q->rear++] = x;
q->len++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
struct position popQ(struct queue* q){
if(!isQEmpty(q)){
q->len--;
return q->q_list[q->front++];
}
}
int change[5] = {-2, -1, 1, 2};
int BFS(int start, int target){
// 新建队列
struct queue Q;
initQ(&Q);
// 表示节点是否访问过
int visited[50005];
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited));
// 将起点入队并设置为已访问
struct position s = {start, 0};
pushQ(&Q, s);
visited[start] = 1;
while(!isQEmpty(&Q)) {
struct position temp = popQ(&Q);
if(temp.pos == target) return temp.dis;
// 广度优先遍历该节点的所有连通节点
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
struct position new = {temp.pos + change[i], temp.dis + 1};
// 如果新节点超出范围或已访问过,直接跳过
if(new.pos < 0 || new.pos >= MAXN || visited[new.pos]){
continue;
}
// 将新节点入队并计为已访问
pushQ(&Q, new);
visited[new.pos] = true;
}
}
return false;
}
#define MAXN 1005
int graph[MAXN][MAXN]; // 用邻接矩阵存储
int visited[MAXN];
int visit(int x){
printf("visit %d\n", x);
}
struct queue{
int q_list[MAXN];
int front, rear, len;
};
void initQ(struct queue *q){
q->front = 0;
q->rear = 0;
q->len = 0;
}
bool isQEmpty(struct queue *q){
// front与rear相等即队列为空
if(q->front == q->rear) return true;
else return false;
}
bool isQFull(struct queue *q){
if(q->rear == MAXN) return true;
else return false;
}
bool pushQ(struct queue *q, int x){
if(!isQFull(q)){
q->q_list[q->rear++] = x;
q->len++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
int popQ(struct queue* q){
if(!isQEmpty(q)){
return q->q_list[q->front++];
q->len--;
}
}
void BFS_ver(int n, int x){
struct queue Q;
initQ(&Q);
visit(x);
visited[x] = 1;
pushQ(&Q, x);
while (!isQEmpty(&Q)){
int temp = popQ(&Q);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(graph[temp][i] != -1){
visit(i);
visited[i] = 1;
pushQ(&Q, i);
}
}
}
}
void BFS_graph(int n){
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited));
int num = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(visited[i] == 0){
BFS_ver(n, i);
num++;
}
}
printf("%d\n", num);
}
DFS(可以用来判断图是否连通、连通分量的个数、计算树的高度、子树的高度)
#define MAXN 1005
int graph[MAXN][MAXN]; // 用邻接矩阵存储
int visited[MAXN];
int visit(int x){
printf("visit %d\n", x);
}
void DFS_ver(int n, int x){
visit(x);
visited[x] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if(graph[x][i] != -1 && visited[i] == 0)
DFS_ver(n, i);
}
}
void DFS_graph(int n){
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited));
int num = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(!visited[i]){
DFS_ver(n, i);
num++;
}
}
printf("%d\n", num);
}
并查集(用于判断图是否连通、求连通分量的个数、求添加多少条边可使图连通)
如果最后Union的树只有一个,则图连通
连通分量个数即为树的个数,即为根节点个数,即为Find(i) == i的个数
连通分量个数为num,添加num-1条边可使图连通
#include<stdio.h>
const int MAXN = 1005;
struct Edge{
int from;
int to;
};
struct Edge graph[MAXN * MAXN];
int father[MAXN];// 每个结点的父亲节点
int height[MAXN];// 每个结点在树中的高度
void Initial(int n){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
father[i] = i;
height[i] = 0;
}
}
int Find(int x){
if(x != father[x]){
father[x] = Find(father[x]);
}
return father[x];
}
void Union(int x, int y){
x = Find(x);
y = Find(y);
if(x != y){// 如果传入的两个点不是一个集合中的
// 矮树作为高树的子树
if(height[x] > height[y]){
father[y] = x;
}
else if(height[x] < height[y]){
father[x] = y;
}
else{
father[y] = x;
height[x]++;
}
}
}
int main(){
int n, m;
while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF){
int a, b;
if(n == 0) break;
scanf("%d", &m);
Initial(n);
while(m--){
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
Union(a, b);
}
int num = 0;// 集合的数目
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
// 寻找根节点,即为树的个数,即为连通分量的个数
if(Find(i) == i) num++;
}
// 该图有number个连通分量,需要添加number-1条边使图连通
printf("%d\n", num - 1);
}
}
带权并查集
最短路算法
无权最短路BFS
单源最短路Dijkstra算法
#include<stdio.h>
#define MAXN 1005
#define INF 100000000
int graph[MAXN][MAXN]; // 用邻接矩阵存储
int n, m, s, t; // n为点个数,m为边个数,s为起点,t为终点
int visited[MAXN], dis[MAXN];
// visited表示该点是否已找到最短距离,dis表示该点到s的最短距离
void Dijsktra(int begin)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
dis[i] = graph[begin][i];
}
// 将起始位置设为已访问,距离为0
visited[begin] = 1;
dis[begin] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int min = INF, min_point = -1;
// 找到距离最短的点
for(int j = 1; j <= n;j++)
if(visited[j] == 0 && dis[j] < min)
min_point = j, min = dis[j];
// 设为已访问
if(min_point == -1) continue;
visited[min_point] = 1;
// 对与min_point相连的点进行松弛操作
for(int j = 1;j <= n; j++)
if(visited[j] == 0 && graph[min_point][j] != INF){
if(dis[j] > dis[min_point] + graph[min_point][j])
dis[j] = dis[min_point] + graph[min_point][j];
}
}
}
int min(int a, int b){return a > b ? b : a;}
int main()
{
int from, to, length;
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &s, &t);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
graph[i][j] = INF;
dis[i] = INF;
visited[i] = 0;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d %d", &from, &to, &length);
// 有可能有重复边,取最小的
graph[from][to] = min(graph[from][to], length);
graph[to][from] = min(graph[to][from], length);
}
Dijsktra(s);
printf("%d",dis[t]);
return 0;
}
多源最短路Floyd算法
const int max_n = 505;
int dis[max_n][max_n]; // 用邻接矩阵存储
void Floyd(int n){
for(int k = 1; k <= n; k++)// 中间结点为k
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) // i、j为两边节点
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) // 尝试在所有i、j直接加入k,看是否会变近
dis[i][j] = min(dis[i][j], dis[i][k] + dis[k][j]);
}
int main(){
int n, m;
int u, v;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
fill(dis, dis + max_n * max_n, INT_MAX);
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
scanf("%d %d", &u, &v);
scanf("%d", &dis[u][v]);
}
Floyd(n);
return 0;
}
最小生成树
Prim算法
首先任取一个顶点加入S,然后每次选取一个与S中元素距离最近的点及边加入S中,最后得到最小生成树。
算法如下,其中priorityQ存的是所有T到所有S的点对及其距离,每次选一个T中最小的。priorityQ中的点可能重复,因为对于同一个点,它的距离是与多个S中的点之间的,只需在某一次作为最近的点被找出来即可。
const int MAXN = 5005;
const int INF = 1000000;
int graph[MAXN][MAXN];
int dis[MAXN]; // dis[i]表示点i距离S中最近的点的距离
int S[MAXN]; // 用true和false表示点是否在S中
int min(int a, int b){return a > b ? b : a;}
int Prim(int n){
int total_cost = 0, cnt = 0;
// 首先选取第一个点加入S,其距离S中点距离即为0
dis[1] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int min = INF, min_point;
// 寻找距离S中点最近的点
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
if(S[j] == 0 && min > dis[j]){
min = dis[j];
min_point = j;
}
}
// 将其加入S,S中点数量++,最小生成树的total_cost加上边min
S[min_point] = 1;
cnt++;
total_cost += min;
// 如果S中包括所有点,最小生成树寻找完成
if(cnt == n) break;
// 遍历所有未加入S的点,看点min_point的加入能否使他们离S更近
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
if(S[j] == 1) continue;
if(dis[j] > graph[min_point][j])
dis[j] = graph[min_point][j];
}
}
return total_cost;
}
// n为点数,m为边数,cost中为所有的边,每条边为一个三维数组,分别存放from、to、length
int miniSpanningTree(int n, int m, int** cost) {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
graph[i][j] = INF;
}
dis[i] = INF;
S[i] = 0;
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int from = cost[i][0];
int to = cost[i][1];
int length = cost[i][2];
// 有重复边,需要用min取最小值
graph[from][to] = min(graph[from][to], length);
graph[to][from] = min(graph[to][from], length);
}
return Prim(n);
}
Kruskal算法
初始时S中包含所有的点,不包含任何一条边,每次选取一条权值最小的边,如果加入该边后S不含回路,则加入,如果含回路,则舍弃。
并查集的使用方法:一开始所有结点都单独成树(Initial函数),如果两个结点连通且不成环,就将两个结点Union,最后得到一个并查集
const int MAXM = 500005;
const int MAXN = 5005;
struct Edge{
int from;
int to;
int length;
};
struct Edge graph[MAXM];
int father[MAXN]; // father存节点i的根节点
int height[MAXN]; // height存以节点i为根节点的树的高度
void Initial(int n){
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++){
father[i] = i;
height[i] = 0;
}
}
// 查找:对于每个元素,不断向上查找,直到找到它的根,根据根是否相同来判断两个元素是否在同一个集合中
int Find(int x){
if(x != father[x])
father[x] = Find(father[x]);
return father[x];
}
// 合并:将一棵树作为另一棵树的子树,从而将两棵树变成一棵更大的树
void Union(int x, int y) {
x = Find(x);
y = Find(y);
// 如果x高于y,将y作为x的子树
if(height[x] > height[y]){
father[y] = x;
}
// 如果y高于x,将x作为y的子树
else if(height[x] < height[y]){
father[x] = y;
}
// 如果两树同高,将y作为x的子树,此时x的高度会增加1
else{
father[y] = x;
height[x]++;
}
}
int compare(const void *a, const void *b){
struct Edge *aa = (struct Edge*)a;
struct Edge *bb = (struct Edge*)b;
if(aa->length > bb->length) return 1;
else return 0;
}
int Kruskal(int n, int m){
Initial(n);
// 使用qsort对所有边按长度排序
qsort(graph, m, sizeof(struct Edge), compare);
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
struct Edge temp = graph[i];
if(Find(temp.from) != Find(temp.to)){
// 如果from和to查到的树的根节点不一样,说明他们不在一个集合中,即不连通,不会成环
Union(temp.from, temp.to);
sum += temp.length;
}
}
return sum;
}
int miniSpanningTree(int n, int m, int** cost, int costRowLen, int* costColLen ) {
// 将[from, to, length]的数组存到graph中
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
struct Edge temp;
temp.from = cost[i][0];
temp.to = cost[i][1];
temp.length = cost[i][2];
graph[i] = temp;
}
return Kruskal(n, m);
}
拓扑排序
AOV网(用于判断有向图是否有环)
static const int MAXN = 100005;
int Edges[MAXM][2];
int in_degree[MAXN];
bool TopologicalSort(int n, int m){
int num_sorted = 0; // 记录已拓扑排序的节点个数
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(in_degree[i] == 0) { // 找一个入度为0的节点
num_sorted++; // 已排序个数++,如果排序个数达到n,排序完成返回true
if(num_sorted == n) return true;
// 遍历以i为from的节点,入度--
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
if(Edges[j][0] == i){
in_degree[Edges[j][1]]--;
}
}
in_degree[i] = -1; // 已排序的in_degree设为-1,避免重复遍历
i = -1; // 从头遍历
}
}
return false;
}
int main(){
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int from, to;
scanf("%d %d", &from, &to);
Edges[i][0] = from;
Edges[i][1] = to; // 注意from和to的顺序
in_degree[to]++;// to的入度++
}
return TopologicalSort(n, m);
}
AOE网与关键路径
以顶点表示事件,以有向边表示活动,以边上权值表示该活动持续的时间。
从源点到汇点的所有路径中,具有最大路径长度的路径称为关键路径,关键路径上的活动称为关键活动。
每个活动的
- 最早开始时间:该活动的前序活动完成,该活动可以开始进行的时间
- 最晚开始时间:该活动的后序活动需按时完成,该活动必须开始的时间
非关键活动可以拖延,不会影响整个工程的完成。而关键活动的拖延会影响整个工程的完成。因此求关键路径可以转化为求所有活动的最早和最晚开始时间,判断二者是否相等。
计算方式是:通过拓扑排序找出活动的前序和后序活动,那么活动的最早开始时间就是其所有前序活动的最晚完成时间,活动的最晚开始时间就是其所有后序活动的最早开始时间减去该活动所需时间。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
vector<int> graph[MAX_N]; // graph[i]存放结点i的后序结点
int inDegree[MAX_N];
long long earliest[MAX_N]; // 最早开始时间
long long latest[MAX_N]; // 最晚开始时间
long long time[MAX_N]; // 花费时间
long long CriticalPath(int n){
vector<int> topology; // 拓扑序列
queue<int> node_in0; // 存入度为0的点
long long total_time = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if(inDegree[i] == 0)
node_in0.push(i);
while(!node_in0.empty()){
int u = node_in0.front();
topology.push_back(u);
node_in0.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < graph[u].size(); i++){
// 遍历u的所有后序结点
int v = graph[u][i];
earliest[v] = max(earliest[v], earliest[u] + time[u]);
inDegree[v]--;
if(inDegree[v] == 0){
node_in0.push(v);
totalTime = max(totalTime, earliest[v] + time[v]);
}
}
}
for(int i = topology.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--){
int u = topology[i];
if(graph[u].size() == 0){
// 如果u是最后的结点,在totalTime最后完成可以不耽误工期
latest[u] = totalTime - time[u];
}
else{
// 如果u不是最晚结点,将其初始化为INT_MAX
latest[u] = INT_MAX;
}
// 遍历u的所有后序结点,寻找其中要求最早的
for(int j = 0; j < graph[i].size(); j++){
int v = graph[u][j];
latest[u] = min(latest[u], latest[v] - time[u]);
}
}
return totalTime;
}
int main(){
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
memset(inDegree, 0, sizeof(inDegree));
memset(earliest, 0, sizeof(earliest));
memset(latest, 0, sizeof(latest));
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%lld", &time[i]);
while(m--){
int from, to; // from是to的前序结点
scanf("%d %d", &from, &to);
graph[from].push_back(to);
inDegree[to]++;
}
long long total_time = CriticalPath(n);
}
动态规划
走台阶问题
可以两步或一步
dp[n] = dp[n - 1] + dp[n - 2]
dp[1] = 1;
dp[2] = 2;
钢管切割问题
给定长度为L的钢管和一个数组v[L],v[i]表示长度为i的钢管的价值,求长度为L的钢管如何切割才能得到最大价值
int dp[10005]; // dp[i]为长度为i的钢管的最大价值
int s[i]; // 长度为i的钢管第一刀应当在s[i]处切割
void cut_rod(int *v, int L){
dp[0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= L; i++){
// 求长度为i的钢管的最大价值
for(int j = 1; j <= i; j++){
if(v[j] + dp[i - j] > dp[i]){
dp[i] = v[j] + dp[i - j];
s[i] = j;
}
}
}
}
int main(){
int L;
int v[10005];
scanf("%d", &L);
for(int i = 1; i <= L; i++){
// 长度为i的钢管的价值
scanf("%d", &v[i]);
}
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
cut_rod(v, L);
printf("max value is %d\n", dp[L]);
int temp_l = L;
while(temp_l > 0){
printf("%d ", s[temp_l]);
temp_l -= s[temp_l];
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
最大连续子序列和
用dp[i]表示以A[i]结尾的连续序列的最大和
那么这一序列要么是A[i]本身,要么是以A[i-1]结尾的最大连续序列再加上A[i]
即dp[i] = max(A[i], dp[i - 1] + A[i])
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<climits>
using namespace std;
int arr[1000005];
int dp[1000005];
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF){
memset(arr, 0, sizeof(arr));
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
dp[0] = arr[0];
int max_num = dp[0];
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
dp[i] = max(arr[i], arr[i] + dp[i - 1]);
if(dp[i] > max_num)
max_num = dp[i];
}
printf("%d\n", max_num);
}
}
最大子矩阵
动态规划思路:
控制行数,设最大子矩阵所在行是从i到j,然后将每一列从i到j元素求和,然后求最大序列和
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<climits>
using namespace std;
int matrix[105][105]; // 原始矩阵
int total[105][105]; // 辅助矩阵,[i, j]位置存放第j列中0-i行元素值
int arr[105]; // 转化为一维矩阵,arr中是第k列从i到j的元素和
int dp[105]; // 为arr进行动规的数组
// 对转化成的一维数组进行动态规划
int MaxSubSequence(int n){
int max_num;
dp[0] = arr[0];
max_num = dp[0];
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
dp[i] = max(arr[i], dp[i - 1] + arr[i]);
max_num = max(max_num, dp[i]);
}
return max_num;
}
// 将矩阵从i到j队列求和转化为一维数组
int MaxSubMatrix(int n){
int max_num = INT_MIN;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = i; j < n; j++){
// 控制行数,子矩阵从第i行到第j行
for(int k = 0; k < n; k++){
// 列为k
if(i == 0){
arr[k] = total[j][k];
}
else{
arr[k] = total[j][k] - total[i - 1][k];
}
// arr中是第k列从i到j的元素和
}
int current = MaxSubSequence(n); // 转化为一维
max_num = max(max_num, current);
}
}
return max_num;
}
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF){
memset(matrix, 0, sizeof(matrix));
memset(total, 0, sizeof(total));
memset(arr, 0, sizeof(arr));
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp));
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
scanf("%d", &matrix[i][j]);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(i == 0)
total[i][j] = matrix[i][j];
else
total[i][j] = total[i - 1][j] + matrix[i][j];
}
}
printf("%d\n", MaxSubMatrix(n));
}
return 0;
}
最长递增子序列
注意子序列和子串的区别:子串一定是连续的,而子序列不是
动规思路:
dp[i]初始化为1,即只有A[i]一个元素
遍历A[i]之前的所有元素,如果A[i]之前的元素A[j]比A[i]小,且dp[j]加上一个元素A[i]得到的子序列比dp[i]大,那么dp[i] = dp[j] + 1,否则dp[i] 不变。即dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int arr[30];
int dp[30];
int main(){
int n, max_num = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
dp[i] = 1;
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++){
if(arr[j] <= arr[i]){
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
}
}
max_num = max(max_num, dp[i]);
}
printf("%d\n", max_num);
return 0;
}
最长公共子序列
给定两个字符串S1和S2,求这两个字符串的公共子串
动规思路:
dp为二维数组,dp[i][j]表示以S1[i]为末尾的字符串和以S2[j]为末尾的字符串的最长公共子序列的长度。
如果S1[i] = S2[j],则dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j - 1] + 1
如果S1[i] != S2[j],则dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1])
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
char s1[105], s2[105];
int dp[105][105];
int main(){
while(scanf("%s%s", s1 + 1, s2 + 1) != EOF){ // 从1开始读入
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp));
int len1 = strlen(s1 + 1);
int len2 = strlen(s2 + 1);
int max_len = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= len1; i++) // 从1遍历到len1
for(int j = 1; j <= len2; j++){
if(s1[i] == s2[j]){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1;
}
else{
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
printf("%d\n", dp[len1][len2]);
}
return 0;
}
背包问题
0-1背包
每种物品只有一个,物品重量为w[i],价值为v[i],让总价值最大
dp[i][j]:前i个物品装进容量为j的背包能获得的最大价值
动规思路:
每个物品只有装进和不装进两种选择。如果不装进,dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j];如果装进,dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-w[i]]+v[i]。
依次遍历i和j即可。
优化思路:
滚动数组。如果装进物品i,dp[j] = dp[j-w[i]] + v[i],如果不装进dp[j] = dp[j]。
第二重循环倒序目的是使每个物品只能取一次。倒序时,当空间为2*w[j]时dp[j] = dp[j - w[j]] + v[i],此时1个w[j]处还没遍历到,值仍为0,2个w[j]得到的价值仍为1个物品的价值v[i]
int w[MAX_N]; // 物品的重量
int v[MAX_N]; // 物品的价值
int dp[MAX_W]; // 背包容量为j时的最大价值
int main(){
int W, N; // 背包容量和物品数量
scanf("%d%d", &W, &n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d%d", &w[i], &v[i]);
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp));
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = W; j >= w[i]; j--)
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j-w[i]] + v[i]);
printf("%d\n", dp[W]);
return 0;
}
完全背包
每个物品可以取无限个,求背包可以获得的最大价值
将第二重循环的倒序改为正序即可。当空间为2*w[j]时,正序遍历一个w[j]位置的值为v[i],2个w[j]的值为2个v[i]
int w[MAX_N]; // 物品的重量
int v[MAX_N]; // 物品的价值
int dp[MAX_W]; // 背包容量为j时的最大价值
int main(){
int W, N; // 背包容量和物品数量
scanf("%d%d", &W, &n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d%d", &w[i], &v[i]);
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp));
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = w; j <= W; j++)
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j-w[i]] + v[i]);
printf("%d\n", dp[W]);
return 0;
}
多重背包
每个物品可以取有限个,求背包可以获得的最大价值
思路:将物品的有限值num转化为num=1+2+22+…+2k+剩下的。将一个物品转化为k+1种数量为1的物品,物品价值依次为1×w、2×w、……、2k×w、剩余值×w,这样可以保证任何组合都等价。
int w[MAX_N]; // 物品的重量
int v[MAX_N]; // 物品的价值
int dp[MAX_W]; // 背包容量为j时的最大价值
int main()
{
int W, N;
scanf("%d%d", &W, &n);
int cnt = 0;
int weight, value, count;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
scanf("%d%d%d", &weight, &value, &count);
for(int j = 1; j <= count; j *= 2){
v[cnt] = j * value;
w[cnt] = j * weight;
cnt++;
count -= j;
}
if(count > 0){
v[cnt] = count * value;
w[cnt] = count * weight;
cnt++;
}
}
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp));
for(int i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
for(int j = M; j <= w[i]; j--)
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j-w[i]]+v[i]);
printf("%d\n", dp[M]);
}
组合背包
输入数量为-1代表无限取用
输入时,如果是无限取用,直接将-1存入count数组中。如果是有限取用,转化为01背包。
遍历时,如果是无限取用,正序遍历,如果是01背包,倒序遍历。
int w[MAX_N]; // 物品的重量
int v[MAX_N]; // 物品的价值
int c[MAX_N]; // 物品的数量
int dp[MAX_W]; // 背包容量为j时的最大价值
int main()
{
int W, N;
scanf("%d%d", &W, &n);
int cnt = 0;
int weight, value, count;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
scanf("%d%d%d", &weight, &value, &count);
if(count == -1){
w[cnt] = weight;
v[cnt] = value;
c[cnt] = count;
cnt++;
}
else{
for(int j = 1; j <= count; j *= 2){
v[cnt] = j * value;
w[cnt] = j * weight;
c[cnt] = 1;
cnt++;
count -= j;
}
if(count > 0){
v[cnt] = count * value;
w[cnt] = count * weight;
c[cnt] = 1;
cnt++;
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(c[i] == -1){
// 如果是无限取用的
for(int j = w[i]; j <= W; j++)
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - w[i]] + v[i]);
}
else{
// 如果是01背包
for(int j = W; j >= w[i]; j--)
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - w[i]] + v[i]);
}
}
printf("%d\n", dp[W]);
}
恰好装满
思路:初始化的不同,只有容量为0时可以装满,此时价值为0,其他位置都初始化为INF(或-1),表示不能恰好装满。
在进行max操作的时候,需要判断dp[j-w[i]]是否大于等于0,只有大于等于0的才能参与运算。
int w[MAX_N]; // 物品的重量
int v[MAX_N]; // 物品的价值
int dp[MAX_W]; // 背包容量为j时的最大价值
int main(){
int W, N; // 背包容量和物品数量
scanf("%d%d", &W, &n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d%d", &w[i], &v[i]);
memset(dp, INF, sizeof(dp));
dp[0] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = w; j <= W; j++)
if(dp[j-w[i]] >= 0)
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j-w[i]] + v[i]);
printf("%d\n", dp[W]);
return 0;
}
动态规划注意:如果dp[0]在for循环外单独赋值的话,注意max_num应初始化为dp[0],而不是INT_MIN
矩阵链乘法
p×q的矩阵A和q×r的矩阵B可以做乘法,其计算次数为p×q×r
给一段矩阵链(n个矩阵,n+1个数字,i、i+1表示矩阵i的两个维度的值)
求矩阵计算的最小代价,并用括号输出路径
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define N 305
const int INF = 1e9;
int a[N],dp[N][N],s[N][N],n;
void getMuls()
{
int i,j,k;
for(k=1; k<=n; k++)
for(i=1; i+k<=n; i++)
{
int num=INF;
for(j=i; j<i+k; j++)
{
int q = dp[i][j]+dp[j+1][i+k]+a[i-1]*a[j]*a[i+k];
if(num>=q) {
num = q;
s[i][i+k] = j;
}
}
dp[i][i+k]=num;
}
}
void print(int i,int j)
{
if(i==j){
printf("A%d",i);
return;
}
printf("(");
print(i,s[i][j]);
print(s[i][j]+1,j);
printf(")");
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d",&n)){
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
getMuls();
printf("%d\n",dp[1][n]);
print(1,n);
printf("\n");
}
}
卡特兰数
满足h[n] = h[0]*h[n-1] + h[1]*h[n-2] + …… + h[n-2]*h[1] + h[n-1]*h[0]
int CatalanNumber(int n){
int dp[25]; // dp[i]表示i个数的排列种数
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp));
dp[0] = 1; // 0个数只有一种
dp[1] = 1; // 1个数也只有一种
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){ // 从2个数开始遍历,直到遍历到n
for(int j = 1; j <= i; j++){ // j为根节点,对于i个数,根节点从1遍历到i,dp[i]j
// 对于i个数,以j为根节点,则左子树有j-1个,右子树有i-j个
dp[i] += dp[j - 1] * dp[i - j];
}
}
return dp[n];
}
卡特兰数可以解决的问题:
括号化
凸多边形三角划分
给定节点组成二叉搜索树
n对括号的正确匹配数目
回溯+dp 切割回文串问题
dp判断是不是回文串:
对于子串[i, j],如果[i+1, j-1]是回文串,且s[i] == s[j],则[i, j]是回文串;否则不是;
int dp[MAXN][MAXN];
void judge(int *s, int n){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = i; j < n; j++){
// from i to j
if(s[i] == s[j]){
if(i == j || i + 1 == j){
dp[i][j] = 1;
}
else if(dp[i + 1][j - 1] == 1){
dp[i][j] = 1;
}
else{
dp[i][j] = 0;
}
}
else{
dp[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
回溯:
首先使用一个具体例子画出树形图
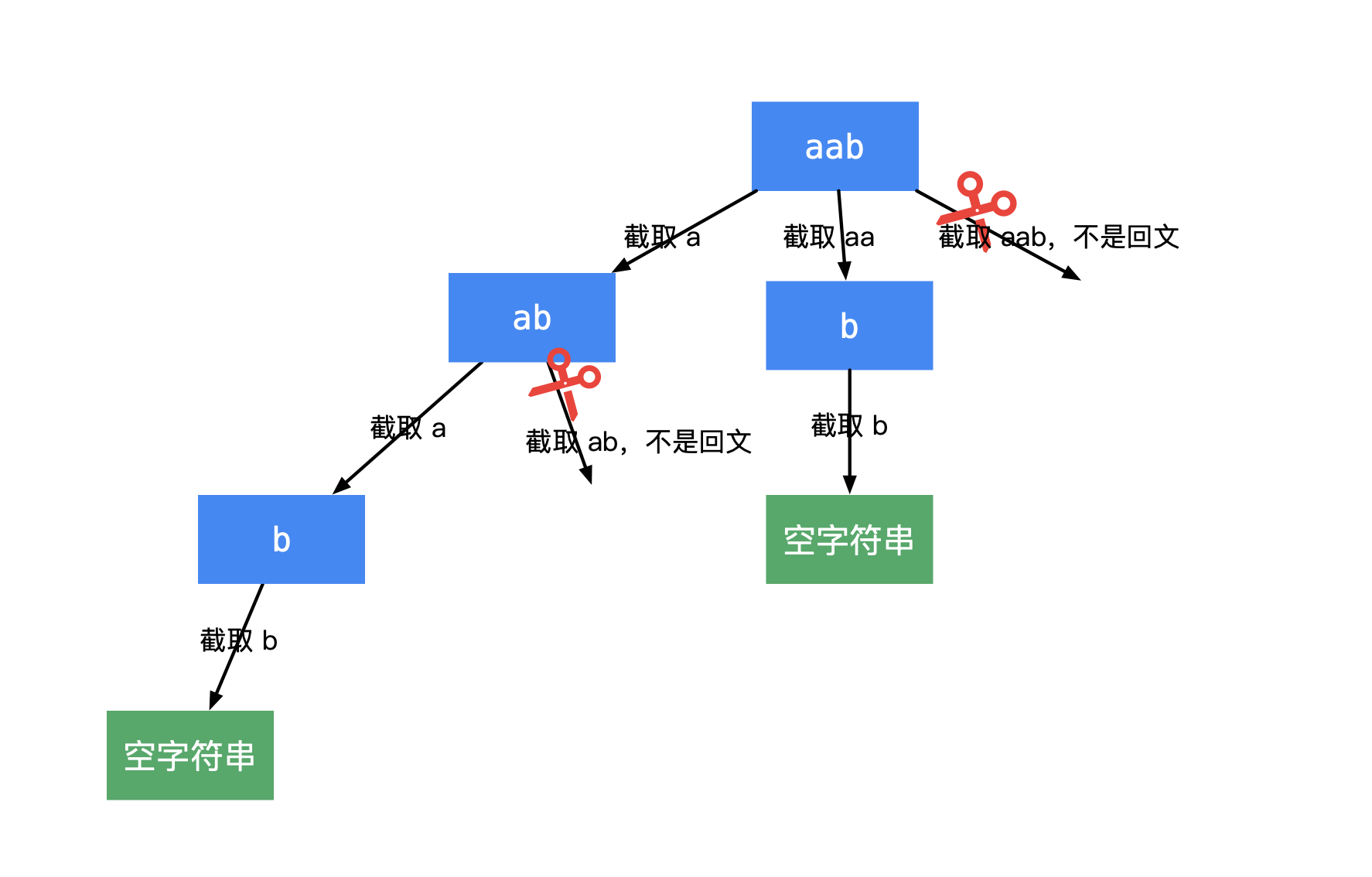
回溯模板
int path[]; // 存放单次结果
int result[][]; // 存放历次结果
void backtrack(){
if(终止条件){
将path中的结果存放到result中;
return;
}
for(遍历横向本层){
处理节点操作;
// 递归纵向遍历
backtrack();
回溯,撤销path中该步的结果;
}
}
切割回文串代码
char path[MAXN][MAXN];
int path_point;
char result[MAXN][MAXN][MAXN];
int result_point;
void backtrack(int *s, int n, int start){
if(start >= n){
// 切割到末尾,切割回文串成功
// 将path中的结果存放到result中
strcpy(result[result_point], path);
result_point++;
return;
}
for(int i = start; i < n; i++){
// 在i后切割:横向遍历切割的位置
// 纵向递归切割的刀数
if(dp[start][i]){
}
}
}
数学问题
进制转换
// m进制转十进制
long long m_into_ten(char* x_m, int x_m_len, int m){
long long ret = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < x_m_len; i++){
long long temp;
if(x_m[i] >= '0' && x_m[i] <= '9')
temp = x_m[i] - '0';
else
temp = x_m[i] - 'a' + 10;
ret = ret * m + temp;
}
return ret;
}
// 十进制转n进制
char* ten_into_n(long long x_10, int n){
char *ret = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * MAX_LEN);
int ret_point = 0;
while(x_10 != 0){
int temp = x_10 % n;
if(temp < 10)
ret[ret_point++] = temp + '0';
else
ret[ret_point++] = temp - 10 + 'a';
x_10 /= n;
}
// reverse
char *ret2 = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * MAX_LEN);
int ret2_point = 0;
for(int i = ret_point - 1; i >= 0; i--)
ret2[ret2_point++] = ret[i];
ret2[ret2_point++] = '\0';
return ret2;
}
最大公约数和最小公约数
最大公约数GCD
辗转相除法:利用“a与b的最大公约数也能够整除a mod b”
int GCD(int a, int b){
if(b == 0)
return a;
else
return GCD(b, a % b);
}
最小公倍数LCM
利用公式“两个数的乘积等于他们的最大公约数 * 最小公倍数”
LCM = a * b / GCD(a, b);
质数
对于数x,从2到sqrt(x),判断是否能整除
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
bool isPrime(int x){
int end = sqrt(x);
for(int i = 2; i <= end; i++)
if(x % i == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
int main(){
int x;
while(scanf("%d", &x) != EOF){
if(x > 1 && isPrime(x))
printf("yes\n");
else
printf("no\n");
}
}
素数筛法
思路:因为一个合数一定是某个质数的倍数,故每次找到一个质数,就将其所有倍数置为false,遍历一遍即可标记出所有的质数和合数
const int MAXN = 10000;
int prime[MAXN]; // 存放所有质数
int prime_point = 0;
bool prime_flag[MAXN]; // 质数是true,合数是false
void initial_flag(){
memset(prime_flag, true, MAXN);
prime_flag[0] = false;
prime_flag[1] = false;
for(int i = 2; i < MAXN; i++){
// 之前作为质数的倍数被设置为false,说明是合数,直接跳过
if(!prime_flag[i])
continue;
// 对于质数,将其放入质数队列,并将其倍数全部设置为合数
prime[prime_point++] = i;
for(int j = i * i; j < MAXN; j += i)
prime_flag[j] = false;
}
return;
}





 笔记涵盖了C语言编程技巧,重点讲解哈希表、排序算法、数据结构如链表、栈、队列及各种树与图的实现,包括查找、遍历与经典算法应用,如最短路与最小生成树算法,适合备考与复习。
笔记涵盖了C语言编程技巧,重点讲解哈希表、排序算法、数据结构如链表、栈、队列及各种树与图的实现,包括查找、遍历与经典算法应用,如最短路与最小生成树算法,适合备考与复习。
















 1111
1111

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








