Mybatis 的动态SQL的简单使用
动态 SQL 是 MyBatis 的强大特性之一。如果你使用过 JDBC 或其它类似的框架,你应该能理解根据不同条件拼接 SQL 语句有多痛苦,例如拼接时要确保不能忘记添加必要的空格,还要注意去掉列表最后一个列名的逗号。利用动态 SQL,可以彻底摆脱这种痛苦。分为:
- if
- choose(when , otherwise)
- trim(where , set)
- foreach
所谓的动态SQL,本质还是SQL语句,只是我们可以在SQL层面,去执行一个逻辑代码
动态SQL就是在拼接SQL语句。我们只要保证SQL的正确性,按照SQL的格式,去排列组合就可以了
建议:先在Mysql中写出完整的SQL,再对应的去修改成为我们的动态SQL实现通用即可!
下面看例子
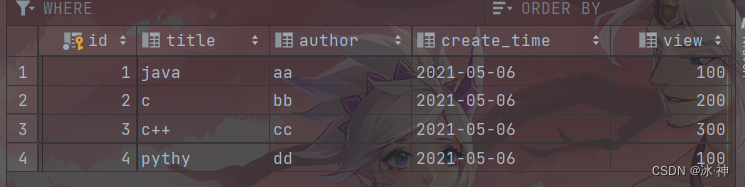
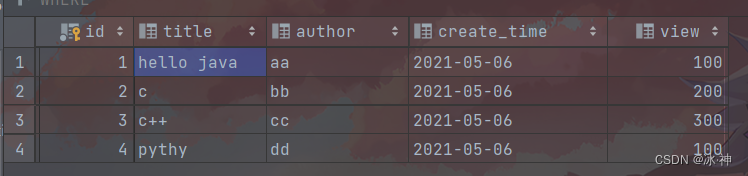
对应数据库
有4条数据
实体类
@Data //导入了lombok包,只需使用注释即可自动生成getter/setter 等
public class Blog {
private int id;
private String title;
private String author;
private Date createTime;
private int view;
}
对应的接口
public interface BlogMapper {
//查找
List<Blog> BlogIf(Map map);
List<Blog> BlogChoose(Map map);
List<Blog> BlogForeach(Map map);
//更新
int updateBlog(Map map);
}
if
使用动态 SQL 最常见情景是根据条件包含 where 子句的一部分。
<select id="BlogIf" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog">
select * from blog where 1=1 <!-- 使用1=1是为了避免if条件都不满足造成where后面无内容 -->
<if test="title!=null" >
and title= #{title}
</if>
<if test="author!=null">
and author=#{author}
</if>
</select>
这条语句提供了可选的查找文本功能。如果不传入 “title”,那么所有的 BLOG 都会返回;如果传入了 “title” 参数,那么就会对 “title” 一列进行模糊查找并返回对应的 BLOG 结果。
如果希望通过 “title” 和 “author” 两个参数进行可选搜索该怎么办呢?首先,我想先将语句名称修改成更名副其实的名称;接下来,只需要加入另一个条件即可。
测试
//不传入参数
public void test(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
HashMap map=new HashMap();
List<Blog> blogs = mapper.BlogIf(map);
for (Blog blog : blogs) {
System.out.println(blog);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
结果:
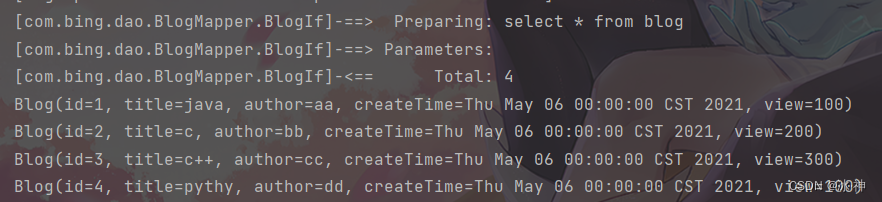
注:这里是使用了Log4j日志的,方便查找错误
可以看出 成功的查出了全部数据
//传入参数
public void test(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
HashMap map=new HashMap();
map.put("title", "java");
map.put("author", "aa");
List<Blog> blogs = mapper.BlogIf(map);
for (Blog blog : blogs) {
System.out.println(blog);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
结果:

choose
有时候,我们不想使用所有的条件,而只是想从多个条件中选择一个使用。针对这种情况,MyBatis 提供了 choose 元素,它有点像 Java 中的 switch 语句。
还是上面的例子,但是策略变为:传入了 “title” 就按 “title” 查找,传入了 “author” 就按 “author” 查找的情形。
<select id="BlogChoose" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog">
select * from blog
<where>
<choose>
<when test="title!=null" >
title= #{title}
</when>
<when test="author!=null">
and author=#{author}
</when>
<otherwise>
and view=#{view}
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
测试
//多给定参数,选择
@Test
public void test(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
HashMap map=new HashMap();
map.put("title", "java");
map.put("author", "bb");
map.put("view",100);
List<Blog> blogs = mapper.BlogChoose(map);
for (Blog blog : blogs) {
System.out.println(blog);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
结果:
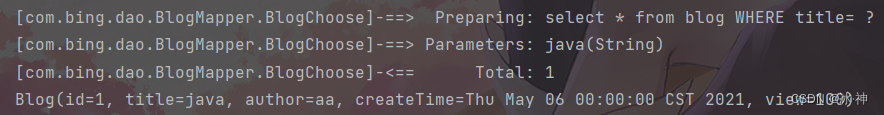
多个条件时,发现只选择了第一个条件查询
@Test
public void test(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
HashMap map=new HashMap();
// map.put("title", "java");
// map.put("author", "bb");
map.put("view",100);
List<Blog> blogs = mapper.BlogChoose(map);
for (Blog blog : blogs) {
System.out.println(blog);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
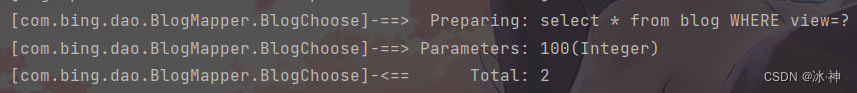
结果:
trim(where , set)
where 元素只会在子元素返回任何内容的情况下才插入 “WHERE” 子句。而且,若子句的开头为 “AND” 或 “OR”,where 元素也会将它们去除。
在动态SQL中 where 最好采用 where标签,因为where标签是智能的
对于 if 的第一个例子我们可以将其改写为
<select id="BlogIf" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog">
select * from blog
<where>
<if test="title!=null" >
title= #{title}
</if>
<if test="author!=null">
and author=#{author}
</if>
</where>
</select>
同理,set 元素可以用于动态包含需要更新的列,忽略其它不更新的列。
set 元素会动态地在行首插入 SET 关键字,并会删掉额外的逗号(这些逗号是在使用条件语句给列赋值时引入的)。
<update id="updateBlog" parameterType="map">
update blog
<set>
<if test="title!=null">
title=#{title}
</if>
<if test="author!=null">
author=#{author}
</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>
测试
@Test
public void test(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
HashMap map=new HashMap();
map.put("title", "hello java");
map.put("id",1);
mapper.updateBlog(map);
sqlSession.close();
}
查看数据库,看是否成功
对比前面的结果,修改成功
foreach
动态 SQL 的另一个常见使用场景是对集合进行遍历(尤其是在构建 IN 条件语句的时候)。
foreach 元素的功能非常强大,它允许你指定一个集合,声明可以在元素体内使用的集合项(item)和索引(index)变量。它也允许你指定开头与结尾的字符串以及集合项迭代之间的分隔符。
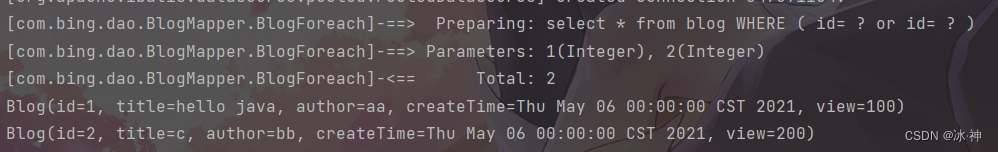
同时查询blog里 id 为1 , 2 的2条记录
<select id="BlogForeach" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog">
select * from blog
<where>
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="and (" close=")" separator="or">
id= #{id}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
测试
public void test(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
HashMap map=new HashMap();
ArrayList<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<>();
map.put("ids",ids);
ids.add(1);
ids.add(2);
List<Blog> blogs = mapper.BlogForeach(map);
for (Blog blog : blogs) {
System.out.println(blog);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
sql片段
前面所用的配置文件里的SQL语句发现有很多重复的语句,我们可以将其提出。
- 使用SQL标签抽取公共的部分
<sql id="if-title-author">
<if test="title!=null" >
title= #{title}
</if>
<if test="author!=null">
and author=#{author}
</if>
</sql>
- 在需要使用的地方使用Include标签引用即可
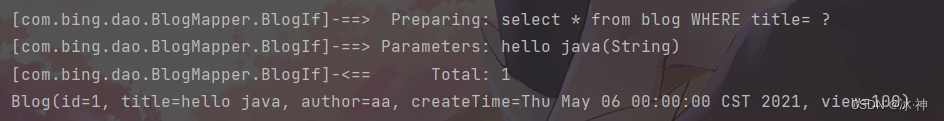
对于 if 里的查询语句,就改写为
<select id="BlogIf" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog">
select * from blog
<where>
<include refid="if-title-author"></include>
</where>
</select>
注意事项:
-
最好基于单表来定义SQL片段!
-
sql片段中最好不要存在where标签
测试
public void test(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
HashMap map=new HashMap();
map.put("title", "hello java");
// map.put("author", "aa");
List<Blog> blogs = mapper.BlogIf(map);
for (Blog blog : blogs) {
System.out.println(blog);
}
sqlSession.close();
}








 本文介绍了Mybatis动态SQL的使用,包括if、choose、trim(where)、foreach等元素,通过实例展示了如何根据条件动态生成SQL语句,提高代码的可读性和维护性。
本文介绍了Mybatis动态SQL的使用,包括if、choose、trim(where)、foreach等元素,通过实例展示了如何根据条件动态生成SQL语句,提高代码的可读性和维护性。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








