本文转载自:扒一扒RPC
因为RPC是基于动态代理的。想必大家都听过RPC,但是可能并没有针对的去了解过,因此本文打算以如下结构讲一讲RPC:
①尽量浅显易懂的描述RPC的工作原理。
②分析一个RPC的Demo。
##一、 走近RPC
###1.1 什么是RPC
RPC是Remote Procedure Call的缩写,即远程过程调用,意思是可以在一台机器上调用远程的服务。在非分布式环境下,我们的程序调用服务都是本地调用,但是随着分布式结构的普遍,越来越多的应用需要解耦,将不同的独立功能部署发布成不同的服务供客户端调用。RPC就是为了解决这个问题的。
###1.2 RPC原理
首先,我们心里带着这样的问题:要怎么样去调用远程的服务呢?
①肯定要知道IP和端口吧(确定唯一一个进程)
②肯定要知道调用什么服务吧(方法名和参数)
③调用服务后可能需要结果吧。
这三点又怎么实现呢?往下看:
RPC的设计由Client,Client stub,Network ,Server stub,Server构成。
其中Client就是用来调用服务的,Cient stub是用来把调用的方法和参数序列化的(因为要在网络中传输,必须要把对象转变成字节),Network用来传输这些信息到Server stub, Server stub用来把这些信息反序列化的,Server就是服务的提供者,最终调用的就是Server提供的方法。
RPC的结构如下图:
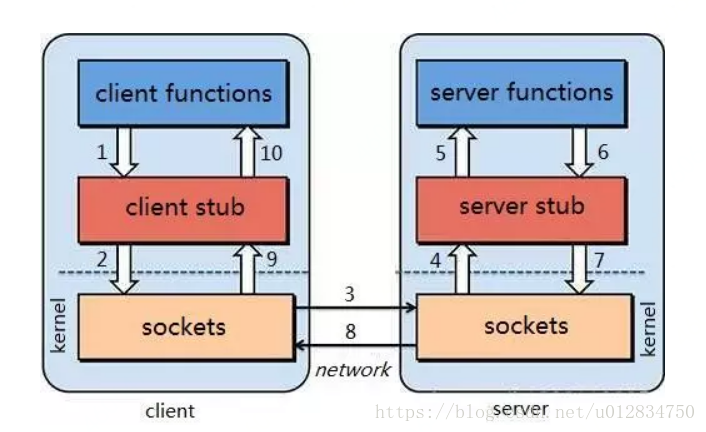
图中1-10序号的含义如下:
(1) Client像调用本地服务似的调用远程服务;
(2) Client stub接收到调用后,将方法、参数序列化
(3) 客户端通过sockets将消息发送到服务端
(4) Server stub 收到消息后进行解码(将消息对象反序列化)
(5) Server stub 根据解码结果调用本地的服务
(6) 本地服务执行(对于服务端来说是本地执行)并将结果返回给Server stub
(7) Server stub将返回结果打包成消息(将结果消息对象序列化)
(8) 服务端通过sockets将消息发送到客户端
(9) Client stub接收到结果消息,并进行解码(将结果消息发序列化)
(10) 客户端得到最终结果。
##二、简单RPC程序
在了解了RPC的大致原理之后,我们给出RPC的示例。这里直接引用梁飞大神的代码,后面给出代码分析:
###2.1 核心框架类
/*
* Copyright 2011 Alibaba.com All right reserved. This software is the
* confidential and proprietary information of Alibaba.com ("Confidential
* Information"). You shall not disclose such Confidential Information and shall
* use it only in accordance with the terms of the license agreement you entered
* into with Alibaba.com.
*/
package com.alibaba.study.rpc.framework;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* RpcFramework
*
* @author william.liangf
*/
public class RpcFramework {
/**
* 暴露服务
*
* @param service 服务实现
* @param port 服务端口
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void export(final Object service, int port) throws Exception {
if (service == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("service instance == null");
if (port <= 0 || port > 65535)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid port " + port);
System.out.println("Export service " + service.getClass().getName() + " on port " + port);
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(port);
for(;;) {
try {
final Socket socket = server.accept();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
try {
ObjectInputStream input = new ObjectInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
try {
String methodName = input.readUTF();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = (Class<?>[])input.readObject();
Object[] arguments = (Object[])input.readObject();
ObjectOutputStream output = new ObjectOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
try {
Method method = service.getClass().getMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
Object result = method.invoke(service, arguments);
output.writeObject(result);
} catch (Throwable t) {
output.writeObject(t);
} finally {
output.close();
}
} finally {
input.close();
}
} finally {
socket.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 引用服务
*
* @param <T> 接口泛型
* @param interfaceClass 接口类型
* @param host 服务器主机名
* @param port 服务器端口
* @return 远程服务
* @throws Exception
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T refer(final Class<T> interfaceClass, final String host, final int port) throws Exception {
if (interfaceClass == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Interface class == null");
if (! interfaceClass.isInterface())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The " + interfaceClass.getName() + " must be interface class!");
if (host == null || host.length() == 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Host == null!");
if (port <= 0 || port > 65535)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid port " + port);
System.out.println("Get remote service " + interfaceClass.getName() + " from server " + host + ":" + port);
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(interfaceClass.getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[] {interfaceClass}, new InvocationHandler() {
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] arguments) throws Throwable {
Socket socket = new Socket(host, port);
try {
ObjectOutputStream output = new ObjectOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
try {
output.writeUTF(method.getName());
output.writeObject(method.getParameterTypes());
output.writeObject(arguments);
ObjectInputStream input = new ObjectInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
try {
Object result = input.readObject();
if (result instanceof Throwable) {
throw (Throwable) result;
}
return result;
} finally {
input.close();
}
} finally {
output.close();
}
} finally {
socket.close();
}
}
});
}
}
###2.2 定义服务接口
/*
* Copyright 2011 Alibaba.com All right reserved. This software is the
* confidential and proprietary information of Alibaba.com ("Confidential
* Information"). You shall not disclose such Confidential Information and shall
* use it only in accordance with the terms of the license agreement you entered
* into with Alibaba.com.
*/
package com.alibaba.study.rpc.test;
/**
* HelloService
*
* @author william.liangf
*/
public interface HelloService {
String hello(String name);
}
###2.3 实现服务
/*
* Copyright 2011 Alibaba.com All right reserved. This software is the
* confidential and proprietary information of Alibaba.com ("Confidential
* Information"). You shall not disclose such Confidential Information and shall
* use it only in accordance with the terms of the license agreement you entered
* into with Alibaba.com.
*/
package com.alibaba.study.rpc.test;
/**
* HelloServiceImpl
*
* @author william.liangf
*/
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
public String hello(String name) {
return "Hello " + name;
}
}
###2.4 暴露服务
/*
* Copyright 2011 Alibaba.com All right reserved. This software is the
* confidential and proprietary information of Alibaba.com ("Confidential
* Information"). You shall not disclose such Confidential Information and shall
* use it only in accordance with the terms of the license agreement you entered
* into with Alibaba.com.
*/
package com.alibaba.study.rpc.test;
import com.alibaba.study.rpc.framework.RpcFramework;
/**
* RpcProvider
*
* @author william.liangf
*/
public class RpcProvider {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
HelloService service = new HelloServiceImpl();
RpcFramework.export(service, 1234);
}
}
###2.5 引用服务
/*
* Copyright 2011 Alibaba.com All right reserved. This software is the
* confidential and proprietary information of Alibaba.com ("Confidential
* Information"). You shall not disclose such Confidential Information and shall
* use it only in accordance with the terms of the license agreement you entered
* into with Alibaba.com.
*/
package com.alibaba.study.rpc.test;
import com.alibaba.study.rpc.framework.RpcFramework;
/**
* RpcConsumer
*
* @author william.liangf
*/
public class RpcConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
HelloService service = RpcFramework.refer(HelloService.class, "127.0.0.1", 1234);
for (int i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE; i ++) {
String hello = service.hello("World" + i);
System.out.println(hello);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
代码写的简单清晰又很能说明问题,不得不佩服大佬的技术。回过头来,我们分析一下这个程序的结构。
再次把RPC的5个组成部分回顾一下:Cient, Client-stub, Network, Server,Server-stub。
首先2.2定义服务接口和2.3实现服务都是在Server端实现的。写完了服务之后需要发布出去,以供客户端调用。于是在2.4暴露服务中调用export方法把服务发布出去。export有一个参数是服务实现的对象service,这就给客户端提供了调用的可能性。我们看看export里都做了什么:
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(port); 创建ServerSocket并绑定接口。 然后是个无限循环,因为一直提供服务嘛,final Socket socket = server.accept(); 以阻塞的方式监听网络连接。开一个线程去处理客户端发过来的信息(反序列化方法名,参数类型,参数对象),这部分功能相当于Server-stub。然后通过反射机制调用服务对象的方法,并把得到的结果序列化返回给客户端。
看客户端,也就是2.5引用服务。通过refer函数得到服务的对象(这个对象就是通过动态代理生成的代理对象)。然后像调用本地方法一样调用远程方法。我们看下refer里都做了什么:
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(interfaceClass.getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[] {interfaceClass}, new InvocationHandler()
{...重写invoke方法})
主要是返回服务实现类的代理对象,我们在分析JDK动态代理的时候知道,当我们调用代理对象的方法时,invoke方法会被执行。在invoke方法中, Socket socket = new Socket(host, port); 创建Socket与服务器取得连接。然后将方法名,方法类型,方法参数序列化发给服务器端,这部分功能相当于Client-stub。然后获得服务器端发送过来的结果。
这样RPC的功能就实现了。
本文转载自:扒一扒RPC





















 1171
1171

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








