比赛地址:http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/contest/view.action?cid=36773#status//G/0
先贴个代码 , 晚上再写题解 . 代码较挫 , 莫见笑
A: 诶,图论基本不会做 , 在高人提示下做出来的。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 10050 , maxm = 100050;
int N , M ,A ,E;
struct Edge{
int u , v ,w;
bool operator < (const Edge & b) const {
return w < b.w;
}
}edge[maxm];
int fa[maxn] ;
int Find(int x){
return fa[x]==x ? x : fa[x] = Find(fa[x]) ;
}
void Init(){
for(int i= 0 ;i<=N;i++) fa[i] = i;
}
int Kruskal(){
int ans = 0;
sort(edge , edge+E);
for(int i=0;i<E;i++){
int fx = Find(edge[i].u) , fy = Find(edge[i].v);
if(fx == fy) continue;
fa[fx] = fy ;
ans += edge[i].w;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int T ,cas = 1;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
scanf("%d%d%d",&N,&M,&A) ;
Init();
E = 0;
int x ,y , z;
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
scanf("%d%d%d",&x , &y , &z);
if(z >= A) continue;
edge[E++] = (Edge) {x , y ,z };
}
int cost = Kruskal();
int cnt = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
if(Find(i) == i) cnt ++;
cost += cnt * A;
printf("Case #%d: %d %d\n",cas++ , cost , cnt);
}
return 0;
}B : 略
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int T , cas = 1;
char a[100] ,b[100];
scanf("%d\n",&T);
while(T--){
gets(a) ,gets(b);
int len = strlen(b);
string AA = (string) a;
string BB = (string) b;
if (AA == BB) { printf("Case %d: Yes\n",cas++); continue; }
string B = (string) b;
string A = "";
for(int i=0; a[i]!='\0' ;i++){
if(a[i]!=' ') A += a[i];
}
if(A==B) { printf("Case %d: Output Format Error\n",cas++) ; continue; }
else { printf("Case %d: Wrong Answer\n",cas++); }
}
return 0;
}C: 预处理出所有必败点 , 再二分查找答案啊。。。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int maxn = 1000050;
int X1[maxn] , Y1[maxn] ;
int vis[maxn];
int FN = 0;
int Find(int x1,int x2 ,int y1,int y2){
int L = max (lower_bound(X1,X1+FN,x1)-X1 , lower_bound(Y1,Y1+FN,y1)-Y1);
int R = min (upper_bound(X1,X1+FN,x2)-X1 , upper_bound(Y1,Y1+FN,y2)-Y1);
return L < R ? R - L : 0 ;
}
LL gcd(LL a,LL b){
LL r;
while(b) r=a%b , a=b ,b=r;
return a;
}
int main()
{
for(int a=1,t=1;a<maxn;a++ ){
if(vis[a]) continue;
int b=a + t++;
if(b>maxn) break;
vis[a] = vis[b] = 1;
X1[FN] = a , Y1[FN++] = b;
}
int T ,cas=1;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
int x1, y1 ,x2 ,y2;
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x1, &y1 , &x2 , &y2);
LL B = Find(x1,x2,y1,y2) + Find(y1,y2,x1,x2);
LL C = (LL)(x2-x1+1)*(y2-y1+1) , A = C - B;
LL d =gcd(A , C);
A/=d , C/=d;
printf("Board %d: %lld / %lld\n",cas++ , A , C);
}
return 0;
}
D: 略
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long LL;
int B,V;
int t[300];
string name[300];
LL toNum(char* s){
LL ret = 0;
int len = strlen(s);
for(int i=0 , t=len-1 ; t>=0 ;i++ ,t--){
if(s[t]=='1') ret += (1<<i);
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d%d",&B,&V)!=EOF){
map<string,LL> mp;
for(int i= 0 ;i<V;i++){
cin>>name[i];
cin>>t[i];
}
char tmp[50];
for(int i=0;i<V;i++){
LL ret = 0;
for(int j=0;j<t[i];j++){
cin>>tmp;
ret = (ret<<(B)) + toNum(tmp) ;
}
mp[name[i]] = ret;
}
int Q;
cin>>Q;
string tt;
for(int i=0;i<Q;i++){
cin>>tt;
if(mp.find(tt) == mp.end()) {
cout<<tt<<"="<<endl; continue;
}
else{
cout<<tt<<"="<<mp[tt]<<endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}E:大水题
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=110;
int w[maxn] , h[maxn] , N;
int main()
{
int cas = 1;
while(scanf("%d",&N)!=EOF){
memset(w , 0 ,sizeof(w));
memset(h , 0 ,sizeof(h));
int x, y;
bool OK = false;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
if(x==y) OK = true;
w[x] = h[y] =1;
}
if(OK) {
printf("Case %d : %d\n",cas++ , 0); continue;
}
int MIN = 200;
for(int i=0;i<=100;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=100;j++){
if(w[i] && h[j]){
MIN = min(MIN , abs(i-j));
}
}
}
if(MIN == 0) {
printf("Case %d : %d\n",cas++ , 1);
}
else printf("Case %d : %d\n",cas++ , (MIN+1)/2);
}
return 0;
}
G: 此题可用LCS模型来解决 , 为了更好的说明 , 在此先复习一下最长公共子序列:
动态规划的一个计算最长公共子序列的方法如下,以两个序列 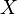 、
、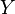 为例子:
为例子:
设有二维数组 ![f[i][j]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/d/2/a/d2ab822a4ef936fa14e3e923b88fd2ae.png) 表示
表示 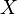 的
的 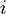 位和
位和 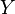 的
的  位之前的最长公共子序列的长度,则有:
位之前的最长公共子序列的长度,则有:
其中, 当
当 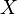 的第
的第 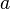 位与
位与 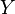 的第
的第  位完全相同时为“1”,否则为“0”。
位完全相同时为“1”,否则为“0”。
此时,![f[i][j]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/d/2/a/d2ab822a4ef936fa14e3e923b88fd2ae.png) 中最大的数便是
中最大的数便是 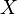 和
和 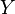 的最长公共子序列的长度,依据该数组回溯,便可找出最长公共子序列。
的最长公共子序列的长度,依据该数组回溯,便可找出最长公共子序列。
该算法的空间、时间复杂度均为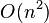
dp[ i ][ j ] = dp[ i -1 ][ j-1 ] + 1 , if " s[i] and s[j] are not bad candies " && "s[ i ] == s[ j ] ";
dp[ i ][ j ] = 0 , otherwise;
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
const int maxn= 1010;
int dp[maxn][maxn];
int id(char c){
if(c>='a' && c<='z') return c-'a';
return c-'A' + 26 ;
}
char a[maxn] , b[maxn] ;
int isbad[100] , A[maxn] , tot;
int main()
{
int T , cas=1;
scanf("%d\n",&T);
while(T--){
memset(isbad,0,sizeof(isbad));
memset(dp , 0, sizeof(dp));
gets(a+1) , gets(b) ;
int len = strlen(a+1) , len2 = strlen(b);
for(int i=0;i<len2;i++){
isbad[id(b[i])] = 1;
}
tot = -1;
for(int i=1;i<=len;i++){
int tmp = id(a[i]);
if(isbad[tmp]) A[i] = tot--;
else A[i] = tmp;
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=len;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<=len ; j++ ){
if(A[i] < 0 || A[j] <0 ) { // bad candies
dp[i][j] = 0;
continue;
}
if(A[i] == A[j] ){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1;
}
else {
dp[i][j] = 0;
}
int MIN = min(dp[i][j] , j-i); // 避免重叠
ans = max (ans , MIN);
}
}
printf("Case #%d: %d\n",cas++ , ans);
}
return 0;
}






 本文提供了ACM竞赛中五个问题的代码实现与解析,涉及图论、字符串处理、动态规划等算法,通过具体实例展示了算法设计与编程技巧。
本文提供了ACM竞赛中五个问题的代码实现与解析,涉及图论、字符串处理、动态规划等算法,通过具体实例展示了算法设计与编程技巧。
![f[1][1] = same(1,1)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/5/4/4/544a258e4af2b4a4d2a075dabc35d002.png)
![f[i][j] = max\{f[i-1][j-1] + same(i,j), f[i-1][j],f[i][j-1]\}](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/6/0/5/6059fb703e7e52232639bf370095e549.png)
















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








