***************图书推荐*************************************************************************************
|
|
|
|
|
|
*********************************************************************************************************************
来源:韩现龙的博客 http://www.cnblogs.com/hanxianlong/archive/2007/12/07/987205.html
Over the last few weeks I've been writing a series of blog posts that cover LINQ to SQL. LINQ to SQL is a built-in O/RM (object relational mapper) that ships in the .NET Framework 3.5 release, and which enables you to model relational databases using .NET classes. You can use LINQ expressions to query the database with them, as well as update/insert/delete data.
Below are the first seven parts in this series:
在上几周中我写了一个概述了LINQ to SQL的帖子系列。LINQ to SQL是集成在.NET Framework3.5中的O/RM(对象关系映射)的实现,它让你非常容易地用.NET类来生成关系型数据库的模型。然后你可以用LINQ 表达式对它来进行查询,更新,插入删除。 下边是我的该系列的前七篇的帖子的链接:
- Part 1: Introduction to LINQ to SQL
- Part 2: Defining our Data Model Classes
- Part 3: Querying our Database
- Part 4: Updating our Database
- Part 5: Binding UI using the ASP:LinqDataSource Control
- Part 6: Retrieving Data Using Stored Procedures
- Part 7: Updating our Database using Stored Procedures
In my last two posts (Part 6 and Part 7) I demonstrated how you can optionally use database stored procedures (SPROCs) to query, insert, update and delete data using a LINQ to SQL data model.
在前两篇帖子中 (Part 6 and Part 7)我描述了如何用LINQ to SQL数据模型通过数据库的存储过程和用户自定义的函数来查询和检索数据。在今天的博客中我将讨论一下如何选择使用存储过程来更新、插入、删除数据。
One of the questions a few people have asked me since doing these posts has been "what if I want total control over the SQL expressions used by LINQ to SQL - but I don't want to use SPROCs to-do it?" Today's blog post will cover that - and discuss how you can use custom SQL expressions that you provide to populate your LINQ to SQL data model classes, as well as perform insert, updates, and deletes.
自从我写了那些帖子之后,许多人问我的问题之一就是“如果我想完全控制linq to sql的sql表达式,并且我又不想用存储过程--我该怎么做?”今天的博客将会讲述这个问题--并且讨论一下如何使用自定义的sql表达式来控制你的linq to sql 数据模型类,对其插入、更新和删除。
Using LINQ Query Expressions with LINQ to SQL
和LINQ to SQL一起使用LINQ 查询表达式
For the purposes of this blog post, let's assume we've used the LINQ to SQL ORM designer in VS 2008 to define a set of data model classes like below for the Northwind database (note: read Part 2 of this series to learn how to use the LINQ to SQL ORM designer to do this):
为了完成今天帖子要讲述的内容,让我们假设已经用VS2008中的LINQ to SQL ORM设计器为Northwind数据库定义一个如下的数据模型类:(在本系列的第2部分Part 2 中讲述了如何用设计器定义此数据模型类):

In Part 3 of this blog series I covered how you can use the new LINQ language support in VB and C# to query the above data model classes and return back a set of objects that represent the rows/columns in the database.
在本系列的第3部分(Part 3),我讲述了如何用在VB和C#中支持的新的LINQ语言来对上面的数据模型类进行查询,并且返回一个代表了数据库中的行/列关系的对象。
For example, we could add a "GetProductsByCategory" helper method to the DataContext class of our data model that uses a LINQ query to return back Product objects from the database:
例如,我们可以向我们的数据模型的DataContext类中添加一个"GetProductsByCategory"的帮助方法 ,该方法用LINQ查询从数据库中进行查询并返回一个Product对象集合:
VB:

C#:

Once we've defined our encapsulated LINQ helper method, we can then write code like below that uses it to retrieve the products, and iterate over the results:
一旦我们定义了LINQ帮助方法,我们可以写如下的代码,用LINQ的帮助方法来检索产品并且对结果进行遍历:
VB:

When the LINQ expression within our "GetProductsByCategory" method is evaluated, the LINQ to SQL ORM will automatically execute dynamic SQL to retrieve the Product data and populate the Product objects. You can use the LINQ to SQL Debug Visualizer to see in the debugger how this LINQ expression is ultimately evaluated.
当"GetProductsByCategory"方法被调用时, LINQ to SQL ORM将会运行动态的SQL来检索产品数据。你可以在LINQ to SQL Debug Visualizer中查看这个LINQ表达式最终是如何生成的。
Using Custom SQL Queries with LINQ to SQL
和LINQ to SQL一起使用自定义的SQL查询
In our sample above we didn't have to write any SQL code to query the database and retrieve back strongly-typed Product objects. Instead, the LINQ to SQL ORM automatically translated the LINQ expression to SQL for us and evaluated it against the database.
在上面的例子中,我们没有写任何的SQL代码来查询数据库和检索出强类型的产品对象。取代之的是,linq to sql orm会自动的将linq表达式翻译为sql语句,并且使用生成的sql语句对数据库进行操作。
But what if we wanted total control over the SQL that is run against our database, and don't want LINQ to SQL to-do it for us in this scenario? One way to accomplish this would be to use a SPROC like I discussed in Part 6 and Part 7 of this series. The other approach is to use the "ExecuteQuery" helper method on the DataContext base class and use a custom SQL expression that we provide.
可是,若是我们想完全控制对我们的数据库进行操作的sql语句,并且不想让linq to sql为我们自动生成的话,该怎么做呢?实现这个目的的方法之一是使用在本系列的第 六(Part 6)和第七( Part 7)部分讲解的存储过程。另外一个方法是使用在DataContext基类中的"ExecuteQuery"帮助方法,使用我们提供的自定义的sql表达式。
Using the ExecuteQuery Method
使用ExecuteQuery方法
The ExecuteQuery method takes a SQL query expression as an argument, along with a set of parameter values that we can use to optionally substitute values into the query. Using it we can execute any raw SQL we want against the database (including custom JOINs across multiple tables).
ExecuteQuery方法将sql查询表达式作为参数,和一系列的我们可以选择使用参数列表。使用这一功能我们可以对数据库执行原始的sql语句(包括自定义的多表之间的连接)。
What makes the ExecuteQuery method really useful is that it allows you to specify how you want the return values of your SQL expression to be typed. You can do this either by passing a type-object as a parameter to the method, or by using a generic-based version of the method.
使ExecuteQuery方法真正有用的是它允许你声明以何种方式将sql表达式返回的值进行格式化。你可以通过如下两种方式来实现:或者向方法中传递一个类型对象作为参数,或者使用一个本方法的generic-based的版本。
For example, we could change the GetProductsByCategory() helper method we created earlier - using a LINQ expression - to instead use the ExecuteQuery method to execute our own raw SQL expression against the database and return "Product" objects as a result:
例如,我们可以修改原来生成的GetProductsByCategory()的帮助方法-使用LINQ表达式--来替代ExecuteQuery方法来执行我们自己的原始的SQL表达式对数据库进行操作并返回"Product"对象:
VB:

C#:

We can then call the GetProductsByCategory() helper method using the exact same code as before:
然后我们可以调用GetProductByCategory()帮助方法,代码可以和前面的代码完全相同:

But unlike before it will be our custom SQL expression that will run against the database - and not dynamic SQL executed in response to using a LINQ query expression.
但是和前面的不同的是,对数据库进行操作的是我们自定义的SQL表达式--而不是linq表达式生成的动态sql语句。
Custom SQL Expressions and Object Tracking for Updates
为更新自定义SQL表达式和对象跟踪
By default when you retrieve a data model object using LINQ to SQL, it will track all changes and updates you make to it. If you call the "SubmitChanges()" method on the DataContext class, it will then transactionally persist all of the updates back to the database. I cover this in more depth in Part 4 of this LINQ to SQL series.
One of the cool features of the ExecuteQuery() method is that it can fully participate in this object tracking and update model. For example, we could write the code below to retrieve all products from a specific category and discount their prices by 10%:
默认情况下,当你用LINQ to SQL从数据模型对象中检索数据时,它会跟踪所有的变化并且当你对对象进行更新时更新这些变化。如果你调用DataContext中的"SbumitChanges()"方法,它将会启动一个事务,并且将所有的变更更新至数据库中。我本系列的第四部分Part 4中对这一点进行的较深刻地讲解。
ExecuteQuery()的其中一个比较酷的我是,它完全参与跟踪和更新模型中。比如,我们可以写如下的代码查询属于某一类别的产品并且将它们的价格打折10%:

Because we typed the return value of our ExecuteQuery call in the GetProductsByCategory method to be of type "Product", LINQ to SQL knows to track the Product objects we returned from it. When we call "SubmitChanges()" on the context object they will be persisted back to the database.
因为我们将ExecuteQuery()方法调用的GetProductByCategory()方法的结果集转换为"Product"的类型,LINQ to SQL知道跟踪返回的Product对象。当我们调用Context对象中的"SubmitChanges()"方法时,它们将会被保存至数据库中。
Custom SQL Expressions with Custom Classes
自定义类中的自定义SQL表达式
The ExecuteQuery() method allows you to specify any class as the return type of a SQL query. The class does not have to be created using the LINQ to SQL ORM designer, or implement any custom interface - you can pass in any plain old class to it.
ExecuteQuery()方法允许你指定任何类来作为SQL查询的返回值类型。该类不是必须用LINQ to SQL ORM设计器生成的或者实现了某些自定义的接口-你可以将旧的类指定给它作为它的返回值类型。
For example, I could define a new ProductSummary class that has a subset of Product properties like below (notice the use of the new C# Automatic Properties feature):
例如,我可以定义一个新的ProductSummary类,该类含有Product的属性是Product类的属性的一个子集,包括如下这些属性(注意新的C#的自动属性Automatic Properties特性):

We could then create a GetProductSummariesByCategory() helper method on our NorthwindDataContext that returns results based on it. Notice how our SQL statement below requests just the subset of product values we need - the ExecuteQuery method then handles automatically setting these on the ProductSummay objects it returns:
然后我们可以在NorthwindDataContext中生成一个将该类作为返回值类型的GetProductSummariesByCatetory()帮助方法。注意下面的SQL声明是如何只请求Product中的我们需要的属性的值的--ExecuteQuery()方法自动处理它返回的ProductSummary对象:

We can then invoke this helper method and iterate over its results using the code below:
然后我们可以执行这个帮助方法并且用下面的代码来对结果集进行遍历:

Custom SQL Expressions for Inserts/Updates/Deletes
用于插入、更新、删除的自定义的SQL表达式
In addition to using custom SQL expressions for queries, we can also execute them to perform custom Insert/Update/Delete logic.
除了对查询使用自定义的SQL表达式,我们也可以执行它们来进行插入、更新、删除的逻辑。
We can accomplish this by creating the appropriate partial Insert/Update/Delete method for the entity we want to change in a partial class on our DataContext. We can then use the ExecuteCommand method on the DataContext base class to write the SQL we want to execute. For example, to override the Delete behavior for Product classes we could define this DeleteProduct partial method:
我们可以通过如下方式实现这个目的:在DataContext的一个局部类中生成一个适当的插入、更新、删除的局部方法。然后使用ExecuteCommand方法来写我们需要执行的SQL语句。例如,为了为产品类覆盖删除的方法,我们可以定义如下的一个DeleteProduct局部方法:
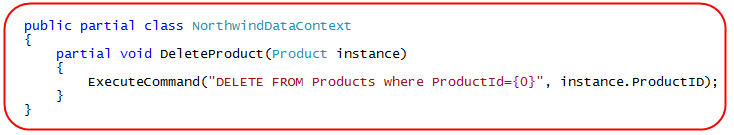
And now if we write the below code to remove a specific Product instance from our database, LINQ to SQL will call the DeleteProduct method - which will cause our custom SQL to execute in place of the default dynamic SQL that LINQ to SQL would otherwise use:
然后如果我们写如下的代码从数据库中移除一个特定的产品实例,LINQ to SQL将会调用DeleteProduct方法--该方法将会引起我们自定义的SQL语句替代自动生成的SQL语句:

Summary
总结
The LINQ to SQL ORM automatically generates and executes dynamic SQL to perform queries, updates, inserts and deletes against a database.
LINQ to SQL ORM自动生成并运行动态的SQL语句来对数据库进行查询、更新、插入和删除。
For advanced scenarios, or cases where you want total control over the SQL query/command executed, you also have the ability to customize the ORM to use either SPROCs, or your own custom SQL Expressions, instead. This provides you with a great deal of flexibility when building and extending your data access layer.
在一些高级的场景中,或者在你想完全控制执行的SQL语句的情况下,你依然能够自定义ORM来或者使用存储过程,或者使用你自己定义的SQL表达式来替代原来它自动生成的SQL语句。这在创建和扩展你的数据层的时候给你提供了非常大的灵活性。
In future blog posts in this series I'll cover some remaining LINQ to SQL concepts including: Single Table Inheritance, Deferred/Eager Loading, Optimistic Concurrency, and handling Multi-Tier scenarios.
在接下来的本系列的帖子中,我将描述一些余下的LINQ to SQL概念,包括:单表继承,延迟/提前加载,优化并发冲突,处理多个场景。
Hope this helps,
希望这些对你有所帮助,
Scott







 本文详细介绍了如何在LINQtoSQL中使用自定义SQL表达式进行查询、更新等操作,提供了多种实现方法及示例代码。
本文详细介绍了如何在LINQtoSQL中使用自定义SQL表达式进行查询、更新等操作,提供了多种实现方法及示例代码。






















 324
324

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








