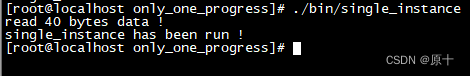
Linux下只允许程序运行一个实例,这里想到两个方法,这个是用到ps,一个是用到文件锁。
1,ps方法:
程序开始运行时读指定文件,如果匹配到程序名则已经有运行的进程,退出。若匹配不到则往文件写一些信息,程序退出时删除文件。
/****************************************************
****** 可以用ps 找到当前是否有同名的进程,有则已经运行。
******
****************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#define PROCESS_NAME "single_instance"
int isRunning();
int main()
{
if(isRunning() == 1)
{
printf("%s has been run !\n", PROCESS_NAME);
return 0;
}
printf("run ok!\n");
system("ps | grep \"single_instance\" > process.pid");
sleep(30);
system("rm -rf process.pid");
return 0;
}
int isRunning()
{
char buf[128] = {0};
FILE *fp = fopen("./process.pid", "rwb");
if(fp != NULL)
{
int readLen = fread(buf, 1, sizeof(buf) - 1, fp);
printf("read %d bytes data !\n", readLen);
}
else
{
return 0;
}
if(strstr(buf, PROCESS_NAME) != NULL)
{
fclose(fp);
return 1;
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
2,文件锁方法:
程序开始运行时,往文件里写入进程号,并锁定文件;此时若再运行一个实例,因前一个实例已经锁定文件,此时是去锁定文件是失败的。
/************************************
* 用文件锁的方式确保只有一个程序在运行
* *********************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#define PROC_NAME "single_instance"
#define PID_FILE_PATH "/var/run/"
static int lockFile(int fd);
static int isRunning(const char *procname);
/* 记录进程pid的文件fd,程序退出时才关闭 */
int g_fd = -1;
int main()
{
if(isRunning(PROC_NAME))
{
exit(-1);
}
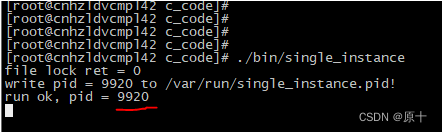
printf("run ok, pid = %d\n", getpid());
sleep(30);
if(g_fd != -1)
{
close(g_fd);
}
return 0;
}
static int lockFile(int fd)
{
struct flock fl;
fl.l_type = F_WRLCK;
fl.l_start = 0;
fl.l_whence = SEEK_SET;
fl.l_len = 0;
fl.l_pid = getpid(); //当前进程号,可写可不写,写了后在用F_GETLK时则可以获取到pid
int ret = fcntl(fd, F_SETLK, &fl);
printf("file lock ret = %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
static int isRunning(const char *procname)
{
char buf[16] = {0};
char fileName[128] = {0};
snprintf(fileName, sizeof(fileName), "%s%s.pid", PID_FILE_PATH, procname);
//创建文件时如果指定了 O_CREAT,则必须添加权限,否则可能无法读取文件而导致失败
int g_fd = open(fileName, O_CREAT | O_RDWR, S_IRWXU);
if(g_fd < 0)
{
printf("open file %s failed !\n", fileName);
return 1;
}
if(-1 == lockFile(g_fd))
{
// printf("%s is alread running !\n", procname);
struct flock fl;
fl.l_type = F_WRLCK;
fl.l_start = 0;
fl.l_whence = SEEK_SET;
fl.l_len = 0;
/*这里获取一下已经运行的实例的进程号*/
if(fcntl(g_fd, F_GETLK, &fl) == 0)
{
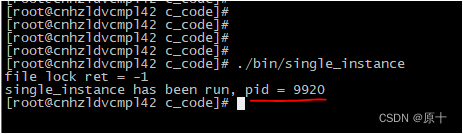
printf("%s has been run, pid = %d\n", PROC_NAME, fl.l_pid);
}
close(g_fd);
return 1;
}
else
{
ftruncate(g_fd, 0);
long pid = getpid();
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%ld", pid);
printf("write pid = %ld to %s!\n", pid, fileName);
write(g_fd, buf, strlen(buf) + 1);
return 0;
}
}
在两个命令行窗口运行如下:
原理:
程序在启动后,打开一个program.pid(或program.lock) 文件(无则创建)然后试图去设置文件锁,如果设置成功,则将该程序的进程pid写入该文件;如果加锁失败,那么说明已经有另外一个实例在运行,则退出此次启动。
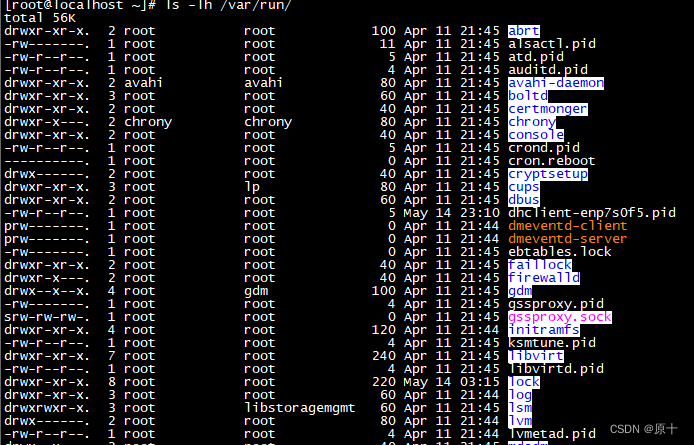
Linux系统下就有很多这样的文件,如:























 249
249

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








