两种容器
1.传统web.xml定义父子容器流程
1.1 配置
一个web应用一个servletContext.
史上最全最强SpringMVC详细示例实战教程
web.xml部分配置:
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<!--用于创建rootApplicationContext-->
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--configure the setting of springmvcDispatcherServlet and configure the mapping-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<!--用于创建servletAppContext-->
<param-value>classpath:springmvc-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<!-- <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> -->
</servlet>
1.2 流程
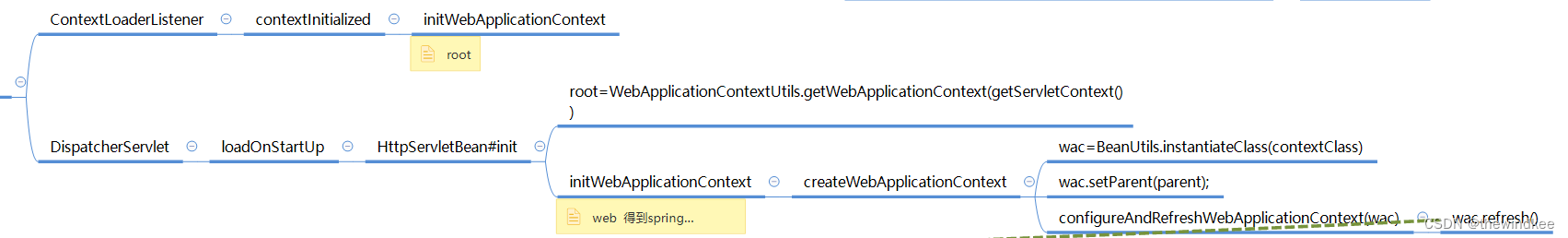
通常,我们在ContextLoaderListener定义一个配置扫描Spring的service和dao的配置文件。
在servlet的DispatcherServlet下定义扫描Controller的配置文件。
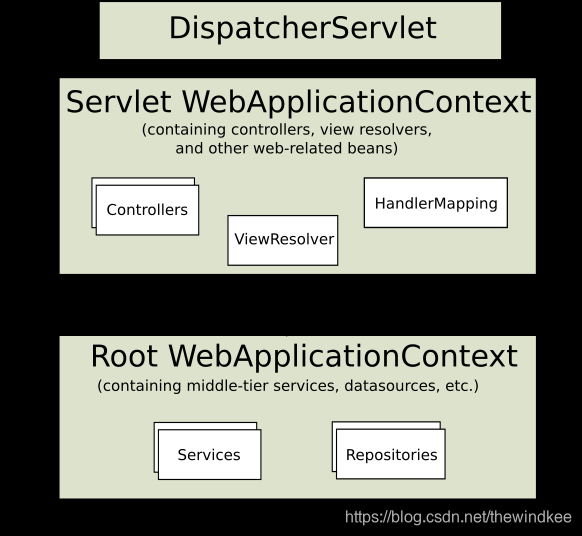
servletContext和两个配置文件的关系如下:
servletContext->contextLoaderListener->rootApplicationContext
servletContext->dynamic->dispacherServlet->servletAppContext(即webapplicationContext)
2.Servlet3.0 Java编码方式代替web.xml配置
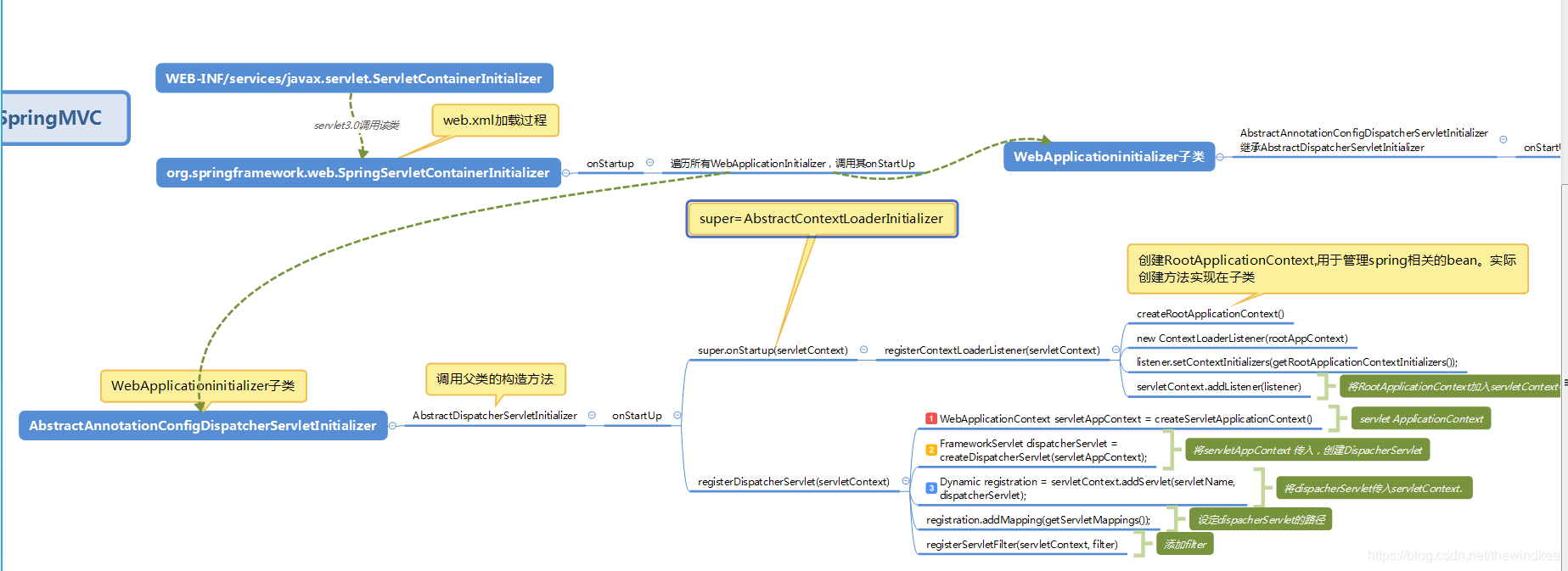
1.由于Servlet 3.0 的设计, 会自动扫描META-INF/services下的javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer实现。spring-web的实现是SpringServletContainerInitializer。自定义META-INF/services+实现ServletContainerInitializer可以代替web.xml。
2.SpringServletContainerInitializer关注所有WebApplicationInitializer并调用其onStartup方法。
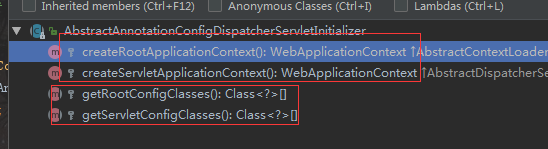
3.WebApplicationinitializer有一个AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer实现。
3.1 其调用父类(AbstractContextLoaderInitializer)的onStartUp方法来创建Root WebApplicationContext ,
3.2 this.registerDispatcherServlet来创建Servlet WebApplicationContext。
3.3 它是模板方法创建了两个容器。
3.4 AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer提供的抽象的实现,我们只需要定义@Configuration对应的类即可。
创建两个容器
2.1 流程
2.2 自定义WebApplicationInitializer
public class MyWebAppInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext container) {
// Create the 'root' Spring application context
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext rootContext =
new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
rootContext.register(AppConfig.class);
// Manage the lifecycle of the root application context
container.addListener(new ContextLoaderListener(rootContext));
// Create the dispatcher servlet's Spring application context
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext dispatcherContext =
new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
dispatcherContext.register(DispatcherConfig.class);
// Register and map the dispatcher servlet
ServletRegistration.Dynamic dispatcher =
container.addServlet("dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(dispatcherContext));
dispatcher.setLoadOnStartup(1);
dispatcher.addMapping("/");
}
参考:https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/web.html#mvc-servlet-context-hierarchy







 本文深入探讨了Spring MVC中两种容器配置方式:传统web.xml定义和Servlet 3.0 Java编码方式。通过对比分析,详细解释了如何使用ContextLoaderListener和DispatcherServlet配置rootApplicationContext与servletAppContext,以及如何利用Servlet 3.0特性自定义WebApplicationInitializer实现容器初始化。
本文深入探讨了Spring MVC中两种容器配置方式:传统web.xml定义和Servlet 3.0 Java编码方式。通过对比分析,详细解释了如何使用ContextLoaderListener和DispatcherServlet配置rootApplicationContext与servletAppContext,以及如何利用Servlet 3.0特性自定义WebApplicationInitializer实现容器初始化。
















 600
600

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








