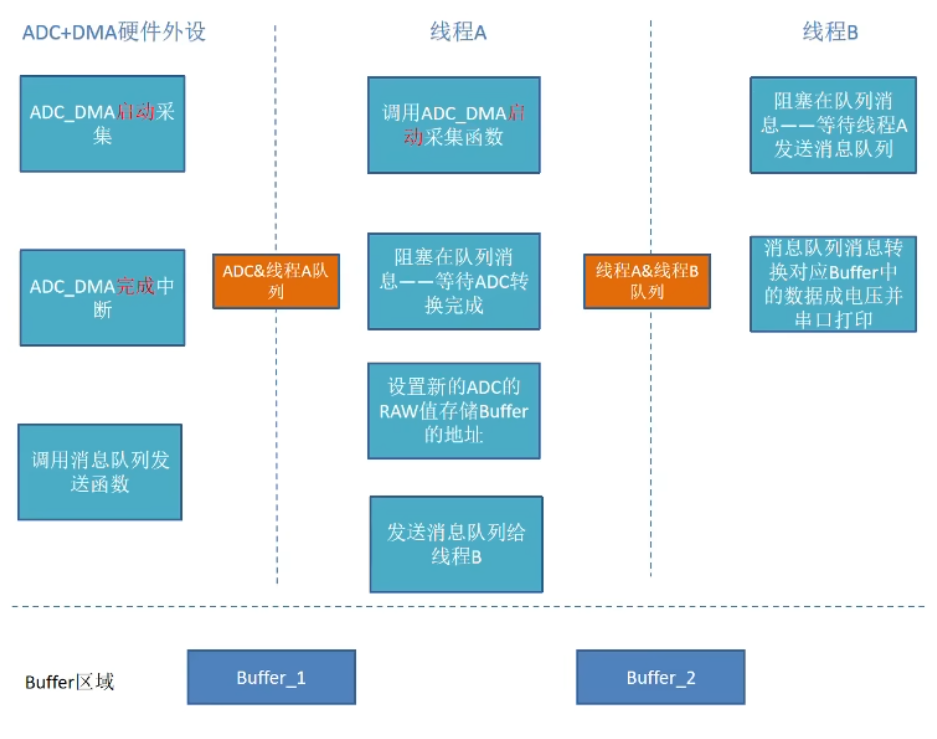
本期目标
理清本工程系统框架
弄懂CubeMx配置相关原理及设置的背后含义
对DMA以及ADC相关的重要API接口使用详解
梳理代码设计流程
SAR型 ADC
单片机里的ADC,一般都是SAR型 ADC,是逐次逼近型ADC 吗这种类型的ADC精度一般都不是很高 ,但是成本都比较低
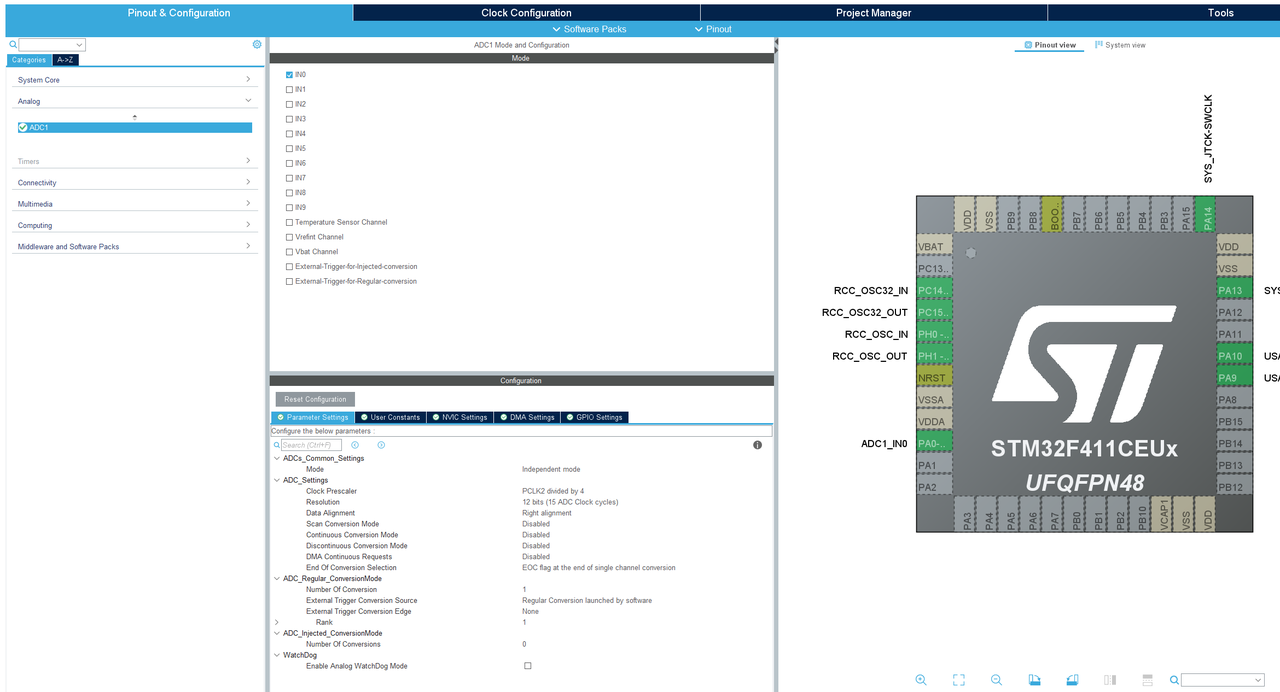
CubeMx配置
ADC设置
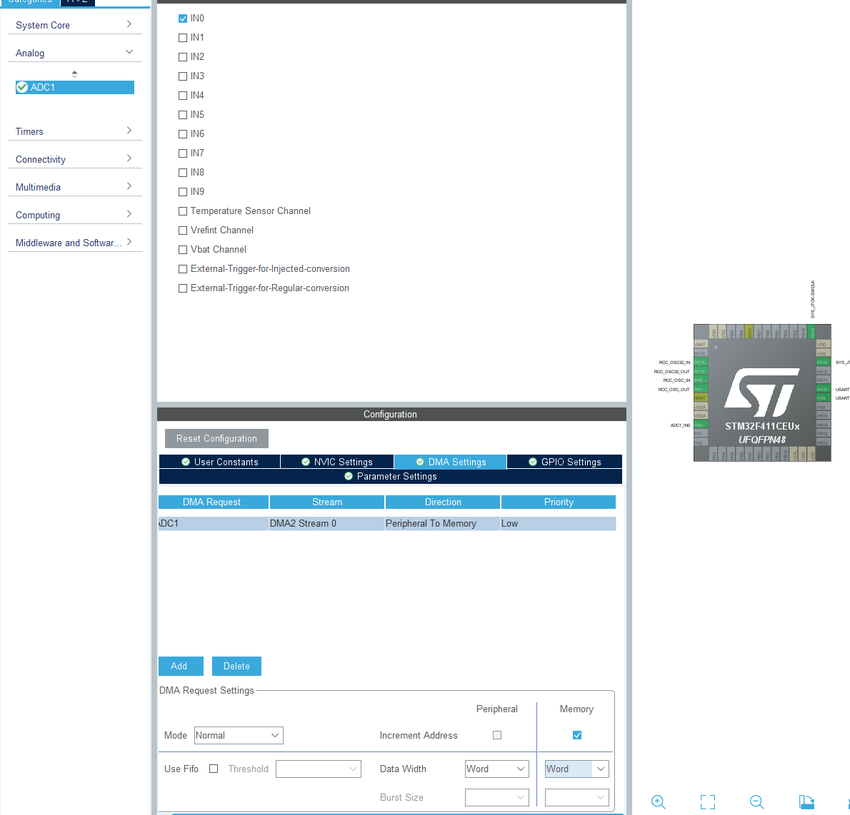
DMA设置
对DMA不熟悉的可以参考以下文章 , 详细讲解了DMA的具体设置、FIFO的作用及其具体操作
DMA初学者必看!帮小白从系统CPU层理解DMA原理-优快云博客
小白也能看懂!从底层原理深入理解DMA控制器的内部架构图及其构成,加深对DMA的掌控-优快云博客
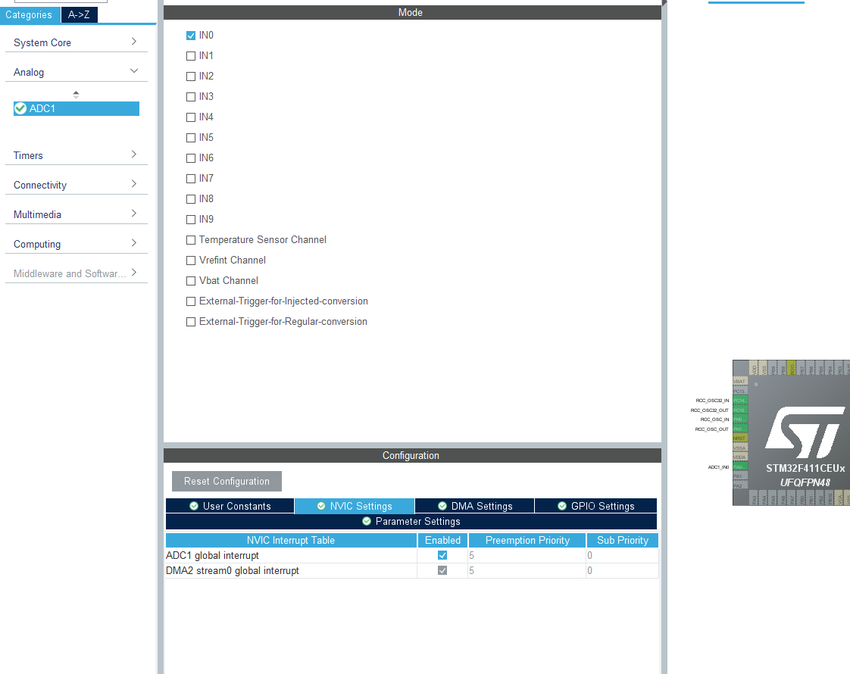
打开中断
代码部分
hadc1.Instance = ADC1;
hadc1.Init.ClockPrescaler = ADC_CLOCK_SYNC_PCLK_DIV4;
hadc1.Init.Resolution = ADC_RESOLUTION_12B;
hadc1.Init.ScanConvMode = DISABLE;
hadc1.Init.ContinuousConvMode = DISABLE;
hadc1.Init.DiscontinuousConvMode = DISABLE;
hadc1.Init.ExternalTrigConvEdge = ADC_EXTERNALTRIGCONVEDGE_NONE;
hadc1.Init.ExternalTrigConv = ADC_SOFTWARE_START;
hadc1.Init.DataAlign = ADC_DATAALIGN_RIGHT;
hadc1.Init.NbrOfConversion = 1;
hadc1.Init.DMAContinuousRequests = DISABLE;
hadc1.Init.EOCSelection = ADC_EOC_SINGLE_CONV;
if (HAL_ADC_Init(&hadc1) != HAL_OK)PCLK2 divided by 4
ADC也需要动力 , 时钟就是他的动力, 对PCLK2 , 进行四分频
Rigiht alignment
右对齐
Scan Conversion Mode
Scan Conversion Mode 是控制:ADC 是否按照配置的通道序列,对多个通道进行依次转换。(我们本次就一个通道,所以未开启)
-
如果是 Enable,ADC 将按照在规则通道(Regular Channels)中配置的通道序列,依次对多个通道进行转换。 每次触发(无论是软件触发还是硬件触发),ADC都会按照顺序对所有配置的通道进行一次完整的转换序列。适用于需要同时采集多个模拟信号的情况,例如多传感器数据采集、数据监测等。
-
如果同时启用了 Continuous Conversion Mode(连续转换模式), ADC 会在完成一次完整的通道序列转换后,立即开始下一次序列的转换,形成一个连续的循环。如果没有启用 Continuous ConversionMode(连续转换模式),ADC在完成一次通道序列转换后停止,等待下一个触发事件。
-
如果同时启用了 Discontinuous Conversion Mode(非连续转换模式),会将通道序列分成若干组,每次触发事件只转换一组通道,
-
-
如果是 Disable,ADC 仅对配置的一个通道进行转换,没有通道序列的概念。每次触发只转换一个通道,简单高效。适用于只需要采集一个模拟信号的简单应用,例如单一传感器的读取。
Continuous Conversion Mode(连续转换模式)是控制:是否持续的对某一个通道不停地转换,你会在 DR 里面一直看到数据更新,EOC 标志位一直会产生。于是你可以通过轮询或者中断的方式一直来取 ADC 的数据。
Discontinuous Conversion Mode(非连续转换模式)是控制:是否 ADC 将进入 非连续转换模式
(Discontinuous Conversion Mode).
-
在非连续转换模式下(Enable),ADC 会将配置的通道序列分成若干个小组,每个小组的大小由Discontinuous Number(非连续数目)参数确定,范围是1到8。(应确保 Scan Conversion Mode 也是Enable 的)
-
ADC会在每个触发事件(比如软件或硬件触发)下,仅转换一个小组的通道,然后停止,等待下一个触发事件。每次非连续转换都需要新的触发事件,这种模式适用于需要在多个触发事件下分批次采样的情况。
-
例如,在实时控制系统中,可能希望在每个控制周期内只采样部分通道(而不是 全部通道),以减少 CPU 负担。比如说,如果你配置了6个通道的序列,且将 Discontinuous Number 设置为 2,那么 ADC 会将这 6个通道分成3组,每组 2个通道。每次触发事件会启动一组(2 个通道)的转换需要 3 次触发事件才能完成所有通道的转换。
-
-
sConfig.Channel = ADC_CHANNEL_0;
sConfig.Rank = 1;
sConfig.SamplingTime = ADC_SAMPLETIME_3CYCLES;ADC_SAMPLETIME_3CYCLES
将逐次逼近设置成大概3个周期之后就将值给计算出来 ,这个值越大越准确 , 有时候ADC数据出问题 , 就是这里设置的太快了
1.申请buffer
freertos.c
定义
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
#include <stdlib.h>
/* USER CODE END Includes */
/* Private typedef -----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PTD */
#define BUFFER_SIZE 1
uint32_t * buffer1 = NULL;
uint32_t * buffer2 = NULL;
/* USER CODE END PTD */task
/* USER CODE END Header_StartDefaultTask */
void StartDefaultTask(void *argument)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN StartDefaultTask */
buffer1 = (uint32_t *)malloc((sizeof(uint32_t)* BUFFER_SIZE));
buffer2 = (uint32_t *)malloc((sizeof(uint32_t)* BUFFER_SIZE));
if(NULL == buffer1)
{
printf("buffer1 malloc failed \r\n");
}
if(NULL == buffer2)
{
printf("buffer2 malloc failed \r\n");
return;
}
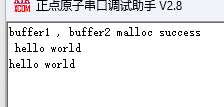
printf("buffer1 , buffer2 malloc success\r\n ");
memset(buffer1, 0xff , (sizeof(uint32_t)* BUFFER_SIZE));
memset(buffer2, 0xff , (sizeof(uint32_t)* BUFFER_SIZE));
/* Infinite loop */
for(;;)
{
printf("hello world \r\n");
osDelay(1000);
}
/* USER CODE END StartDefaultTask */
}
2.启动DMA传输并进入中断
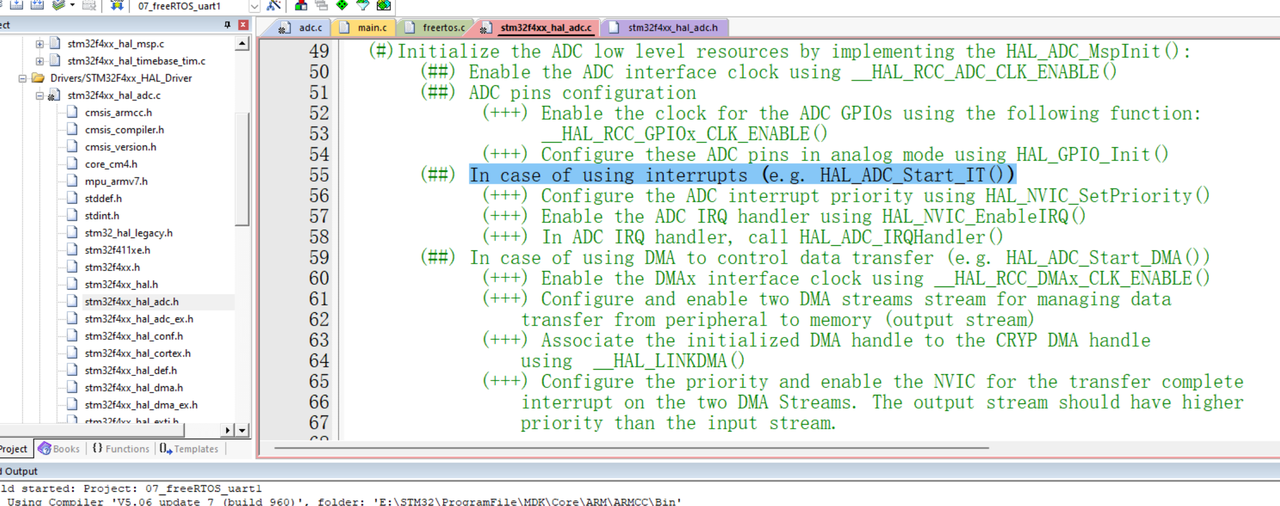
此处是使用中断的方式, 意为当数据采集完毕后会使用产生中断
本篇使用的是下面的方式
(##) In case of using DMA to control data transfer (e.g. HAL_ADC_Start_DMA())
(+++) Enable the DMAx interface clock using __HAL_RCC_DMAx_CLK_ENABLE()
(+++) Configure and enable two DMA streams stream for managing data
transfer from peripheral to memory (output stream)
(+++) Associate the initialized DMA handle to the CRYP DMA handle
using __HAL_LINKDMA()
(+++) Configure the priority and enable the NVIC for the transfer complete
interrupt on the two DMA Streams. The output stream should have higher
priority than the input stream.在启动ADC传输以后 , 会把数据放到DR寄存器里 , 如果是中断模式 , 会产生一个中断去取走DR寄存器里面的值 , 而是产生一个DMA request ,然后启动对应的DMA通道 , 然后把DR寄存器里面的值搬运到指定的地址(buffer1/buffer2)上
HAL_ADC_Start_DMA()
最主要的就是知晓这个函数怎么用
/**
* @brief Enables ADC DMA request after last transfer (Single-ADC mode) and enables ADC peripheral
* @param hadc pointer to a ADC_HandleTypeDef structure that contains
* the configuration information for the specified ADC.
* @param pData The destination Buffer address.
* @param Length The length of data to be transferred from ADC peripheral to memory.
* @retval HAL status
*/点击函数跳转定义,可以看到这个函数的简介
“启动DMA request 在每次传输完ADC后 , 并且启动ADC外设”
HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_ADC_Start_DMA(ADC_HandleTypeDef* hadc, uint32_t* pData, uint32_t Length)
第一个形参是ADC的句柄
于ADC.c文件里面有定义
所以我们要使用的时候就要在所使用的文件里extern引用
/* USER CODE BEGIN Variables */
extern ADC_HandleTypeDef hadc1;
extern DMA_HandleTypeDef hdma_adc1;
/* USER CODE END Variables */第二个形参是DMA将要将数据搬运到的地址 , 就是我们前面定义的buffer1/2
第三个形参是要从ADC采集多少次数据
HAL_ADC_Start_DMA(&hadc1, buffer1, BUFFER_SIZE);
HAL_ADC_Start_DMA(&hadc1, buffer2, BUFFER_SIZE);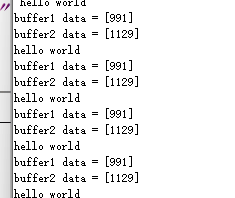
void StartDefaultTask(void *argument)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN StartDefaultTask */
buffer1 = (uint32_t *)malloc((sizeof(uint32_t)* BUFFER_SIZE));
buffer2 = (uint32_t *)malloc((sizeof(uint32_t)* BUFFER_SIZE));
if(NULL == buffer1)
{
printf("buffer1 malloc failed \r\n");
}
if(NULL == buffer2)
{
printf("buffer2 malloc failed \r\n");
return;
}
printf("buffer1 , buffer2 malloc success\r\n ");
memset(buffer1, 0xff , (sizeof(uint32_t)* BUFFER_SIZE));
memset(buffer2, 0xff , (sizeof(uint32_t)* BUFFER_SIZE));
printf("Unit test ADC + DMA\r\n ");
HAL_ADC_Start_DMA(&hadc1, buffer1, BUFFER_SIZE);
HAL_ADC_Start_DMA(&hadc1, buffer2, BUFFER_SIZE);
/* Infinite loop */
for(;;)
{
printf("hello world \r\n");
printf("buffer1 data = [%d] \r\n" , buffer1[0]);
printf("buffer2 data = [%d] \r\n" , buffer2[0]);
osDelay(1000);
}
/* USER CODE END StartDefaultTask */
}为了防止ADC调用出错 , 应当接收函数的返回值 , 以观察函数是否异常
HAL_StatusTypeDef ret1 = HAL_OK;
HAL_StatusTypeDef ret2 = HAL_OK;
ret1 = HAL_ADC_Start_DMA(&hadc1, buffer1, BUFFER_SIZE);
ret2 = HAL_ADC_Start_DMA(&hadc1, buffer2, BUFFER_SIZE);
if(HAL_OK != ret1)
{
printf("HAL_ADC1 call failed ");
}
if(HAL_OK != ret2)
{
printf("HAL_ADC2 call failed ");
}至此我们的API : HAL_ADC_Start_DMA() 就调用成功了
HAL_ADC_ConvCpltCallback()
当DMA输出到Buffer1后 ,触发DMA中断(中断做的第一件事: 发送消息队列或任务通知(邮箱)给线程A) 。 (涉及函数:xTaskNotifyFromISR或xQueueGenericSendFromISR)
(+) At The end of data transfer by HAL_ADC_ConvCpltCallback() function is executed and user can
add his own code by customization of function pointer HAL_ADC_ConvCpltCallback __weak void HAL_ADC_ConvCpltCallback(ADC_HandleTypeDef* hadc)
{
/* Prevent unused argument(s) compilation warning */
UNUSED(hadc);
/* NOTE : This function Should not be modified, when the callback is needed,
the HAL_ADC_ConvCpltCallback could be implemented in the user file
*/
}将此函数复制到freertos文件调用
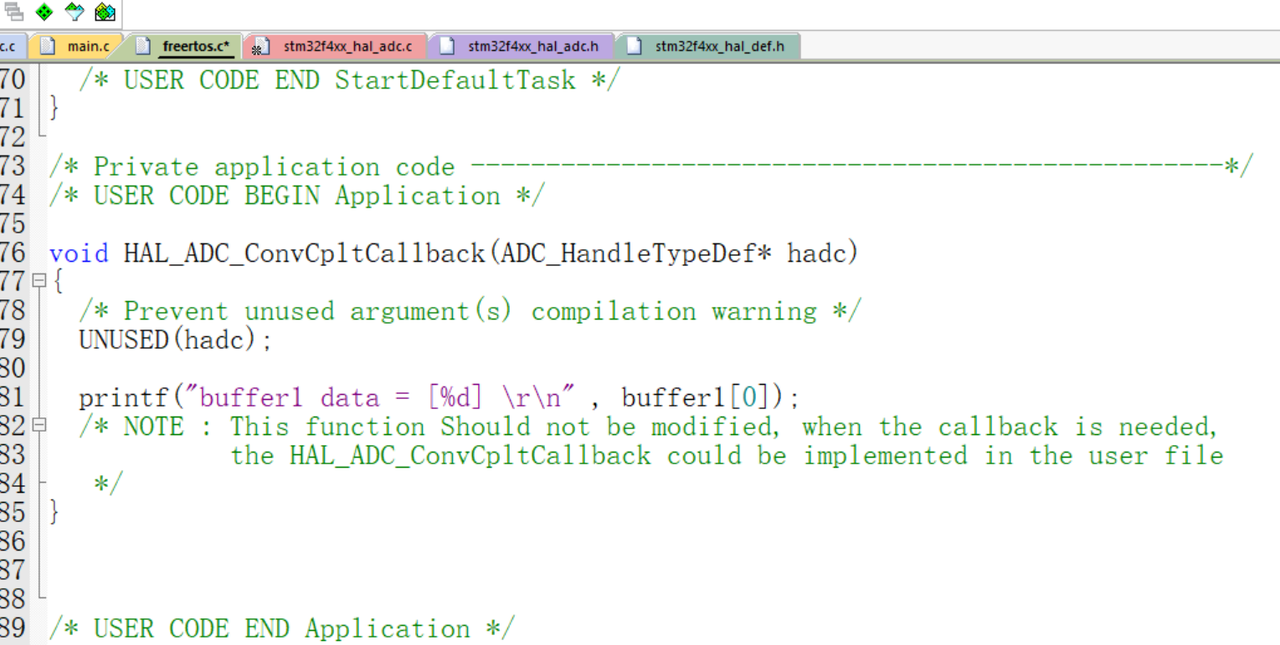
void HAL_ADC_ConvCpltCallback(ADC_HandleTypeDef* hadc)
{
/* Prevent unused argument(s) compilation warning */
UNUSED(hadc);
printf("buffer1 data = [%d] \r\n" , buffer1[0]);
/* NOTE : This function Should not be modified, when the callback is needed,
the HAL_ADC_ConvCpltCallback could be implemented in the user file
*/
}打印一串数据到串口,验证是否可行
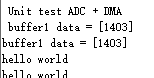
可以看到函数被运行了
HAL_ADC_ErrorCallback()
同样的 , 要设置一个验错机制
(+) In case of transfer Error, HAL_ADC_ErrorCallback() function is executed and user can
add his own code by customization of function pointer HAL_ADC_ErrorCallback
void HAL_ADC_ErrorCallback(ADC_HandleTypeDef *hadc)
{
/* Prevent unused argument(s) compilation warning */
UNUSED(hadc);
/* NOTE : This function Should not be modified, when the callback is needed,
the HAL_ADC_ErrorCallback could be implemented in the user file
*/
printf("ADC trasfer error \r\n");
}3.发送消息对列或任务通知(邮箱)给线程A
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "queue.h"
/* USER CODE END Includes */第一步先包含头文件
* \defgroup xQueueSend xQueueSend
* \ingroup QueueManagement
*/
#define xQueueSend( xQueue, pvItemToQueue, xTicksToWait ) xQueueGenericSend( ( xQueue ), ( pvItemToQueue ), ( xTicksToWait ), queueSEND_TO_BACK )
/**
* queue. h
* <pre>
BaseType_t xQueueOverwrite(
QueueHandle_t xQueue,
const void * pvItemToQueue找到对应函数
xQueueSend( xQueue, pvItemToQueue, xTicksToWait )
第一个形参依旧是句柄
所以要先创建队列 , 再传参进来
第二个形参
P就是指针
v是variables(变量)
传入的是变量的地址
第三个形参是等待时间
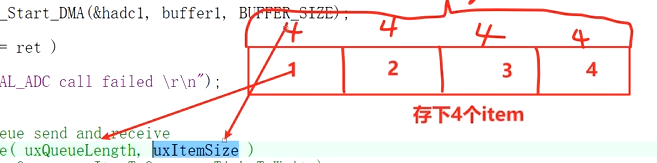
xQueueCreate( uxQueueLength, uxItemSize )
在点h文件里找到队列创建函数
第一个形参是队列的长度
第二个形参是队列里每一个元素的大小
假如一个队列被分成了四份,这个份数就是由第一个形参决定
而分成了四份后的大小就是由第二个形参决定
假设第二个形参是4
那么总的队列长度就是4x4 = 16
xQueue1 = xQueueCreate( QUEUE_LENGTH, // The number of items the queue can hold.
ITEM_SIZE // The size of each item in the queue
&( ucQueueStorage[ 0 ] ), // The buffer that will hold the items in the queue.
&xQueueBuffer ); // The buffer that will hold the queue structure.创建队列使用样板
xQueueReceive()
BaseType_t xQueueReceive( QueueHandle_t xQueue, void * const pvBuffer, TickType_t xTicksToWait )
void StartDefaultTask(void *argument)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN StartDefaultTask */
buffer1 = (uint32_t *)malloc((sizeof(uint32_t)* BUFFER_SIZE));
buffer2 = (uint32_t *)malloc((sizeof(uint32_t)* BUFFER_SIZE));
if(NULL == buffer1)
{
printf("buffer1 malloc failed \r\n");
}
if(NULL == buffer2)
{
printf("buffer2 malloc failed \r\n");
return;
}
printf("buffer1 , buffer2 malloc success\r\n ");
memset(buffer1, 0xff , (sizeof(uint32_t)* BUFFER_SIZE));
memset(buffer2, 0xff , (sizeof(uint32_t)* BUFFER_SIZE));
printf("Unit test ADC + DMA\r\n ");
HAL_StatusTypeDef ret1 = HAL_OK;
HAL_StatusTypeDef ret2 = HAL_OK;
ret1 = HAL_ADC_Start_DMA(&hadc1, buffer1, BUFFER_SIZE);
ret2 = HAL_ADC_Start_DMA(&hadc1, buffer2, BUFFER_SIZE);
if(HAL_OK != ret1)
{
printf("HAL_ADC1 call failed ");
}
if(HAL_OK != ret2)
{
printf("HAL_ADC2 call failed ");
}
//UnitTest Queue send and receive
QueueHandle_t xQueue1 = NULL;
xQueue1 = xQueueCreate(10 , 4 );
if(NULL == xQueue1)
{
printf("Queue create failed \r\n");
return ;
}
uint32_t queue_data_1 = 123;
BaseType_t ret_queue = pdPASS;
ret_queue = xQueueSend( xQueue1, &queue_data_1, 0 );
printf("QueueSend ret_queue = [%ld]\r\n" , ret_queue);
ret_queue = pdPASS;
uint32_t queue_data_2 = 0xff;
ret_queue = xQueueReceive( xQueue1, &queue_data_2, 0 );
printf("xQueueSend ret_queue = [%ld]\r\n" , ret_queue);
printf("xQueueReceive queue_data_2 = [%d]\r\n" , queue_data_2);
/* Infinite loop */
for(;;)
{
printf("hello world \r\n");
//printf("buffer1 data = [%d] \r\n" , buffer1[0]);
//printf("buffer2 data = [%d] \r\n" , buffer2[0]);
osDelay(1000);
}
/* USER CODE END StartDefaultTask */
}xQueueSendFromISR()
当你在中断里面发送这个函数的时候 , 如果有优先级更高的队列接收任务,正在等待队列唤醒,他会在发送队列的过程中立马切换任务, 去执行优先级更高的任务 , 以保证系统的实时性
对于立刻切换的这个动作 , 一定会使用PendSV中断 , 但是这个中断在任何时候优先级都是最低的 , 所以就不可能在我们当前这个DMA里面去中断
所以在这里用这个函数会被卡死
ret_queue = xQueueSend( xQueue1, &dma_pattern_cplt, 0 );
而xQueueSendFromISR这个函数相较于xQueueSend , 在任务切换时做了一个延迟的动作
xHigherPriorityTaskWoken
在发送过程中,这个函数(xQueueSendFromISR)如果发现有更高优先级的任务要切换 , 它将会把xHigherPriorityTaskWoken置为true
如果xHigherPriorityTaskWoken置为true了 , 系统就会暂时先把PendSV置位,等退出了当前中断函数,并且比PendSV更高优先级的中断都结束了,再去执行PendSV
if( xHigherPriorityTaskWoken )
{
taskYIELD ();
}就是这个taskYIELD , 其原理就是会在这里进行一个悬起 ,在离开这个中断之后就会立即响应此悬起 , 从而完成任务切换
注意:
xQueue1 = xQueueCreate(10 , 4 );
if(NULL == xQueue1)
{
printf("Queue create failed \r\n");
return ;
}创建队列的代码要放在ADC启动前 ,ADC一启动,中断立马就产生,但是队列还没创建 , 会出问题
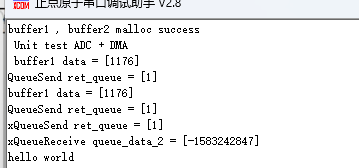
前面实现了ADC的启动 ,并且进入对应中断,发送ADC转换数据到任务1 , 然后任务1进行接收并且打印的功能
但是现在看起来这个转换只能进行一次 , 下面要对代码进行改进,以实现以下功能
4.线程A接收到邮箱后,实现两个任务
-
任务一:将DMA的下次目标Buffer设置为Buffer2
-
任务二:发送消息队列(邮箱)给线程B,然后回到邮箱接收处阻塞住
先将接收移到for循环里
for(;;)
{
printf("hello world \r\n");
ret_queue = xQueueReceive( xQueue1, &queue_data_2, portMAX_DELAY);
printf("xQueueSend ret_queue = [%ld]\r\n" , ret_queue);
printf("xQueueReceive queue_data_2 = [%d]\r\n" , queue_data_2);
// osDelay(1000);
}portMAX_DELAY
阻塞的意义:
如果没有接收到队列信息后,会一直阻塞在这里,知道有中断发送过来后,才会离开
邮箱
xQueue1 = xQueueCreate(10 , 4 );
每个元素的大小是四个字节
回到正题
想要实现接收邮箱的切换实际上很简单 , 设立一个标志位切换就好了
uint32_t DMA_point = 0; //
for(;;)
{
printf("hello world \r\n");
ret_queue = xQueueReceive( xQueue1, &queue_data_2, portMAX_DELAY);
printf("xQueueSend ret_queue = [%ld]\r\n" , ret_queue);
printf("xQueueReceive queue_data_2 = [%d]\r\n" , queue_data_2);
if( 0 == DMA_point)
{
printf("buffer1 data = [%d] \r\n" , buffer1[0]);
HAL_ADC_Start_DMA(&hadc1 , buffer2 , BUFFER_SIZE); //将接收下一个数据的地址换成buffer2
DMA_point = 1 ;
}
else
{
DMA_point = 0 ;
printf("buffer2 data = [%d] \r\n" , buffer2[0]);
HAL_ADC_Start_DMA(&hadc1 , buffer1 , BUFFER_SIZE); //将接收下一个数据的地址换成buffer2
}在point = 0 的时候由buffer1接收
在point = 1 的时候由buffer2接收
在接收完之后对point进行对应的操作,从而切换接收数组
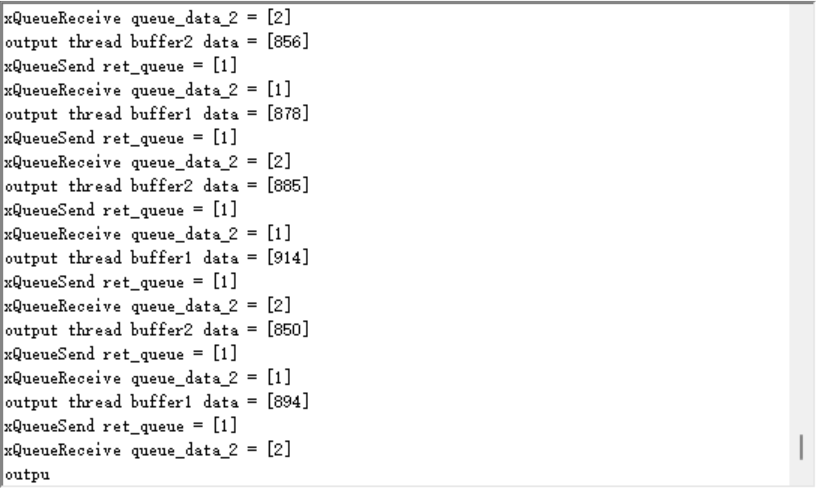
由此完成 可以看到数据非常丝滑的在切换
可以看到数据非常丝滑的在切换
以上实现了DMA的循环接收,但是解包还没完成,只是在接收到数据后打印到了串口 , 现在需要在另一个线程完成解包动作
创建新的线程
osThreadId_t adc_output_TaskHandle;
const osThreadAttr_t adc_output_attributes = {
.name = "adcoutputTask",
.stack_size = 128 * 4,
.priority = (osPriority_t) osPriorityNormal,
};
void adc_output_Task(void *argument);
adc_output_TaskHandle = osThreadNew(adc_output_Task, NULL, &adc_output_attributes);
void adc_output_Task(void *argument)
{
printf("adc_output thread \r\n");
/* Infinite loop */
for(;;)
{
}
/* USER CODE END StartDefaultTask */
}打印串口观察是否创建成功
由需求可知 , 当接收到了数据之后 , 要通知线程B进行解包, 所以要再创建一个队列
#define BUFFER2_READY 0x02
QueueHandle_t xQueue2 = NULL;
void adc_output_Task(void *argument)
{
printf("adc_output thread \r\n");
BaseType_t ret = pdPASS;
uint32_t queue2_receive= BUFFER1_READY;
/* Infinite loop */
for(;;)
{
ret = xQueueReceive( xQueue2, &queue2_receive, portMAX_DELAY);
printf("xQueueSend ret_queue = [%ld]\r\n" , ret);
printf("xQueueReceive queue_data_2 = [%d]\r\n" , queue2_receive);
if(BUFFER1_READY == queue2_receive)
{
printf("output thread buffer1 data = [%d] \r\n" , buffer1[0]);
}
else
{
printf("output thread buffer2 data = [%d] \r\n" , buffer2[0]);
}
}
/* USER CODE END StartDefaultTask */
}
至此代码实现
代码总览
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "FreeRTOS.h"
#include "task.h"
#include "main.h"
#include "cmsis_os.h"
/* Private includes ----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "queue.h"
/* USER CODE END Includes */
/* Private typedef -----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PTD */
#define BUFFER_SIZE 1
uint32_t * buffer1 = NULL;
uint32_t * buffer2 = NULL;
/* USER CODE END PTD */
/* Private define ------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PD */
/* USER CODE END PD */
/* Private macro -------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PM */
#define DMA_ADC_CPLT_INT 0xA1
#define BUFFER1_READY 0x01
#define BUFFER2_READY 0x02
/* USER CODE END PM */
/* Private variables ---------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Variables */
extern ADC_HandleTypeDef hadc1;
extern DMA_HandleTypeDef hdma_adc1;
QueueHandle_t xQueue1 = NULL;
QueueHandle_t xQueue2 = NULL;
uint32_t DMA_point = 0; //
/* USER CODE END Variables */
/* Definitions for defaultTask */
osThreadId_t defaultTaskHandle;
const osThreadAttr_t defaultTask_attributes = {
.name = "defaultTask",
.stack_size = 128 * 4,
.priority = (osPriority_t) osPriorityNormal,
};
osThreadId_t adc_output_TaskHandle;
const osThreadAttr_t adc_output_attributes = {
.name = "adcoutputTask",
.stack_size = 128 * 4,
.priority = (osPriority_t) osPriorityNormal,
};
void adc_output_Task(void *argument);
/* Private function prototypes -----------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN FunctionPrototypes */
/* USER CODE END FunctionPrototypes */
void StartDefaultTask(void *argument);
void MX_FREERTOS_Init(void); /* (MISRA C 2004 rule 8.1) */
/**
* @brief FreeRTOS initialization
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
void MX_FREERTOS_Init(void) {
/* USER CODE BEGIN Init */
/* USER CODE END Init */
/* USER CODE BEGIN RTOS_MUTEX */
/* add mutexes, ... */
/* USER CODE END RTOS_MUTEX */
/* USER CODE BEGIN RTOS_SEMAPHORES */
/* add semaphores, ... */
/* USER CODE END RTOS_SEMAPHORES */
/* USER CODE BEGIN RTOS_TIMERS */
/* start timers, add new ones, ... */
/* USER CODE END RTOS_TIMERS */
/* USER CODE BEGIN RTOS_QUEUES */
/* add queues, ... */
/* USER CODE END RTOS_QUEUES */
/* Create the thread(s) */
/* creation of defaultTask */
defaultTaskHandle = osThreadNew(StartDefaultTask, NULL, &defaultTask_attributes);
adc_output_TaskHandle = osThreadNew(adc_output_Task, NULL, &adc_output_attributes);
/* USER CODE BEGIN RTOS_THREADS */
/* add threads, ... */
/* USER CODE END RTOS_THREADS */
/* USER CODE BEGIN RTOS_EVENTS */
/* add events, ... */
/* USER CODE END RTOS_EVENTS */
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header_StartDefaultTask */
/**
* @brief Function implementing the defaultTask thread.
* @param argument: Not used
* @retval None
*/
/* USER CODE END Header_StartDefaultTask */
void StartDefaultTask(void *argument)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN StartDefaultTask */
DMA_point = 0 ;//DMA_point = 0 往buffer1存入数据
//DMA_point = 1 往buffer2存入数据
buffer1 = (uint32_t *)malloc((sizeof(uint32_t)* BUFFER_SIZE));
buffer2 = (uint32_t *)malloc((sizeof(uint32_t)* BUFFER_SIZE));
if(NULL == buffer1)
{
printf("buffer1 malloc failed \r\n");
}
if(NULL == buffer2)
{
printf("buffer2 malloc failed \r\n");
return;
}
printf("buffer1 , buffer2 malloc success\r\n ");
memset(buffer1, 0xff , (sizeof(uint32_t)* BUFFER_SIZE));
memset(buffer2, 0xff , (sizeof(uint32_t)* BUFFER_SIZE));
printf("Unit test ADC + DMA\r\n ");
xQueue1 = xQueueCreate(10 , 4 );
if(NULL == xQueue1)
{
printf("Queue create failed \r\n");
return ;
}
HAL_StatusTypeDef ret1 = HAL_OK;
HAL_StatusTypeDef ret2 = HAL_OK;
ret1 = HAL_ADC_Start_DMA(&hadc1, buffer1, BUFFER_SIZE);
ret2 = HAL_ADC_Start_DMA(&hadc1, buffer2, BUFFER_SIZE);
if(HAL_OK != ret1)
{
printf("HAL_ADC1 call failed \r\n");
}
if(HAL_OK != ret2)
{
printf("HAL_ADC2 call failed \r\n");
}
xQueue2 = xQueueCreate(10 , 4 );
if(NULL == xQueue2)
{
printf("Queue create failed \r\n");
return ;
}
//HAL_StatusTypeDef ret1 = HAL_OK;
if(HAL_OK != ret1)
{
printf("xQueue2 init failed \r\n");
}
//UnitTest Queue send and receive
BaseType_t ret_queue = pdPASS;
uint32_t queue_data_2 = 0xff;
uint32_t queue_pattern= BUFFER1_READY;
/* Infinite loop */
for(;;)
{
printf("hello world \r\n");
ret_queue = xQueueReceive( xQueue1, &queue_data_2, portMAX_DELAY);
printf("xQueueSend ret_queue = [%ld]\r\n" , ret_queue);
printf("xQueueReceive queue_data_2 = [%d]\r\n" , queue_data_2);
if( 0 == DMA_point)
{
//printf("buffer1 data = [%d] \r\n" , buffer1[0]);
uint32_t queue_pattern= BUFFER1_READY;
ret_queue = xQueueSend(xQueue2 ,&queue_pattern, portMAX_DELAY);
printf("xQueueSend to xQueue2 ret_queue = [%ld]\r\n" , ret_queue);
HAL_ADC_Start_DMA(&hadc1 , buffer2 , BUFFER_SIZE); //将接收下一个数据的地址换成buffer2
DMA_point = 1 ;
}
else
{
DMA_point = 0 ;
printf("buffer2 data = [%d] \r\n" , buffer2[0]);
uint32_t queue_pattern= BUFFER2_READY;
ret_queue = xQueueSend(xQueue2 ,&queue_pattern, portMAX_DELAY);
printf("xQueueSend to xQueue2 ret_queue = [%ld]\r\n" , ret_queue);
HAL_ADC_Start_DMA(&hadc1 , buffer1 , BUFFER_SIZE); //将接收下一个数据的地址换成buffer2
}
// osDelay(1000);
}
/* USER CODE END StartDefaultTask */
}
/* Private application code --------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Application */
void adc_output_Task(void *argument)
{
printf("adc_output thread \r\n");
BaseType_t ret = pdPASS;
uint32_t queue2_receive= BUFFER1_READY;
/* Infinite loop */
for(;;)
{
ret = xQueueReceive( xQueue2, &queue2_receive, portMAX_DELAY);
printf("xQueueSend ret_queue = [%ld]\r\n" , ret);
printf("xQueueReceive queue_data_2 = [%d]\r\n" , queue2_receive);
if(BUFFER1_READY == queue2_receive)
{
printf("output thread buffer1 data = [%d] \r\n" , buffer1[0]);
}
else
{
printf("output thread buffer2 data = [%d] \r\n" , buffer2[0]);
}
}
/* USER CODE END StartDefaultTask */
}
void HAL_ADC_ConvCpltCallback(ADC_HandleTypeDef* hadc)
{
/* Prevent unused argument(s) compilation warning */
UNUSED(hadc);
/* NOTE : This function Should not be modified, when the callback is needed,
the HAL_ADC_ConvCpltCallback could be implemented in the user file
*/
printf("buffer1 data = [%d] \r\n" , buffer1[0]);
BaseType_t xHigherPriorityTaskWoken;//PendSV悬起置位为true
xHigherPriorityTaskWoken = pdFALSE;//初始化
uint32_t dma_pattern_cplt = DMA_ADC_CPLT_INT;
BaseType_t ret_queue = pdPASS;
ret_queue = xQueueSendFromISR( xQueue1, &dma_pattern_cplt, &xHigherPriorityTaskWoken );
if( xHigherPriorityTaskWoken )
{
taskYIELD ();
}
printf("QueueSend ret_queue = [%ld]\r\n" , ret_queue);
}
void HAL_ADC_ErrorCallback(ADC_HandleTypeDef *hadc)
{
/* Prevent unused argument(s) compilation warning */
UNUSED(hadc);
/* NOTE : This function Should not be modified, when the callback is needed,
the HAL_ADC_ErrorCallback could be implemented in the user file
*/
printf("ADC trasfer error \r\n");
}
/* USER CODE END Application */
























 2017
2017

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








