Java ArrayList源码解析(基于JDK 12,对比JDK 8)
自从接触到ArrayList以来,一直觉得很方便,但是从来没有系统、全面的学习了解过ArraryList的实现原理。最近学习了一下ArrayList的源码学习一下,顺便记录一下,防止后面遗忘太快。现在的jdk版本更新比以前快了很多,截止发文已经更新到了JDK 15了,本文查看的源码是JDK 12的,native 方法阅读的是jdk 8的,也有对比jdk 12 与jdk 8的部分源码.
重要的事情说三遍,
本文查看的源码的jdk 12,部分源码对比jdk 8!!!
本文查看的源码的jdk 12,部分源码对比jdk 8!!!
本文查看的源码的jdk 12,部分源码对比jdk 8!!!
阅读前须知:
源码中使用的 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, s - index)与 Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class)这两个方法是属于浅拷贝,关于浅拷贝以及System.arraycopy方法的底层C/C++方法可以看这两篇文章:
1、浅拷贝与深拷贝:https://www.cnblogs.com/shakinghead/p/7651502.html
2、System.arraycopy方法的底层C/C++方法:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/fu_zhongyuan/article/details/88663818
我在网上找了一下该方法浅拷贝的指向原理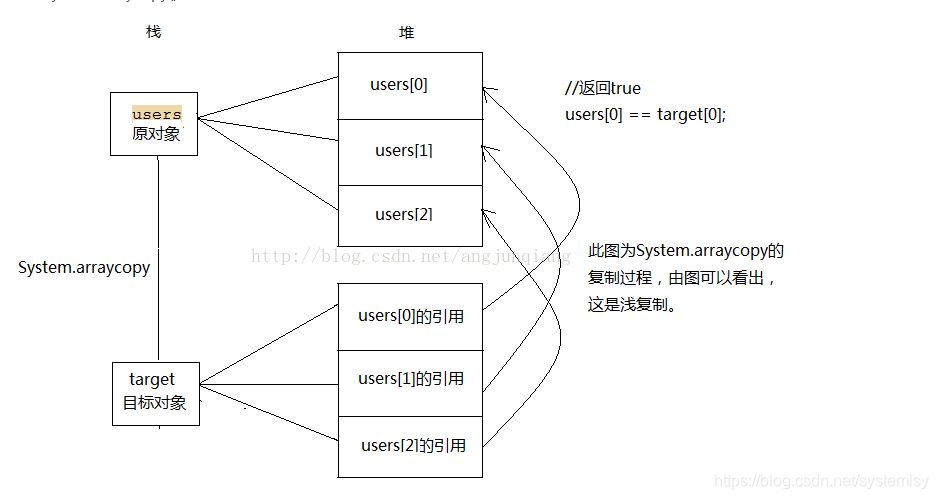
一、 ArrayList初始化
ArrayList有三种初始化方法:
1、初始化一种指定集合大小的空ArrayList;
2、初始化一个空的ArrayList;
3、初始化一个含有指定元素的ArrayLsit。
具体源码与注释一起放在下面了
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {
};
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {
};
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// defend against c.toArray (incorrectly) not returning Object[]
// (see e.g. https://bugs.openjdk.java.net/browse/JDK-6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
然后自己写了一个测试demo,试了一下这三个初始化方法,发现挺好用的
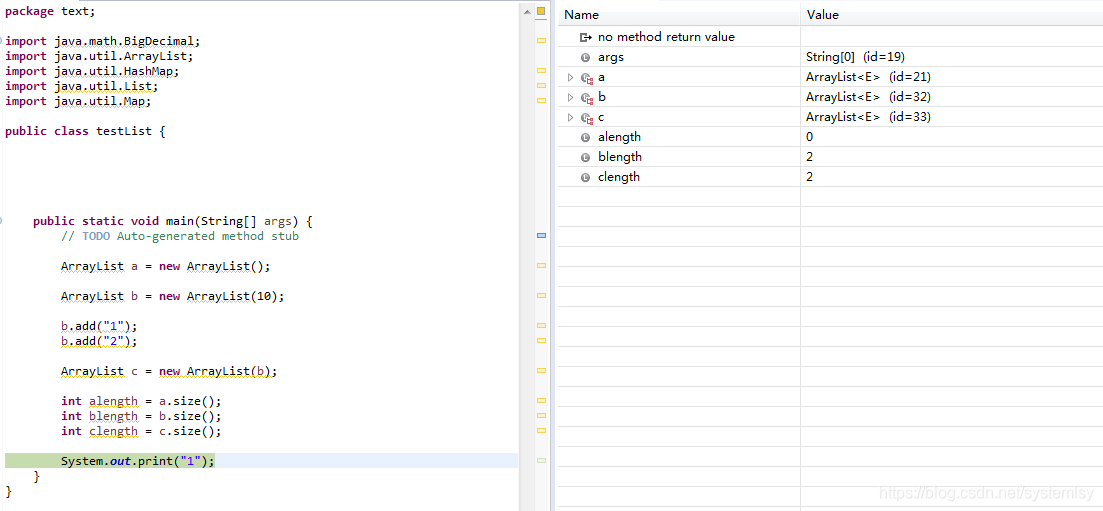
ArrayList常用方法
常用的方法无非就是增删改查
get( )与set()
改查这两个方法就很简单了,简单的先放在前面说
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with
* the specified element.
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
ArrayList新增
从下面源码可以看出,我们平时喜欢的使用的add(E e)其实调用的是上面的实现方法add(E e, Object[] elementData, int s),这里需要提的一点事add(int index, E element)这种指定元素、数组下标的新增方法。在这个方法里面使用了两个方法:grow()方法和arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length),前者将数组容量扩大了一位,后者调用本地的native方法。
相关源码附在下面了:
/**
* This helper method split out from add(E) to keep method
* bytecode size under 35 (the -XX:MaxInlineSize default value),
* which helps when add(E) is called in a C1-compiled loop.
*/
private void add(E e, Object[] elementData, int s) {
if (s == elementData.length)
elementData = grow();
elementData[s] = e;
size = s + 1;
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
add(e, elementData, size);
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
modCount++;
final int s;
Object[] elementData;
if ((s = size) == (elementData = this.elementData).length)
elementData = grow();
System.arraycopy(elementData, index,
elementData, index + 1,
s - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size = s + 1;
}
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
* @throws OutOfMemoryError if minCapacity is less than zero
*/
private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) {
return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData,
newCapacity(minCapacity));
}
private Object[] grow() {
return grow(size + 1);
}
@HotSpotIntrinsicCandidate
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos,
int length);
addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)与 addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) 方法
这两个方法都是可以直接添加集合的方法,不同的是一个是尾部添加,一个是从索引处开始添加,源码贴在下面了。对比了JDK12 与JDK 8发现这两个方法没有做修改。
/**
* Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of
* this list, in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's Iterator. The behavior of this operation is
* undefined if the specified collection is modified while the operation
* is in progress. (This implies that the behavior of this call is
* undefined if the specified collection is this list, and this
* list is nonempty.)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
modCount++;
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Object[] elementData;
final int s;
if (numNew > (elementData = this.elementData).length - (s = size))
elementData = grow(s + numNew);
System.arraycopy(a, 




 本文详细解析了Java ArrayList在JDK 12中的源码,对比了JDK 8的部分内容,涵盖了初始化、增加、删除、查找和修改等方法。特别讨论了`System.arraycopy`和`Arrays.copyOf`的浅拷贝原理,并通过实例演示了ArrayList的操作流程。
本文详细解析了Java ArrayList在JDK 12中的源码,对比了JDK 8的部分内容,涵盖了初始化、增加、删除、查找和修改等方法。特别讨论了`System.arraycopy`和`Arrays.copyOf`的浅拷贝原理,并通过实例演示了ArrayList的操作流程。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








