耦合问题
耦合是程序之间的依赖程度,确切一点说就是上层代码对下层代码的依赖程度,依赖程度越高说明耦合程度越高,在开发当中耦合当然是越低越好,降低耦合的方案有很多种,而且这些方案结合使用才能达到解决耦合的最大效果.其中使用接口就是解耦合的方案之一.
就拿数据库操作来说,如果没有定义一个标准(接口)让数据库操作类按照这标准来开发,那么当程序需要更换数据库时,主方法(也可以理解为客户端)中的代码就需要大量修改.这样就是客户端对下层代码的依赖程度很高.
当我们定义一个标准(接口)让数据库操作类来实现这个接口时,就会在一定程度上降低耦合.
定义一个操作数据库的类的标准(接口)
public interface IDAO {
/**
*统计数据量的方法
* @param kw
*@return
*@throws Exception
*/
public int selectCount(String kw) throws Exception;
让操作数据库的类去实现标准
public class OracleDAOImpl implements IDAO {
1/取得连
private static Connection conn=Connectionuitl.getConnection().
@overridepublic int selectCount(string kw) throws Exception {
string sgl="SELECT COUNT (*)"FROM emp"WHERE ename LIKE ?";
try {
Preparedstatement pst =conn.preparestatement(sql);pst.setobject(1, "%"+kw+"%");
ResultSet rst=pst.executeQuery();
rst.next();//i指针往下移动才能获取结果集中的数据
return rst.getInt(1);
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
Connectionuitl.cLose(conn);
}
return 0;
public class SglServerDAOImpl implements IDAO {
//取得连接
private static Connection conn = ConnectionUit1.getConnection();
@override
publicint selectCount(string kw) {
string sql="SELECT COUNT (*).FROM emp"WHERE ename LIKE ?";
try {
Preparedstatement pst = conn.preparestatement(sql);
pst.setobiect(1, "%"+kw+"%");
ResultSet rst=pst.executequery();
rst.next();//i指针往下移动才能获取结果集中的数据
return rst.getInt(1);
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printstackTrace();
}finally{
Connectionuitl.clase(conn);
}
return 0;
public class ClientTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//操作Oralce数据库中的数据
IDAO dao=new OracleDAOImpl();
dao.selectCount("A");
}
}
此时发现如果数据库换了,那么客户端的代码也不需要做大的改动,在一定程度上降低了代码的耦合度,但是耦合还是存在,因为还是要修改客户端中的代码,如果要继续降低这种耦合就需要使用到工厂设计模式,如果使用了工厂设计模式,那么"new oracleDAOImpl()"的操作形式就不会在客户端出现了,而是转移到工厂类中了,进一步降低了耦合度,但是还是需回上要微小的修改,如果还要继续降低耦合度,就要使用到IOC容器(叫做控制反转容器).
程序的分层
我们开发的最终目的是让客户从浏览器端或者APP操作数据,实现这个功能大致需要访问数据库、业务算法处理、请求的分发处理,这三个功能,而这三个功能的代码我们可以放到一起这样也是能实现的,但是存在一个问题,如果放到一起了代码变得臃肿,不方便维护,于是就出现了代码分层的概念,把代码按照功能分为三层,这种代码的组织架构形式叫做MVC模式。什么是MVC模式就是按照程序的功能将他们分成三个层,分别是Model层(模型层)、View层(显示层)、Controller层(控制层)。
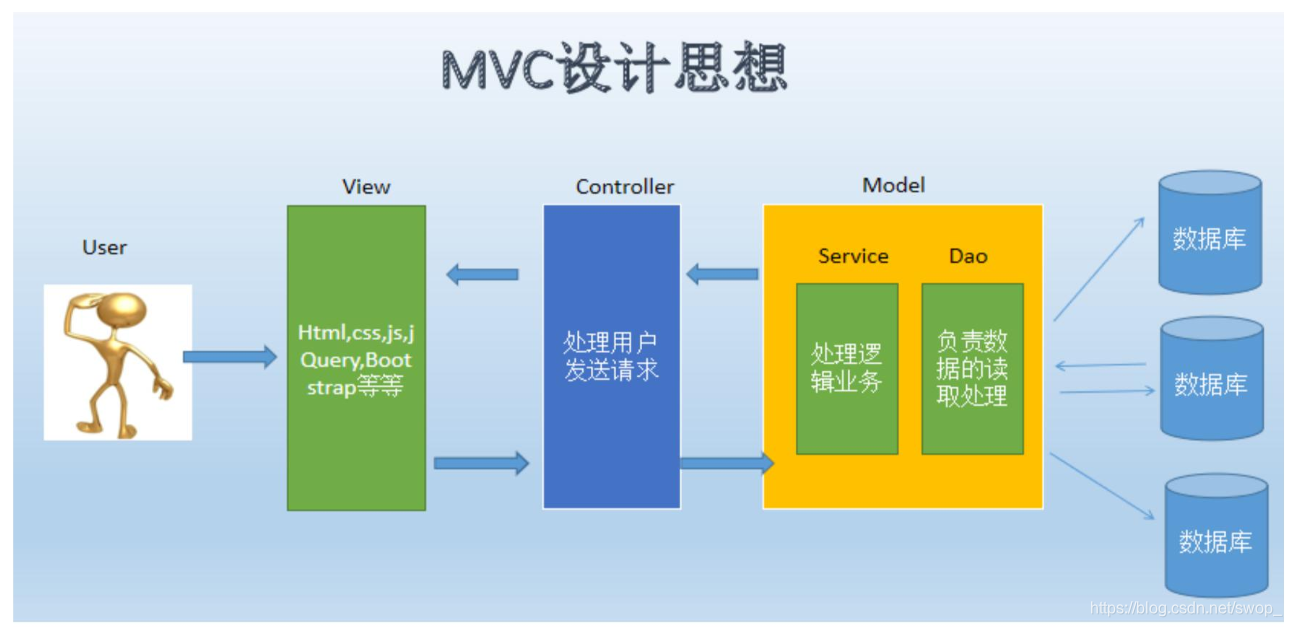
Modle层: Modle层又可以细分为两层,分别是dao层、service层,这两层的主要功能:
-
service层:主要负责一些业务处理,比如取得连接、关闭数据库连接、事务回滚或者一些复杂的逻辑业务处理就放到service
-
dao层:负责访问数据库进行数据的操作,取得结果集,之后将结果集中的数据取出封装到vo类对象之后返回给service层。
Controller层:叫做控制层,主要的功能是处理用户发送的请求。
View层:叫做显示层,主要是负责现实数据。
分层的直接体现是将不同功能的代码保存到不同的包中
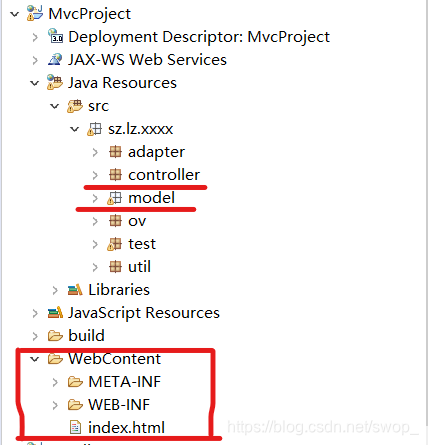
代码的调用顺序为:view—>controller—>service—>dao,不能上层代码对下层代码的依赖程度过高,要满足这个要求救需要为每一层定义标准(接口)
dao层的设计
就用emp数据包作为例子设计出emp数据包的操作类,首先定义出自己的操作标准(接口).主要目的是为了解耦.
创建出Emp对象(放到vo包中)
package sz.lz.xxxx.ov;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
public class Emp implements Serializable {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Integer empno;
private String ename;
private String job;
private Integer mgr;
private Date hiredate;
private Double sal;
private Double comm;
private Integer deptno;
public Emp() {
}
public Emp(Integer empno, String ename, String job, Integer mgr, Date hiredate, Double sal, Double comm,
Integer deptno) {
this.empno = empno;
this.ename = ename;
this.job = job;
this.mgr = mgr;
this.hiredate = hiredate;
this.sal = sal;
this.comm = comm;
this.deptno = deptno;
}
public Integer getEmpno() {
return empno;
}
public void setEmpno(Integer empno) {
this.empno = empno;
}
public String getEname() {
return ename;
}
public void setEname(String ename) {
this.ename = ename;
}
public String getJob() {
return job;
}
public void setJob(String job) {
this.job = job;
}
public Integer getMgr() {
return mgr;
}
public void setMgr(Integer mgr) {
this.mgr = mgr;
}
public Date getHiredate() {
return hiredate;
}
public void setHiredate(Date hiredate) {
this.hiredate = hiredate;
}
public Double getSal() {
return sal;
}
public void setSal(Double sal) {
this.sal = sal;
}
public Double getComm() {
return comm;
}
public void setComm(Double comm) {
this.comm = comm;
}
public Integer getDeptno() {
return deptno;
}
public void setDeptno(Integer deptno) {
this.deptno = deptno;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((comm == null) ? 0 : comm.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((deptno == null) ? 0 : deptno.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((empno == null) ? 0 : empno.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((ename == null) ? 0 : ename.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((hiredate == null) ? 0 : hiredate.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((job == null) ? 0 : job.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((mgr == null) ? 0 : mgr.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((sal == null) ? 0 : sal.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Emp other = (Emp) obj;
if (comm == null) {
if (other.comm != null)
return false;
} else if (!comm.equals(other.comm))
return false;
if (deptno == null) {
if (other.deptno != null)
return false;
} else if (!deptno.equals(other.deptno))
return false;
if (empno == null) {
if (other.empno != null)
return false;
} else if (!empno.equals(other.empno))
return false;
if (ename == null) {
if (other.ename != null)
return false;
} else if (!ename.equals(other.ename))
return false;
if (hiredate == null) {
if (other.hiredate != null)
return false;
} else if (!hiredate.equals(other.hiredate))
return false;
if (job == null) {
if (other.job != null)
return false;
} else if (!job.equals(other.job))
return false;
if (mgr == null) {
if (other.mgr != null)
return false;
} else if (!mgr.equals(other.mgr))
return false;
if (sal == null) {
if (other.sal != null)
return false;
} else if (!sal.equals(other.sal))
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp [empno=" + empno + ", ename=" + ename + ", job=" + job + ", mgr=" + mgr + ", hiredate=" + hiredate
+ ", sal=" + sal + ", comm=" + comm + ", deptno=" + deptno + "]";
}
}
1.简单java类中的基本数据类型必须是其包装类
2.要实现Serializable接口,方便以后程序的扩展
写出dao层Emp数据表的接口
public interface IEmpDao{
/**
* 增加雇员数据
* @param v 保存了插入数据的对象
* @return 插入的行数
* @throws Exception
*/
public int insert(Emp v) throws Exception;
/**
* 修改数据
* @param v 保存了要修改的对象的数据
* @return 修改的行数
* @throws Exception
*/
public int update(Emp v) throws Exception;
/**
* 根据编号删除数据
* @param k 编号
* @return 删除的行数
* @throws Exception
*/
public int deldeteById(Integer k) throws Exception;
/**
* 批量删除
* @param ids 保存了需要删除数据的编号集合
* @return 删除的行数
* @throws Exception
*/
public int deldeteBatch(List<Integer> ids) throws Exception;
/**
* 根据编号查询数据
* @param k 编号
* @return 如果有数据则返回对象没有则为空
* @throws Exception
*/
public V selectById(Integer k) throws Exception;
/**
* 根据姓名模糊分页查询
* @param kw 模糊查询关键字
* @param cp 当前页
* @param ls 每页显示的数据量
* @return 返回保存有对象的集合
* @throws Exception
*/
public List<Emp> selectSpliAll(String kw,Integer cp, Integer ls) throws Exception;
/**
* 统计数据量
* @param kw 模糊查询关键字
* @return 返回查询到的数据量
* @throws Exception
*/
public int selectCount(String kw) throws Exception;
}
定义出接口的实现类
package sz.lz.xxxx.model.dao.impl;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import sz.lz.xxxx.model.dao.IEmpDao;
import sz.lz.xxxx.ov.Emp;
import sz.lz.xxxx.util.DButil;
public class EmpDaoimpl implements IEmpDao {
private Connection conn;
public EmpDaoimpl() {}
public EmpDaoimpl(Connection conn) {
this.conn = conn;
}
public Connection getConn() {
return conn;
}
public void setConn(Connection conn) {
this.conn = conn;
}
@Override
public int insert(Emp emp) throws Exception {
String sql ="INSERT INTO emp(empno,ename,job,sal,comm,hiredate,mgr,deptno) VALUES(?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?)";
return DButil.save(conn, sql, emp, false);
}
@Override
public int update(Emp emp) throws Exception {
String sql ="UPDATE emp SET ename=?,job=?,mgr=?,sal=?,comm=?,deptno=? WHERE empno =?";
return DButil.uperDate(conn, sql,emp);
}
@Override
public int deldeteById(Integer k) throws Exception {
return DButil.DeleteDate(conn, "empno","emp",k);
}
@Override
public int deldeteBatch(List<Integer> ids) throws Exception {
return DButil.DeleteDate(conn, "empno", "emp", ids);
}
@Override
public Emp selectById(Integer k) throws Exception {
String sql = "SELECT * FROM emp WHERE empno=?";
Emp emp=null;
ArrayList<Object> selectDate = DButil.selectDate(conn, sql, Emp.class, k);
for(Object obj:selectDate) {
emp = (Emp) obj;
}
return emp;
}
@Override
public List<Emp> selectSpliAll(String kw, Integer cp, Integer ls) throws Exception {
return DButil.selectSplistAll(kw, cp, ls,conn);
}
@Override
public int selectCount(String kw) throws Exception {
String sql = "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM emp WHERE ename LIKE ? ";
kw = "%"+kw+"%";
return DButil.countDate(conn, sql, kw);
}
}
创建dept表的数据访问接口
此时发现了两个接口的方法的形式是一样的,只是参数类型不同,其实上在开发中肯定会存在多张数据表,每张数据表都可能有自己对应的数据访问层(dao)的接口,但是操作的方法都差不多,只是参数不一样而已,这样就出现了形式一样的代码但是要重复的去编写,为了解决重复的代码可以将这些形式相同的方法提取到一个父接口中,子接口只需要继承这个父接口即可,但是参数是不一样的,所以在定义父接口的时候使用泛型来解决。
定义公共的父接口
package sz.lz.xxxx.model.dao;
import java.util.List;
/**
*
* @param <V> 表示应的实体类的类
* @param <K> 实体类对应的数据表中的主键值得类型
*/
public interface IBaseDao<V, K> {
/**
* 增加雇员数据
* @param v 保存了插入数据的对象
* @return 插入的行数
* @throws Exception
*/
public int insert(V v) throws Exception;
/**
* 修改数据
* @param v 保存了要修改的对象的数据
* @return 修改的行数
* @throws Exception
*/
public int update(V v) throws Exception;
/**
* 根据编号删除数据
* @param k 编号
* @return 删除的行数
* @throws Exception
*/
public int deldeteById(K k) throws Exception;
/**
* 批量删除
* @param ids 保存了需要删除数据的编号集合
* @return 删除的行数
* @throws Exception
*/
public int deldeteBatch(List<K> ids) throws Exception;
/**
* 根据编号查询数据
* @param k 编号
* @return 如果有数据则返回对象没有则为空
* @throws Exception
*/
public V selectById(K k) throws Exception;
/**
* 根据姓名模糊分页查询
* @param kw 模糊查询关键字
* @param cp 当前页
* @param ls 每页显示的数据量
* @return 返回保存有对象的集合
* @throws Exception
*/
public List<V> selectSpliAll(String kw,Integer cp, Integer ls) throws Exception;
/**
* 统计数据量
* @param kw 模糊查询关键字
* @return 返回查询到的数据量
* @throws Exception
*/
public int selectCount(String kw) throws Exception;
}
之后使用子类继承公共的接口,多个子接口中就不会再编写类似的方法,而是直接继承父接口的方法
package sz.lz.xxxx.model.dao;
import sz.lz.xxxx.ov.Dept;
public interface IDeptDao extends IBaseDao<Dept,Integer> {
//除了继承的方法还可以定义自己特有的方法
}
package sz.lz.xxxx.model.dao;
import sz.lz.xxxx.ov.Emp;
public interface IEmpDao extends IBaseDao<Emp,Integer>{
//除了继承的方法还可以定义自己特有的方法
}
然后在让实现类实现相应的接口
适配器模式的使用
在dao层开发中发现了所有的实现类都要覆写父接口中的所有方法,但是有可能父接口中的某些方法对于当前的实现类无用的(并不需要这个方法的功能),此时就可以使用适配器设计模式让实现子类可以选择性的覆写父接口中的方法。
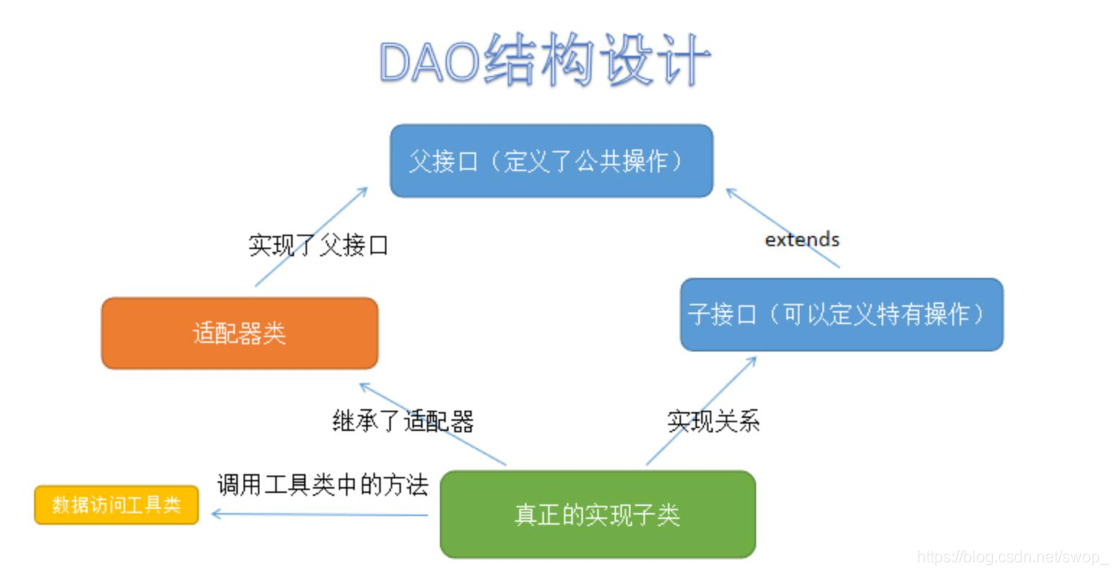
定义出适配器类
package sz.lz.xxxx.adapter;
import java.util.List;
import sz.lz.xxxx.model.dao.IBaseDao;
public class DaoAdapter<V,K> implements IBaseDao<V, K> {
@Override
public int insert(V v) throws Exception {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int update(V v) throws Exception {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int deldeteById(K k) throws Exception {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int deldeteBatch(List<K> ids) throws Exception {
return 0;
}
@Override
public V selectById(K k) throws Exception {
return null;
}
@Override
public List<V> selectSpliAll(String kw, Integer cp, Integer ls) throws Exception {
return null;
}
@Override
public int selectCount(String kw) throws Exception {
return 0;
}
}
改变子类的继承结构
package sz.lz.xxxx.model.dao.impl;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import sz.lz.xxxx.adapter.DaoAdapter;
import sz.lz.xxxx.model.dao.IEmpDao;
import sz.lz.xxxx.ov.Emp;
import sz.lz.xxxx.util.DButil;
//
public class EmpDaoimpl extends DaoAdapter<Emp,Integer> implements IEmpDao {
private Connection conn;
public EmpDaoimpl() {}
public EmpDaoimpl(Connection conn) {
this.conn = conn;
}
public Connection getConn() {
return conn;
}
public void setConn(Connection conn) {
this.conn = conn;
}
@Override
public int insert(Emp emp) throws Exception {
String sql ="INSERT INTO emp(empno,ename,job,sal,comm,hiredate,mgr,deptno) VALUES(?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?)";
return DButil.save(conn, sql, emp, false);
}
@Override
public int update(Emp emp) throws Exception {
String sql ="UPDATE emp SET ename=?,job=?,mgr=?,sal=?,comm=?,deptno=? WHERE empno =?";
return DButil.uperDate(conn, sql,emp);
}
@Override
public int deldeteById(Integer k) throws Exception {
return DButil.DeleteDate(conn, "empno","emp",k);
}
}
发现子类不需要强制性的去覆写父接口中的方法,而可以根据需求选择性的去覆写,使得代码变得灵活.
service层的设计
之前设计了数据层(dao层),同时也说过mvc设计模式,其中M表示Mode层(模型层),模型层包括了数据层(dao)和业务层(servive).业务层最终是被控制层调用了,此时如果修改了业务层的代码那么控制层的代码也随之要修改,耦合度较高,要解决这样的问题还是需要为业务层定义出一套标准(个接口)
定义server层的接口
package sz.lz.xxxx.model.service;
import java.util.Map;
import sz.lz.xxxx.ov.Emp;
public interface IEmpService {
/**
* 实现数据的增加调用 dao层的insert方法
* @param vo 包含了要插入数据的对象的
* @return 是否成功
* @throws Exception
*/
public boolean addEmp(Emp vo) throws Exception;
/**
* 实现数据的增加调用 dao层的update方法
* @param vo 包含了要修改数据的对象的
* @return 是否成功
* @throws Exception
*/
public boolean editEmp(Emp vo) throws Exception;
/**
* 根据编号删除数据调用 dao层的delete方法
* @param id 需要删除数据的ID
* @return 是否成功
* @throws Exception
*/
public boolean removeEmpById(Integer id) throws Exception;
/**
* 根据编号查找数据调用 dao层的select方法
* @param k
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public Emp findEmpById(Integer k) throws Exception;
/**
* 实现模糊分页查询调用dao层的方法:
* 调用selectSplitAll() 取得雇员信息集合
* 调用SelectCount() 取得查询到的数据量
*
* @param kw 模糊查询关键字
* @param cp 当前页
* @param ls 每页显示的数据量
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public Map<String , Object> findAllSplit(String kw ,Integer cp,Integer ls)throws Exception;
}
定义server层的接口的实现类
package sz.lz.xxxx.model.service.impl;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import sz.lz.xxxx.model.dao.impl.EmpDaoimpl;
import sz.lz.xxxx.model.service.IEmpService;
import sz.lz.xxxx.ov.Emp;
import sz.lz.xxxx.util.DruidConnectionPool;
public class EmpServiceimpl implements IEmpService{
private Connection conn = DruidConnectionPool.getConnection();
private EmpDaoimpl emp = new EmpDaoimpl(conn);
public EmpServiceimpl() {
}
public EmpServiceimpl(Connection conn) {
this.conn = conn;
}
@Override
public boolean addEmp(Emp vo) throws Exception {
try {
return emp.insert(vo)>0;
} catch (Exception e) {
}finally {
DruidConnectionPool.Close(conn);
}
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean editEmp(Emp vo) throws Exception {
try {
return emp.update(vo)>0;
} catch (Exception e) {
}finally {
DruidConnectionPool.Close(conn);
}
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean removeEmpById(Integer id) throws Exception {
try {
return emp.deldeteById(id)>0;
} catch (Exception e) {
}finally {
DruidConnectionPool.Close(conn);
}
return false;
}
@Override
public Emp findEmpById(Integer k) throws Exception {
try {
return emp.selectById(k);
} catch (Exception e) {
}finally {
DruidConnectionPool.Close(conn);
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Map<String, Object> findAllSplit(String kw, Integer cp, Integer ls) throws Exception {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
try {
map.put("empList", emp.selectSpliAll(kw, cp, ls));
int count = emp.selectCount(kw);
int allpages =(int)Math.ceil(count*1.0/ls) ;
map.put("allpages", allpages);
map.put("count", count);
map.put("cp", cp);
map.put("ls", ls);
map.put("kw", kw);
} catch (Exception e) {
}finally {
DruidConnectionPool.Close(conn);
}
return map;
}
}
最后结构大致如下
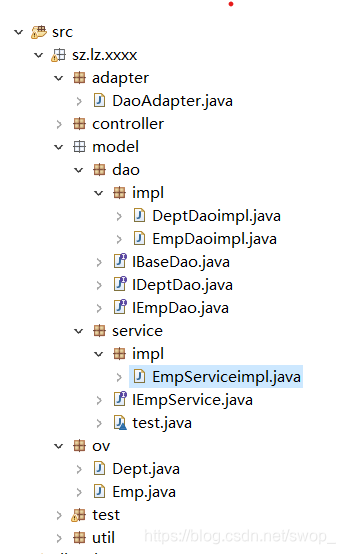





 博客围绕程序开发展开,先介绍耦合问题,指出使用接口、工厂设计模式和IOC容器可降低耦合。接着阐述程序分层概念,采用MVC模式将代码按功能分为Model、View、Controller层,其中Model层又分dao和service层。还介绍了dao层和解耦设计,以及service层的接口设计。
博客围绕程序开发展开,先介绍耦合问题,指出使用接口、工厂设计模式和IOC容器可降低耦合。接着阐述程序分层概念,采用MVC模式将代码按功能分为Model、View、Controller层,其中Model层又分dao和service层。还介绍了dao层和解耦设计,以及service层的接口设计。
















 7万+
7万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








