主要是自己在项目中(中小型项目) 有支付下单业务(只是办理VIP,没有涉及到商品库存),目前用户量还没有上来,目前没有出现问题,但是想到如果用户量变大,下单并发量变大,可能会出现一系列的问题,趁着空闲时间,做了这个demo测试相关问题。
可能遇到的问题如下:
1.订单重复
2.高并发下,性能变慢
解决方式:ThreadPoolExecutor线程池 + Queue队列
开发工具:IDEA 15
1.首先是springBoot的项目框架如下
2.业务测试流程涉及的类,如下
BusinessThread 类
package com.springboot.demo.Threads;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2018/5/9.
*/
@Component
@Scope("prototype")//spring 多例
public class BusinessThread implements Runnable{
private String acceptStr;
public BusinessThread(String acceptStr) {
this.acceptStr = acceptStr;
}
public String getAcceptStr() {
return acceptStr;
}
public void setAcceptStr(String acceptStr) {
this.acceptStr = acceptStr;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//业务操作
System.out.println("多线程已经处理订单插入系统,订单号:"+acceptStr);
//线程阻塞
/*try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("多线程已经处理订单插入系统,订单号:"+acceptStr);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}*/
}
}
TestThreadPoolManager 类
package com.springboot.demo.Threads;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2018/5/10.
*/
@Component
public class TestThreadPoolManager implements BeanFactoryAware {
//用于从IOC里取对象
private BeanFactory factory; //如果实现Runnable的类是通过spring的application.xml文件进行注入,可通过 factory.getBean()获取,这里只是提一下
// 线程池维护线程的最少数量
private final static int CORE_POOL_SIZE = 2;
// 线程池维护线程的最大数量
private final static int MAX_POOL_SIZE = 10;
// 线程池维护线程所允许的空闲时间
private final static int KEEP_ALIVE_TIME = 0;
// 线程池所使用的缓冲队列大小
private final static int WORK_QUEUE_SIZE = 50;
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
factory = beanFactory;
}
/**
* 用于储存在队列中的订单,防止重复提交,在真实场景中,可用redis代替 验证重复
*/
Map<String, Object> cacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 订单的缓冲队列,当线程池满了,则将订单存入到此缓冲队列
*/
Queue<Object> msgQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Object>();
/**
* 当线程池的容量满了,执行下面代码,将订单存入到缓冲队列
*/
final RejectedExecutionHandler handler = new RejectedExecutionHandler() {
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
//订单加入到缓冲队列
msgQueue.offer(((BusinessThread) r).getAcceptStr());
System.out.println("系统任务太忙了,把此订单交给(调度线程池)逐一处理,订单号:" + ((BusinessThread) r).getAcceptStr());
}
};
/**创建线程池*/
final ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(CORE_POOL_SIZE, MAX_POOL_SIZE, KEEP_ALIVE_TIME, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue(WORK_QUEUE_SIZE), this.handler);
/**将任务加入订单线程池*/
public void addOrders(String orderId){
System.out.println("此订单准备添加到线程池,订单号:" + orderId);
//验证当前进入的订单是否已经存在
if (cacheMap.get(orderId) == null) {
cacheMap.put(orderId, new Object());
BusinessThread businessThread = new BusinessThread(orderId);
threadPool.execute(businessThread);
}
}
/**
* 线程池的定时任务----> 称为(调度线程池)。此线程池支持 定时以及周期性执行任务的需求。
*/
final ScheduledExecutorService scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
/**
* 检查(调度线程池),每秒执行一次,查看订单的缓冲队列是否有 订单记录,则重新加入到线程池
*/
final ScheduledFuture scheduledFuture = scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//判断缓冲队列是否存在记录
if(!msgQueue.isEmpty()){
//当线程池的队列容量少于WORK_QUEUE_SIZE,则开始把缓冲队列的订单 加入到 线程池
if (threadPool.getQueue().size() < WORK_QUEUE_SIZE) {
String orderId = (String) msgQueue.poll();
BusinessThread businessThread = new BusinessThread(orderId);
threadPool.execute(businessThread);
System.out.println("(调度线程池)缓冲队列出现订单业务,重新添加到线程池,订单号:"+orderId);
}
}
}
}, 0, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
/**获取消息缓冲队列*/
public Queue<Object> getMsgQueue() {
return msgQueue;
}
/**终止订单线程池+调度线程池*/
public void shutdown() {
//true表示如果定时任务在执行,立即中止,false则等待任务结束后再停止
System.out.println("终止订单线程池+调度线程池:"+scheduledFuture.cancel(false));
scheduler.shutdown();
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
TestController 类
package com.springboot.demo;
import com.springboot.demo.Threads.TestThreadPoolManager;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.UUID;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2018/5/9.
*/
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Autowired
TestThreadPoolManager testThreadPoolManager;
/**
* 测试模拟下单请求 入口
* @param id
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/start/{id}")
public String start(@PathVariable Long id) {
//模拟的随机数
String orderNo = System.currentTimeMillis() + UUID.randomUUID().toString();
testThreadPoolManager.addOrders(orderNo);
return "Test ThreadPoolExecutor start";
}
/**
* 停止服务
* @param id
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/end/{id}")
public String end(@PathVariable Long id) {
testThreadPoolManager.shutdown();
Queue q = testThreadPoolManager.getMsgQueue();
System.out.println("关闭了线程服务,还有未处理的信息条数:" + q.size());
return "Test ThreadPoolExecutor start";
}
}
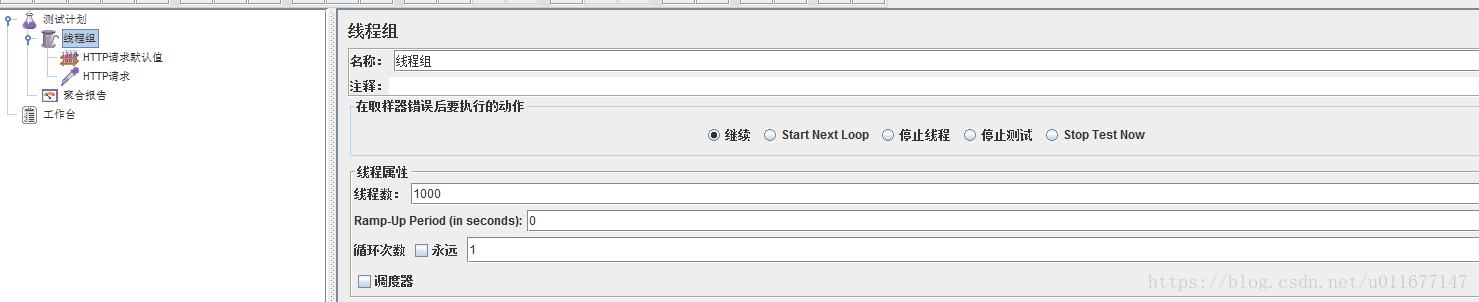
3.使用JMeter模拟并发下单请求 (JMeter使用可自行百度)
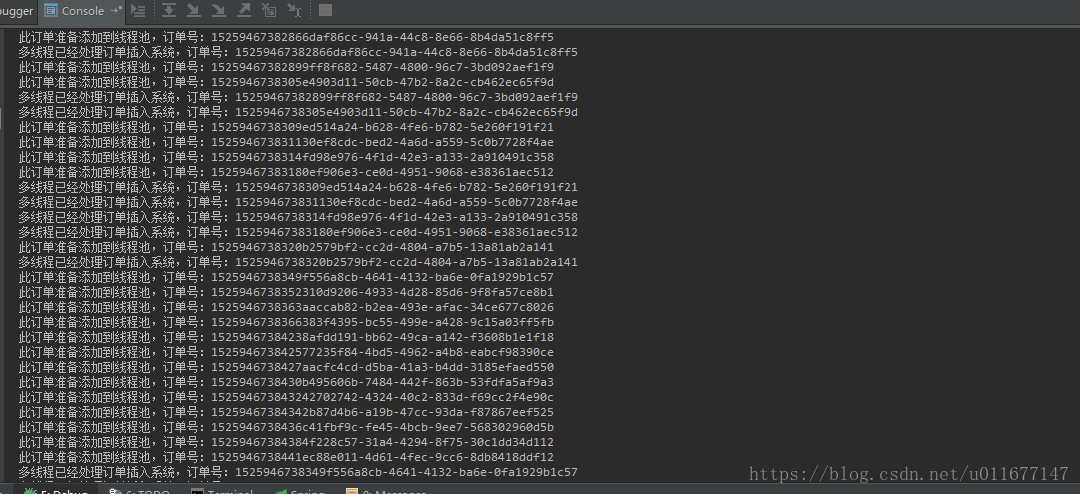
4.打印的日志说明,开始的订单直接执行插入到系统,当线程池的容量已经满了,则使用RejectedExecutionHandler方法把后面的订单添加到 Queue缓冲队列,使用ScheduledFuture方法定时(我这里是每秒一次)检查Queue队列,重新把队列里面的订单添加到线程池,执行后面的插入任务。部分日志如下







 本文介绍了一种在高并发环境下处理订单重复及性能问题的方法,采用ThreadPoolExecutor线程池结合Queue队列,通过Spring Boot框架实现,有效避免了订单重复提交,并在用户量激增时保持系统稳定。
本文介绍了一种在高并发环境下处理订单重复及性能问题的方法,采用ThreadPoolExecutor线程池结合Queue队列,通过Spring Boot框架实现,有效避免了订单重复提交,并在用户量激增时保持系统稳定。
















 1852
1852

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








