目录
EventLoop::runInLoop(Functor cb)
EventLoop::queueInLoop(Functor cb)
成员变量:
int wakeupFd_:
linux内核的eventfd创建出来的
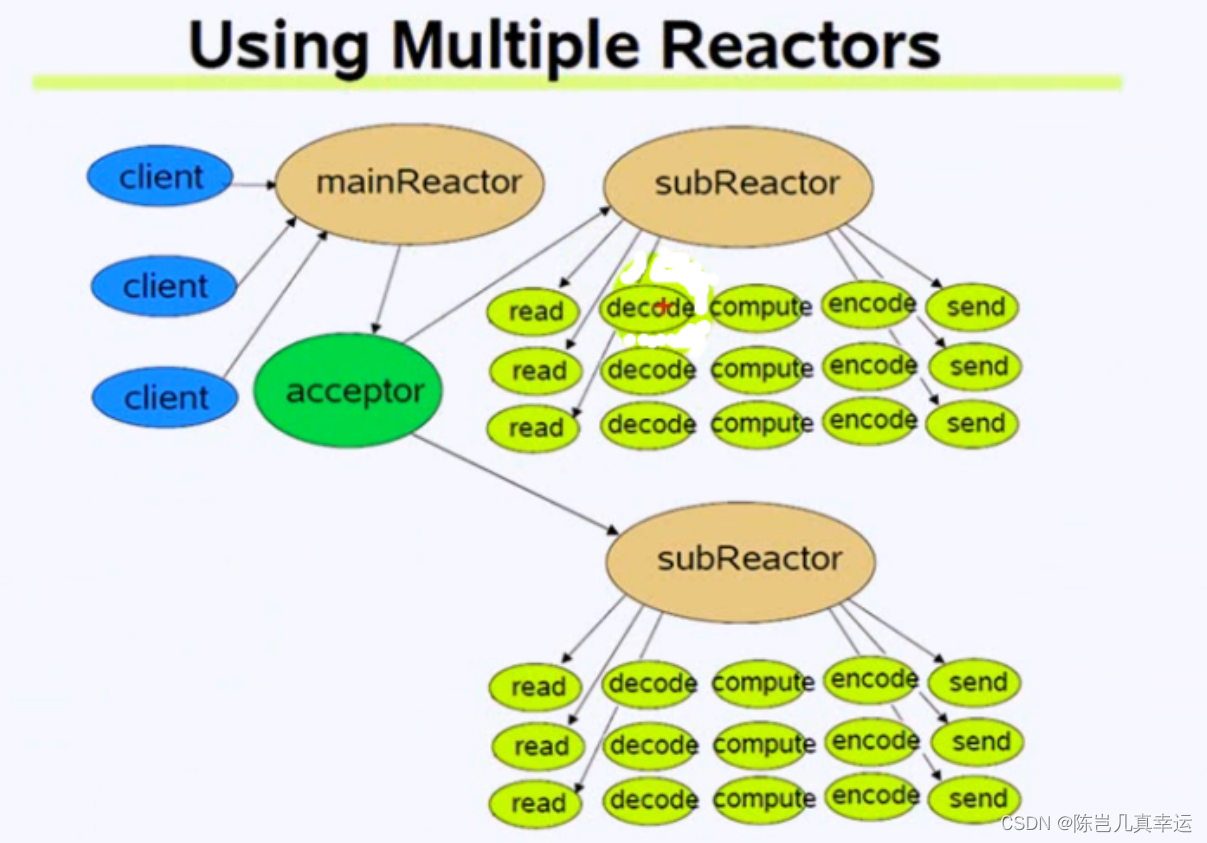
mainReactor如何将唤醒subReactor去处理有事件发生的channel?把新用户连接的channel分发给subReactor?
(当mainLoop获取一个新用户的channel,通过轮询算法选择一个subLoop)
由linux内核中的eventfd() 函数创建一个无名的事件文件描述符(项目中的wakeupFd_ ),可以通过读写(read、write)该文件描述符来进行事件的通知和等待。
事件计数器的初始值由 initval 指定,它表示事件的初始数量。对该文件描述符的读取操作将会阻塞,直到事件计数器的值大于0。写入操作将会增加事件计数器的值。
#include <sys/eventfd.h> int eventfd(unsigned int initval, int flags);int wakeupFd_ :
唤醒wakeupfd_://创建wakeupfd,用来notify唤醒subReactor处理新来的channel int createEventfd() { int evtfd = ::eventfd(0, EFD_NONBLOCK | EFD_CLOEXEC); if (evtfd < 0) { LOG_FATAL("eventfd error:%d \n", errno); } return evtfd; }唤醒loop所在的线程的(mainReactor用来唤醒subReactor)
成员函数:
EventLoop()构造函数:
__thread 是c++中的一个线程局部存储关键字,用于声明一个线程局部变量,即每个线程都拥有自己的变量副本,各个线程之间互不干扰。
这里定义一个线程局部变量指针,t_loopInThisThread,表示该线程还没有创建EventLoop对象,如果这个指针不为空了我们就不再创建对象了,保证一个线程只有一个EventLoop。
用在我们的EventLoop构造函数中。

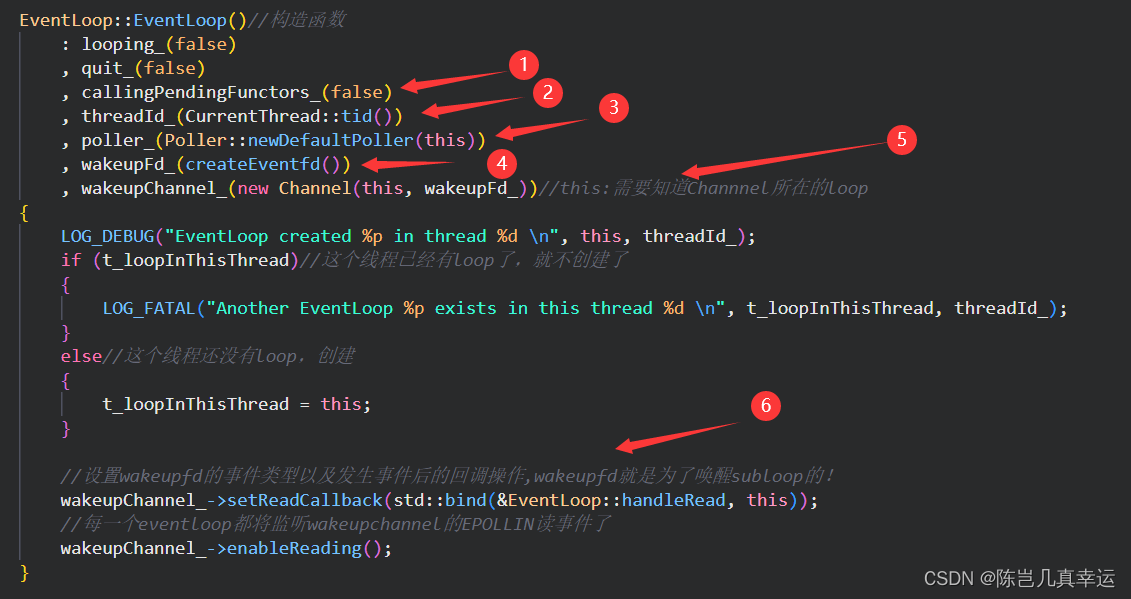
①:判断是否需要执行回调;
②:获取当前线程id;
③:创建epollpoller实例;
④:创建wakeupFd_:
这里我们将由wakeupFd_创建出来的Channel对象,并将其地址存入wakeupChannel_中,调用了Channel中的setReadCallback函数设置了它的读操作回调函数handleRead,并调用了Channel中的enableReading函数设置了事件类型为EPOLLIN。
⑤:将wakeupFd_和当前loop打包成wakeupChannel_。
⑥:执行回调函数handlRead。
~EventLoop():

析构函数就将事件类型设置为全部感兴趣,然后把Channel从所属的EventLoop中移除,关闭fd,将t_loopInThisThread置空(防止一个线程创建多个EventLoop)。
EventLoop::loop()
主要任务是调用底层Poller,开启事件分发器。
主要完成的内容是,调用poller的poll方法底层调用epoll_wait把活跃Channel都放到activeChannels_容器中,然后进行遍历执行handleEvent判断具体事件类型,执行相应回调函数。
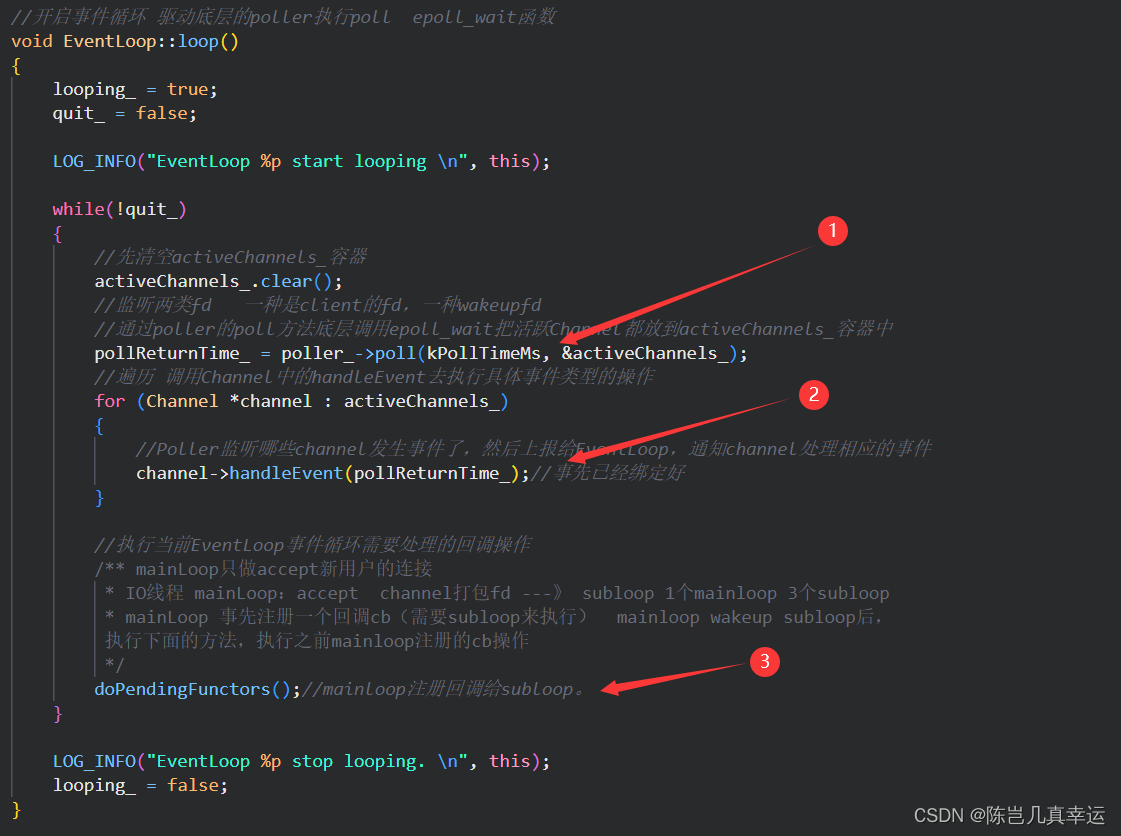
①:通过poller的poll方法底层调用epoll_wait把活跃Channel都放到activeChannels_容器中;
②:遍历 调用Channel中的handleEvent去执行具体事件类型的操作
③: 处理mainLoop给subLoop设置的回调函数:doPendingFunctors()
EventLoop::quit()
退出事件循环
退出事件循环 :
1、loop在自己的线程中调用quit ;
- 不会阻塞在poll函数上,因为在自己的线程上执行一个函数,肯定从poll函数上返回了!
2、在非loop的线程中,调用loop的quit;
- 如果是在其它线程中,调用的quit 比如说: 在一个subloop(worker)中,调用了mainLoop(lO)的quit;
- 调用mainloop的quit,这时候,应该先给mainloop它唤醒 ,它就从poll返回回来:
- 此时你已经将其quit 置为true,在回到loop函数的while循环中,已经不满足表达式了! 就结束了
EventLoop::runInLoop(Functor cb)
直接在当前loop中执行cb,不在当loop中执行queuInLoop

EventLoop::queueInLoop(Functor cb)
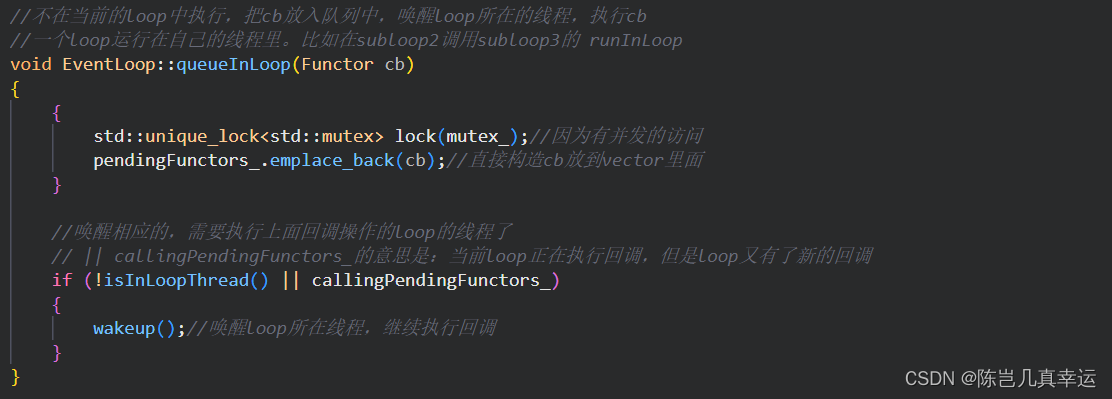
if中的两种情况:
1. loop执行的回调,但是当前运行的线程不是loop对应的线程,将这个loop的线程唤醒!
2. callingPendingFunctors_为true,表示当前的loop正在执行回调,没有阻塞在loop的pol上 (pol是调用的epoll wait)
但是如果此时mainloop又给当前loop写了新的回调! 等doPendingFunctors函数执行完后,又会阻塞在lp的poll上,没有事件向pendingFunctors 写入新的回调;
此时应该在执行回调过程中,应该唤醒loop所在线程,向pendingFunctors 写入新的回调
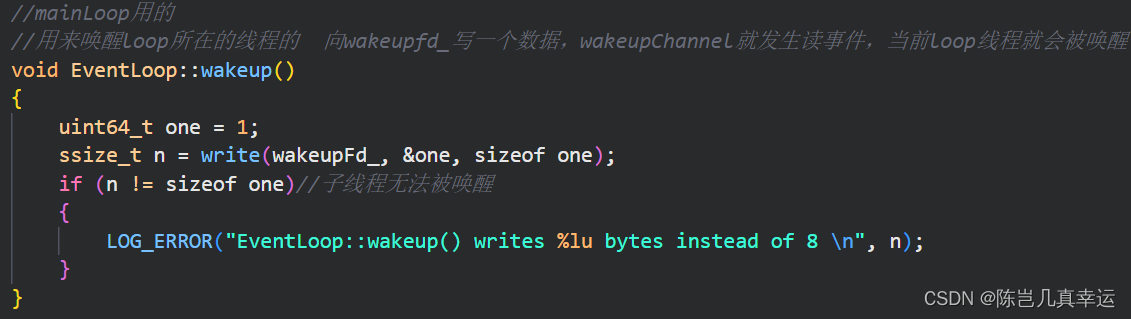
wakeup():
//mainLoop用的
//用来唤醒loop所在的线程的 向wakeupfd_写一个数据,wakeupChannel就发生读事件,当前loop线程就会被唤醒
void EventLoop::wakeup()
{
uint64_t one = 1;
ssize_t n = write(wakeupFd_, &one, sizeof one);
if (n != sizeof one)//子线程无法被唤醒
{
LOG_ERROR("EventLoop::wakeup() writes %lu bytes instead of 8 \n", n);
}
}
EventLoop.h
#pragma once
//Reactor模型中的事件循环 相当与事件分发器 epoll
//事件循环类 主要包含了两个大模块 Channel Poller(epoll的抽象)
#include <functional>
#include <vector>
#include <atomic>//C++ 11
#include <memory>
#include <mutex>
#include "noncopyable.h"
#include "Timestamp.h"
#include "CurrentThread.h"
class Channel;
class Poller;
//事件循环类 主要包含了两个大模块 Channel Poller(epoll的抽象)
class EventLoop : noncopyable
{
public:
using Functor = std::function<void()>;//定义一个回调的类型
//using代替typedef,进行类型的重命名
EventLoop();
~EventLoop();
//开启事件循环
void loop();
//退出事件循环
void quit();
//返回当前时间
Timestamp pollReturnTime() const { return pollReturnTime_; }
//在当前loop中执行cb,cb是回调操作
void runInLoop(Functor cb);
//把cb放入队列中,唤醒loop所在的线程,执行cb
void queueInLoop(Functor cb);
//用来唤醒loop所在的线程的(mainReactor用来唤醒subReactor)
void wakeup();
//EventLoop的方法,其中调用的是Poller的方法
void updateChannel(Channel *channel);
void removeChannel(Channel *channel);
bool hasChannel(Channel *channel);
//判断EventLoop对象是否在自己的线程里面
bool isInLoopThread() const { return threadId_ == CurrentThread::tid(); }
private:
void handleRead();//唤醒wake up
void doPendingFunctors();//执行回调
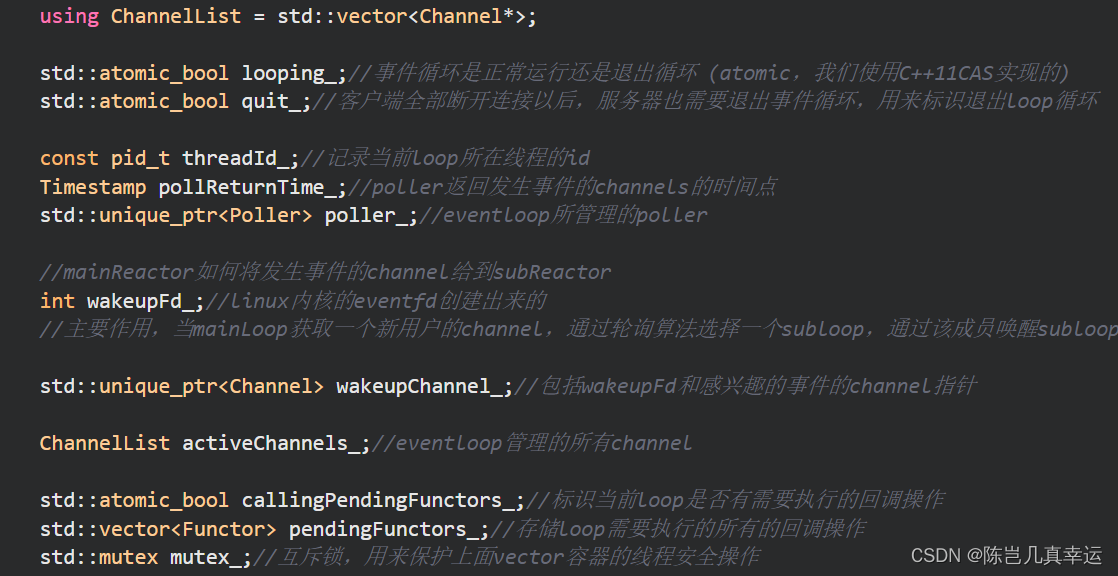
using ChannelList = std::vector<Channel*>;
std::atomic_bool looping_;//事件循环是正常运行还是退出循环 (atomic,我们使用C++11CAS实现的)
std::atomic_bool quit_;//客户端全部断开连接以后,服务器也需要退出事件循环,用来标识退出loop循环
const pid_t threadId_;//记录当前loop所在线程的id
Timestamp pollReturnTime_;//poller返回发生事件的channels的时间点
std::unique_ptr<Poller> poller_;//eventloop所管理的poller
//mainReactor如何将发生事件的channel给到subReactor
int wakeupFd_;//linux内核的eventfd创建出来的
//主要作用,当mainLoop获取一个新用户的channel,通过轮询算法选择一个subloop,通过该成员唤醒subloop处理channel
std::unique_ptr<Channel> wakeupChannel_;//包括wakeupFd和感兴趣的事件
ChannelList activeChannels_;//eventloop管理的所有channel
std::atomic_bool callingPendingFunctors_;//标识当前loop是否有需要执行的回调操作
std::vector<Functor> pendingFunctors_;//存储loop需要执行的所有的回调操作
std::mutex mutex_;//互斥锁,用来保护上面vector容器的线程安全操作
};
EventLoop.cc
#include "EventLoop.h"
#include "Logger.h"
#include "Poller.h"
#include "Channel.h"
#include <sys/eventfd.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <memory>
//防止一个线程创建多个EventLoop __thread:thread_local线程局部存储关键字用于声明一个线程局部变量
//当一个eventloop创建起来它就指向那个对象,在一个线程里再去创建一个对象,由于这个指针不为空,就不创建
__thread EventLoop *t_loopInThisThread = nullptr;
//定义默认的Poller IO复用接口的超时时间
const int kPollTimeMs = 10000;//10秒钟
//创建wakeupfd,用来notify唤醒subReactor处理新来的channel
int createEventfd()
{
int evtfd = ::eventfd(0, EFD_NONBLOCK | EFD_CLOEXEC);
if (evtfd < 0)
{
LOG_FATAL("eventfd error:%d \n", errno);
}
return evtfd;
}
EventLoop::EventLoop()//构造函数
: looping_(false)
, quit_(false)
, callingPendingFunctors_(false)
, threadId_(CurrentThread::tid())
, poller_(Poller::newDefaultPoller(this))
, wakeupFd_(createEventfd())
, wakeupChannel_(new Channel(this, wakeupFd_))//this:需要知道Channnel所在的loop
{
LOG_DEBUG("EventLoop created %p in thread %d \n", this, threadId_);
if (t_loopInThisThread)//这个线程已经有loop了,就不创建了
{
LOG_FATAL("Another EventLoop %p exists in this thread %d \n", t_loopInThisThread, threadId_);
}
else//这个线程还没有loop,创建
{
t_loopInThisThread = this;
}
//设置wakeupfd的事件类型以及发生事件后的回调操作,wakeupfd就是为了唤醒subloop的!
wakeupChannel_->setReadCallback(std::bind(&EventLoop::handleRead, this));
//每一个eventloop都将监听wakeupchannel的EPOLLIN读事件了
wakeupChannel_->enableReading();
}
EventLoop::~EventLoop()//析构函数
{
wakeupChannel_->disableAll();
wakeupChannel_->remove();
::close(wakeupFd_);
t_loopInThisThread = nullptr;
}
//开启事件循环 驱动底层的poller执行poll
void EventLoop::loop()
{
looping_ = true;
quit_ = false;
LOG_INFO("EventLoop %p start looping \n", this);
while(!quit_)
{
//先清空activeChannels_容器
activeChannels_.clear();
//监听两类fd 一种是client的fd,一种wakeupfd
//通过poller的poll方法底层调用epoll_wait把活跃Channel都放到activeChannels_容器中
pollReturnTime_ = poller_->poll(kPollTimeMs, &activeChannels_);
//遍历 调用Channel中的handleEvent去执行具体事件类型的操作
for (Channel *channel : activeChannels_)
{
//Poller监听哪些channel发生事件了,然后上报给EventLoop,通知channel处理相应的事件
channel->handleEvent(pollReturnTime_);//事先已经绑定好
}
//执行当前EventLoop事件循环需要处理的回调操作
/** mainLoop只做accept新用户的连接
* IO线程 mainLoop:accept channel打包fd ---》 subloop 1个mainloop 3个subloop
* mainLoop 事先注册一个回调cb(需要subloop来执行) mainloop wakeup subloop后,
执行下面的方法,执行之前mainloop注册的cb操作
*/
doPendingFunctors();//mainloop注册回调给subloop。
}
LOG_INFO("EventLoop %p stop looping. \n", this);
looping_ = false;
}
//退出事件循环 1.loop在自己的线程中调用quit 2.在非loop的线程中,调用loop的quit
/**
* mainLoop
*
* 通过wakeupfd no ==================== 生产者-消费者的线程安全的队列
mainloop生产 subloop消费 逻辑好处理 但是muduo库没有这个 是通过wakefd通信
线程间直接notify唤醒
*
* subLoop1 subLoop2 subLoop3
*/
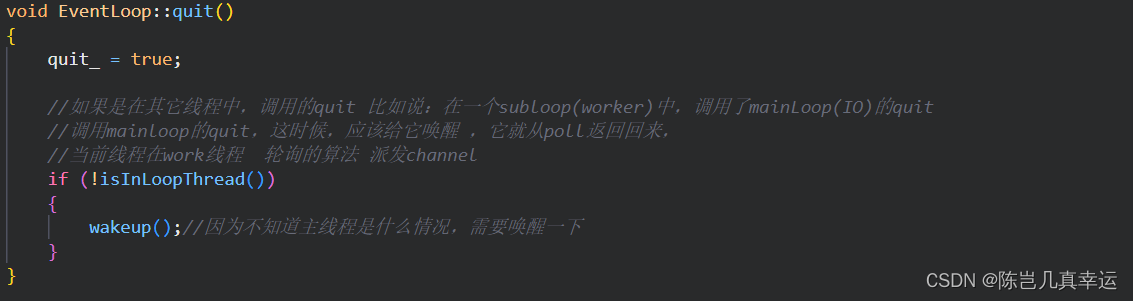
void EventLoop::quit()
{
quit_ = true;
//如果是在其它线程中,调用的quit 比如说:在一个subloop(worker)中,调用了mainLoop(IO)的quit
//调用mainloop的quit,这时候,应该给它唤醒 ,它就从poll返回回来,
//当前线程在work线程 轮询的算法 派发channel
if (!isInLoopThread())
{
wakeup();//因为不知道主线程是什么情况,需要唤醒一下
}
}
//直接在当前loop中执行cb(callback)
void EventLoop::runInLoop(Functor cb)
{
if (isInLoopThread())//在当前的loop线程中,执行cb
{
cb();
}
else//在非当前loop线程中执行cb , 就需要唤醒loop所在线程,执行cb
{
queueInLoop(cb);
}
}
//不在当前的loop中执行,把cb放入队列中,唤醒loop所在的线程,执行cb
//一个loop运行在自己的线程里。比如在subloop2调用subloop3的 runInLoop
void EventLoop::queueInLoop(Functor cb)
{
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);//因为有并发的访问
pendingFunctors_.emplace_back(cb);//直接构造cb放到vector里面
}
//唤醒相应的,需要执行上面回调操作的loop的线程了
// || callingPendingFunctors_的意思是:当前loop正在执行回调,但是loop又有了新的回调
if (!isInLoopThread() || callingPendingFunctors_)
{
wakeup();//唤醒loop所在线程,继续执行回调
}
}
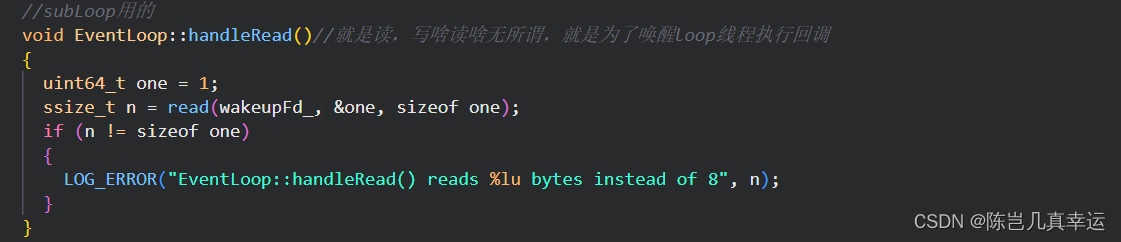
//subLoop用的
void EventLoop::handleRead()//就是读,写啥读啥无所谓,就是为了唤醒loop线程执行回调
{
uint64_t one = 1;
ssize_t n = read(wakeupFd_, &one, sizeof one);
if (n != sizeof one)
{
LOG_ERROR("EventLoop::handleRead() reads %lu bytes instead of 8", n);
}
}
//mainLoop用的
//用来唤醒loop所在的线程的 向wakeupfd_写一个数据,wakeupChannel就发生读事件,当前loop线程就会被唤醒
void EventLoop::wakeup()
{
uint64_t one = 1;
ssize_t n = write(wakeupFd_, &one, sizeof one);
if (n != sizeof one)//子线程无法被唤醒
{
LOG_ERROR("EventLoop::wakeup() writes %lu bytes instead of 8 \n", n);
}
}
//EventLoop的方法 =》 Poller的方法
void EventLoop::updateChannel(Channel *channel)
{
poller_->updateChannel(channel);
}
void EventLoop::removeChannel(Channel *channel)
{
poller_->removeChannel(channel);
}
bool EventLoop::hasChannel(Channel *channel)
{
return poller_->hasChannel(channel);
}
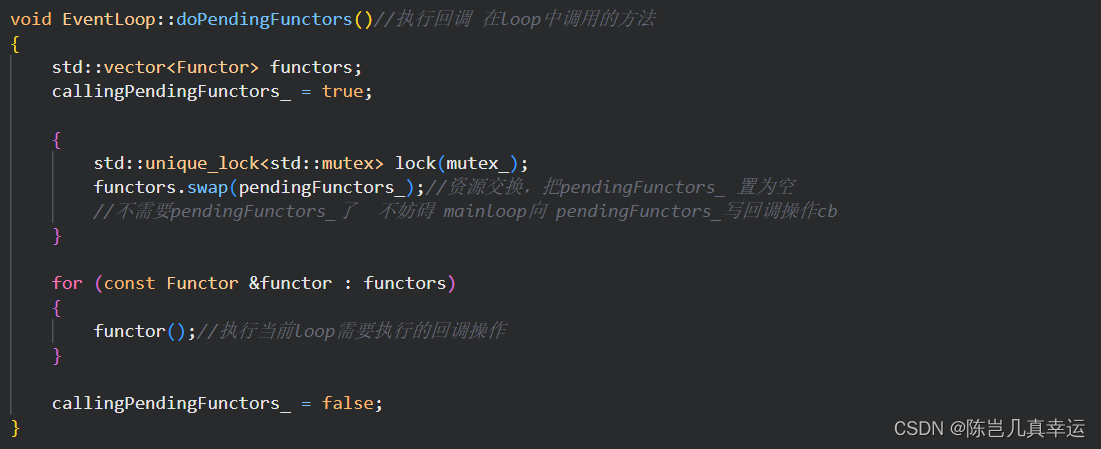
void EventLoop::doPendingFunctors()//执行回调 在loop中调用的方法
{
std::vector<Functor> functors;
callingPendingFunctors_ = true;
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
functors.swap(pendingFunctors_);//资源交换,把pendingFunctors_ 置为空
//不需要pendingFunctors_了 不妨碍 mainloop向 pendingFunctors_写回调操作cb
}
for (const Functor &functor : functors)
{
functor();//执行当前loop需要执行的回调操作
}
callingPendingFunctors_ = false;
}





 文章详细介绍了EventLoop的实现,包括成员变量wakeupFd_的用途,用于唤醒线程的eventfd创建,以及EventLoop的构造函数中确保线程唯一性。事件循环的核心方法loop()负责处理事件,quit()用于退出循环,runInLoop()和queueInLoop()分别在当前循环和异步执行回调。同时,wakeup()函数用于唤醒线程执行回调。
文章详细介绍了EventLoop的实现,包括成员变量wakeupFd_的用途,用于唤醒线程的eventfd创建,以及EventLoop的构造函数中确保线程唯一性。事件循环的核心方法loop()负责处理事件,quit()用于退出循环,runInLoop()和queueInLoop()分别在当前循环和异步执行回调。同时,wakeup()函数用于唤醒线程执行回调。

















 8166
8166

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








