函数指针
函数指针是指向函数的指针变量。它存储了函数的地址,可以通过函数指针来调用对应的函数。
是在运行状态下动态选择调用不同的函数。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
bool mygreater(T a, T b)
{
return a > b;
}
template<typename T>
bool myless(T a, T b)
{
return a < b;
}
template<typename T, typename Compare >
bool compare(T a, T b, Compare comp)
{
//这里函数指针调用函数,是没有办法内联的,
//效率比较低,因为有函数调用的开销
return comp(a, b);
}
int main()
{
cout << compare(10, 20, mygreater<int>) << endl;
cout << compare(10, 20, myless<int>) << endl;
}
函数对象
C++函数对象实现:
1.通过函数对象调用operator(), 可以省略函数的调用开销,比通过函数指针调用函数(不能够inline内联调用)效率高。
2.因为函数对象是用类生成的,所以可以添加相关的成员变量,用来记录函数对象使用时更对的信息。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
class mygreater
{
public:
bool operator()(T a, T b) //二元函数对象
{
return a > b;
}
};
template<typename T>
class myless
{
public:
bool operator()(T a, T b)//二元函数对象
{
return a < b;
}
};
template<typename T, typename Compare >
bool compare(T a, T b, Compare comp)
{
//这里是使用运算符重载 operator()
return comp(a, b);
}
int main()
{
cout << compare(10, 20, mygreater<int>()) << endl;
cout << compare(10, 20, myless<int>()) << endl;
}
函数对象应用
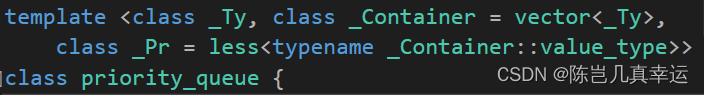
自定义小根堆
#include<iostream> #include<queue> #include<set> #include<vector> using namespace std; int main() { priority_queue<int>queu1; for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) { queu1.push(rand() % 100); } while (!queu1.empty()) { cout << queu1.top()<<" "; queu1.pop(); } cout << endl; using MinHeap = priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>>; MinHeap queu2; for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) { queu2.push(rand() % 100); } while (!queu2.empty()) { cout << queu2.top() << " "; queu2.pop(); } return 0; }
自定义set
#include<iostream> #include<queue> #include<set> #include<vector> using namespace std; int main() { set<int,greater<int>> set1; for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) { set1.insert(rand() % 10); } for (int v : set1) { cout << v << " "; } cout << endl; return 0; }





 本文介绍了C++中的函数指针和函数对象的概念,函数指针存储函数地址用于动态调用,但效率较低,而函数对象通过operator()调用,效率更高且可扩展。文章通过示例展示了如何使用模板和自定义比较函数在优先级队列和集合中实现特定排序行为。
本文介绍了C++中的函数指针和函数对象的概念,函数指针存储函数地址用于动态调用,但效率较低,而函数对象通过operator()调用,效率更高且可扩展。文章通过示例展示了如何使用模板和自定义比较函数在优先级队列和集合中实现特定排序行为。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








