Python 中的进程、线程、协程:原理 × 对比 × 实战
这是一份可直接做笔记/培训的结构化讲解。包含定义、底层机制、调度方式、优缺点、代码范式、典型架构、调参与避坑。
⸻
- 三者各是什么?
1.1 进程(Process)
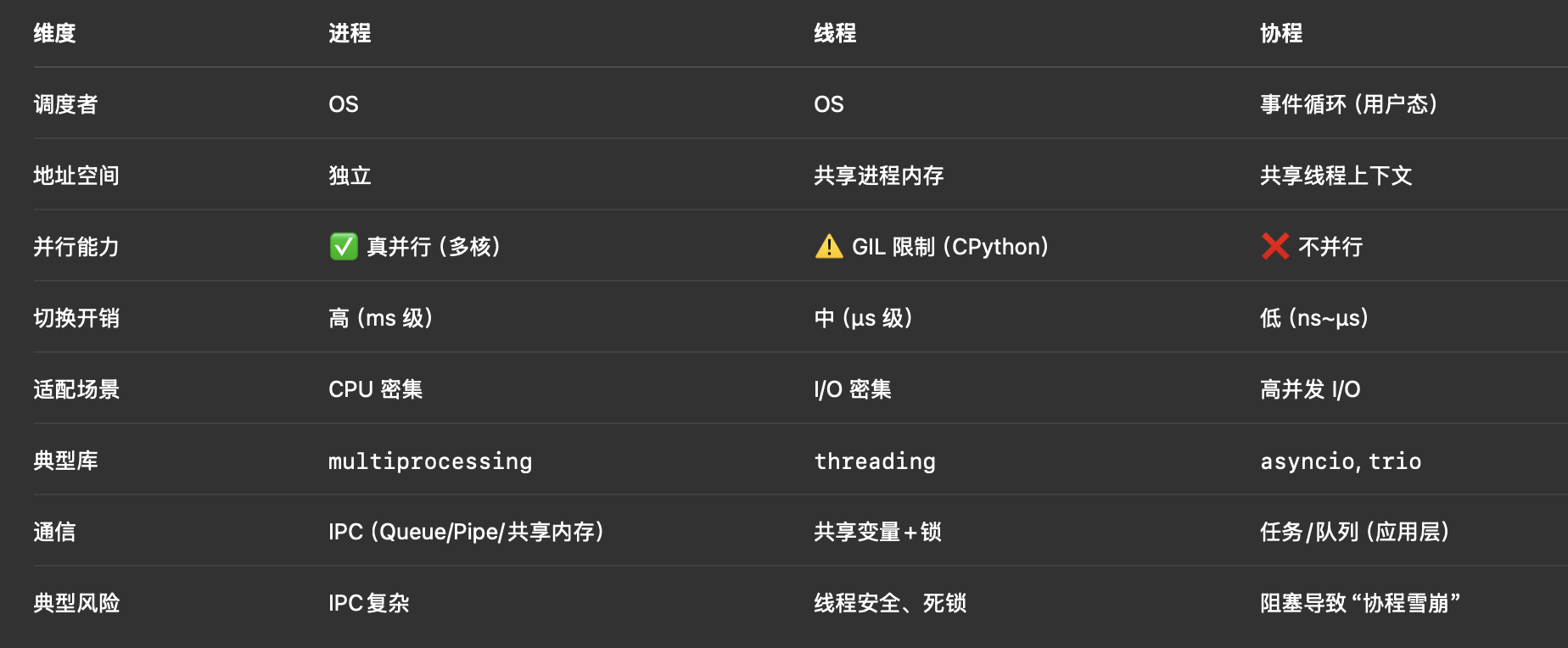
• 定义:操作系统资源分配的最小单位,拥有独立地址空间与解释器实例。
• 关键点:彼此隔离、稳定性强、可多核并行(每个进程有自己的 GIL)。
• 代价:创建/切换成本高,进程间通信(IPC)复杂(Pipe/Queue/Socket/共享内存)。
1.2 线程(Thread)
• 定义:进程内的执行流,共享该进程的内存与句柄。
• 关键点:切换成本低于进程;在 CPython 中受 GIL 限制 → 同一时刻仅一个线程执行字节码。
• 适用:I/O 密集(网络/磁盘/数据库),不适合纯 CPU 计算。
1.3 协程(Coroutine, asyncio)
• 定义:用户态的“轻量级任务”,运行在单线程事件循环中,靠 await 主动让出。
• 关键点:切换极轻、可高并发 I/O;不并行,CPU 密集会阻塞事件循环。
• 适用:高并发网络服务、异步爬虫、流式处理。
⸻
- 底层调度方式与执行模型
操作系统(内核) 调度实体:进程/线程 ←→ 抢占式(时间片, 中断)
└─ 每个进程
└─ (可选) 多线程:受 GIL 影响(CPython)
└─ (可选) 事件循环:协程任务列表(协作式,遇到 await 切换)
• 进程/线程:由操作系统抢占式调度(时间片轮转、上下文切换)。
• 协程:由事件循环在用户态协作式调度(仅在 await/I/O 处切走)。
⸻
- 对比一览(背下来就行)
⸻
- 代码范式速览(最小可运行示例)
4.1 进程:CPU 并行
from multiprocessing import Pool
def cpu_task(n): return sum(i*i for i in range(10**7)) + n
if __name__ == "__main__":
with Pool(4) as p:
print(p.map(cpu_task, range(8))) # 4 进程并行
4.2 线程:I/O 并发
import threading, time, requests
def io_task(i):
r = requests.get("https://httpbin.org/delay/1")
print(i, r.status_code)
threads = [threading.Thread(target=io_task, args=(i,)) for i in range(10)]
[t.start() for t in threads]; [t.join() for t in threads]
4.3 协程:I/O 高并发
import asyncio, aiohttp
async def io_task(i):
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as s:
async with s.get("https://httpbin.org/delay/1") as r:
print(i, r.status)
asyncio.run(asyncio.gather(*(io_task(i) for i in range(100))))
要点:协程版本能轻松把并发扩大到几千/几万连接;线程版本会更重、切换成本更高。
⸻
- GIL 与三者的关系(CPython)
• 进程:每个进程一份 GIL → 可多核并行。
• 线程:共享同一个 GIL → 同一时刻只有一个线程执行字节码。
• 协程:运行在单线程之上 → 完全受 GIL 约束,但 I/O 空转时不占用 CPU,靠 await 切换,吞吐依旧高。
进阶:数值计算等 C 扩展(NumPy、PyTorch)常在重算时主动释放 GIL,因此在多线程中也能并行加速。
⸻
- 典型架构组合(服务端常用三层)
Gunicorn(多进程 workers) → 每个 worker 内 Uvicorn(事件循环, asyncio 协程) → 线程池/进程池执行阻塞点
• 多进程:利用多核、隔离故障。
• 协程:承载海量连接。
• 线程/进程池:兜住阻塞库/CPU 重算,避免卡死事件循环。
⸻
- 该怎么选?(决策树)
- 是否 CPU 密集?
• 是 → 多进程(multiprocessing / ProcessPoolExecutor)。 - 是否高并发 I/O?
• 是 → 协程(asyncio / uvloop / aiohttp / FastAPI)。 - 遗留/第三方库是同步阻塞?
• 先选 线程(ThreadPoolExecutor)或把阻塞丢到进程池。 - 服务端生产部署
• 网关/Nginx 前置 → Gunicorn --workers N + UvicornWorker + asyncio。
- 是否 CPU 密集?
⸻
- 性能与调参实务
8.1 进程
• 并行度:≈ CPU 核数(CPU 密集),或 2×核数+1(混合/IO 偏多)。
• COW:preload_app + 写时复制节省 RSS(对 GPU 显存无效)。
• IPC:大对象用共享内存/零拷贝(multiprocessing.shared_memory)。
8.2 线程
• 线程安全:Lock/RLock/Semaphore;避免细粒度锁嵌套 → 谨防死锁。
• 阻塞外包:concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor;异步中用 asyncio.to_thread()。
8.3 协程
• 核心原则:所有 I/O 都要 await;任何阻塞都应丢到执行器。
• 连接池:DB/HTTP 客户端使用异步池(asyncpg, aiomysql, aiohttp)。
• 背压:asyncio.Queue 控制生产/消费速率,避免“雪崩”。
• 事件循环优化:uvloop(Unix 上显著提升吞吐与延迟)。
⸻
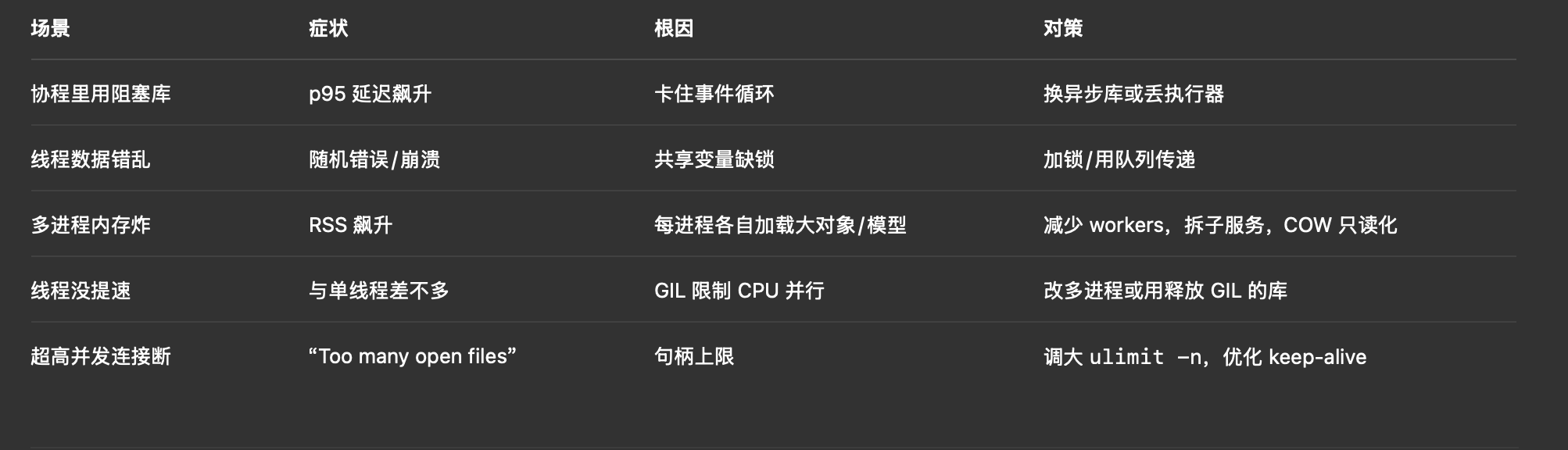
- 常见坑与对策
⸻
- 实战模板(组合拳)
10.1 FastAPI 服务(协程 + 线程池兜阻塞)
# app.py
import asyncio
from fastapi import FastAPI
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
app = FastAPI()
executor = ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=8)
def blocking_io(path: str) -> str:
with open(path, "rb") as f:
return f.read().decode("utf-8", "ignore")
@app.get("/file")
async def read_file(path: str):
content = await asyncio.get_running_loop().run_in_executor(executor, blocking_io, path)
return {"len": len(content)}
部署(多进程 + 协程):
gunicorn app:app \
-w 12 \
-k uvicorn.workers.UvicornWorker \
-b 0.0.0.0:8000 \
--timeout 120 --graceful-timeout 30 \
--keep-alive 10 \
--max-requests 5000 --max-requests-jitter 500 \
--preload
10.2 CPU 计算用进程池
import asyncio
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor
def heavy_cpu(n: int) -> int:
return sum(i*i for i in range(10**7)) + n
async def main():
loop = asyncio.get_running_loop()
with ProcessPoolExecutor() as pool:
results = await asyncio.gather(*(loop.run_in_executor(pool, heavy_cpu, i) for i in range(8)))
print(results)
asyncio.run(main())
⸻
- FAQ(高频疑问)
Q1. 线程能否绕开 GIL 实现并行?
A:不能(CPython)。但C 扩展在重算时可释放 GIL,多线程也能并行那些部分。
Q2. 协程是否一定比线程快?
A:I/O 高并发场景通常更省资源、延迟更稳;但少量并发或阻塞多时不一定。
Q3. 多进程 IPC 太麻烦怎么办?
A:尽量 无共享(share-nothing),用队列传递消息;或把重算下沉为独立服务(RPC/HTTP/消息队列)。
Q4. asyncio 与多线程能否同时用?
A:可以。协程为主,阻塞点用 to_thread();或固定线程池承接同步库。
Q5. 以后 Python 没有 GIL 了吗?
A:Python 3.13+ 有“可选无 GIL(free-threading)”试验分支,生态迁移中。当前生产仍以有 GIL为默认前提做架构。
⸻
- 速记口诀
• 算力并行选进程,连接并发选协程;同步阻塞用线程,混搭三层最稳妥。
• 任何阻塞都要隔离出事件循环;任何共享都要设计边界。





















 7641
7641

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










