


<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='utf-8'>
<title>浮动</title>
<style type="text/css">
.con{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
border: 1px solid black;
margin: 30px auto 0;
position: relative;
}
.box1,.box2{
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
}
.box1{
background-color: blue;
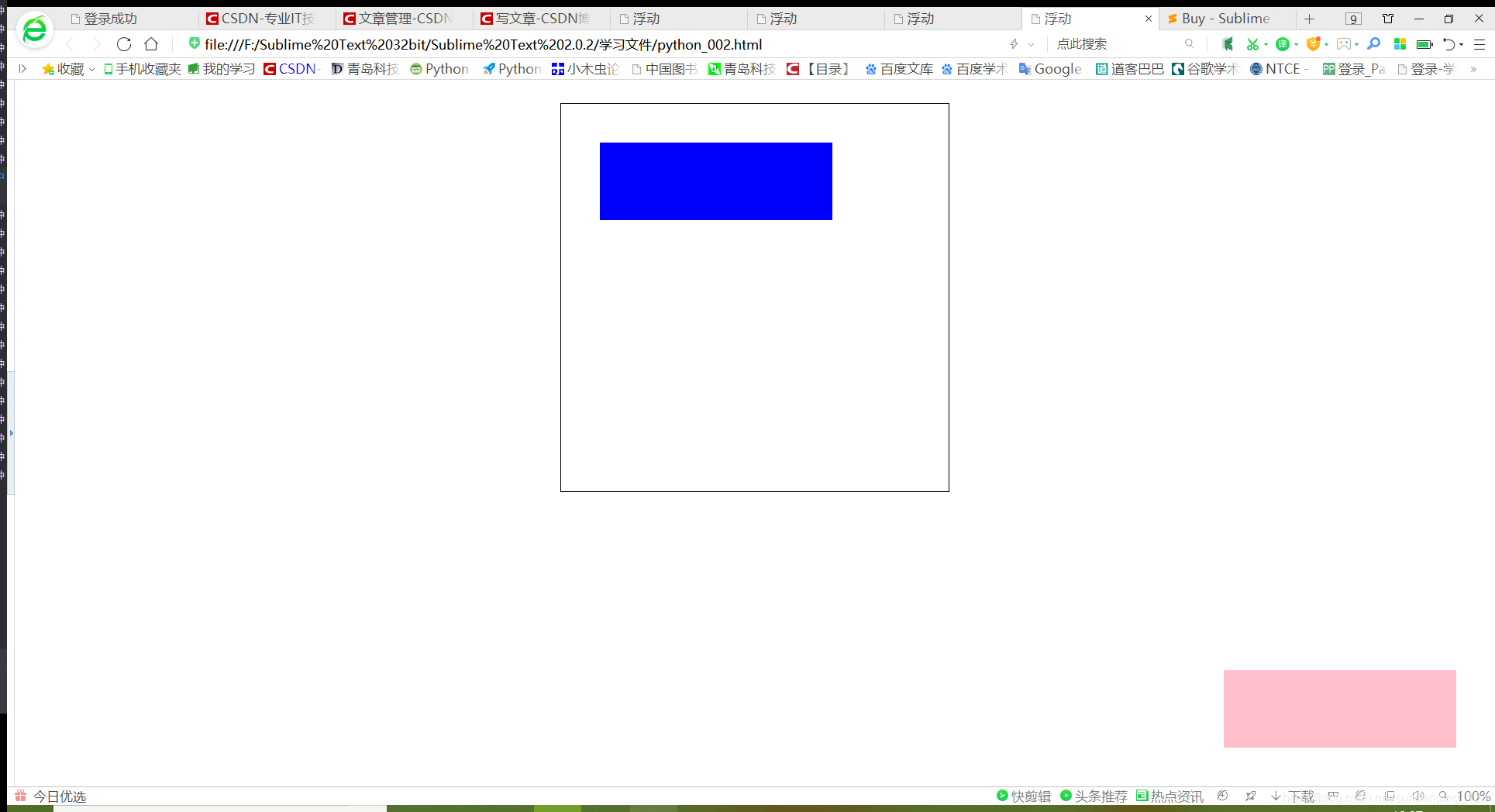
/*绝对定位 如果父级元素没有定位,那么此时就是相对于网页的定位;如果父级元素设置定位,那么此时就是相对于父级元素进行定位。 本程序设置的是相对于父级元素的定位。*/
position: absolute;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}
.box2{
background-color: pink;
/*固定定位*/
position: fixed;
right:50px;
bottom:50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="con">
<div class='box1'></div>
<div class='box2'></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
下面看一下层级之间的关系;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='utf-8'>
<title>浮动</title>
<style type="text/css">
.con{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
border: 1px solid black;
margin: 30px auto 0;
position: relative;
}
.con div{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
position: absolute;
}
.box1{
background-color: blue;
left: 20px;
top: 20px;
}
.box2{
background-color: pink;
left: 40px;
top: 40px;
}
.box3{
background-color: yellow;
left: 60px;
top: 60px;
}
.box4{
background-color: green;
left: 80px;
top: 80px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="con">
<div class='box1'></div>
<div class='box2'></div>
<div class='box3'></div>
<div class='box4'></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
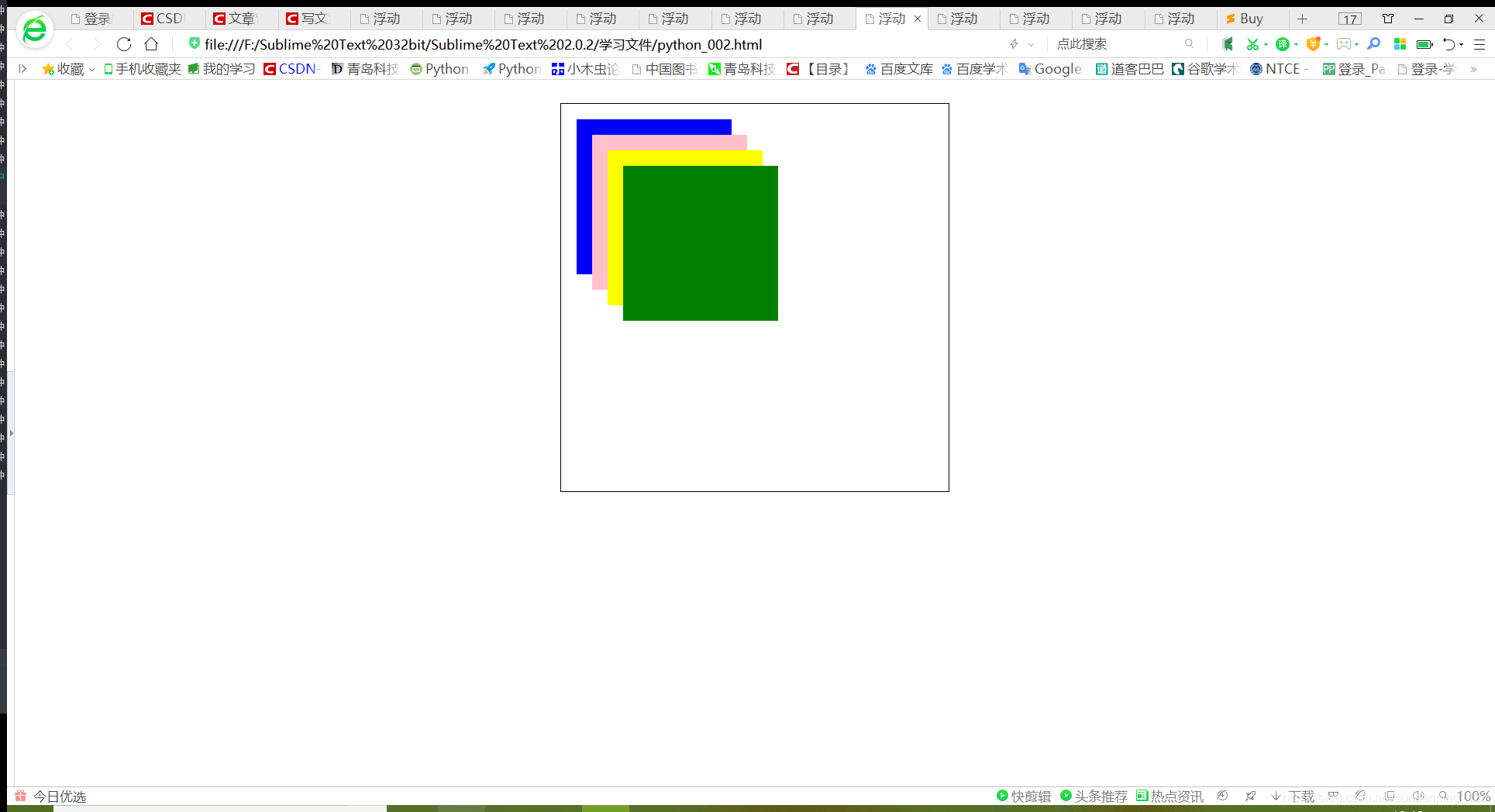
可以看出,最后定义的块元素在最上面。
那么为了应用方便,肯定可以自定义:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='utf-8'>
<title>浮动</title>
<style type="text/css">
.con{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
border: 1px solid black;
margin: 30px auto 0;
position: relative;
}
.con div{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
position: absolute;
}
.box1{
background-color: blue;
left: 20px;
top: 20px;
z-index: 10;
}
.box2{
background-color: pink;
left: 40px;
top: 40px;
z-index: 11;
}
.box3{
background-color: yellow;
left: 60px;
top: 60px;
}
.box4{
background-color: green;
left: 80px;
top: 80px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="con">
<div class='box1'></div>
<div class='box2'></div>
<div class='box3'></div>
<div class='box4'></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
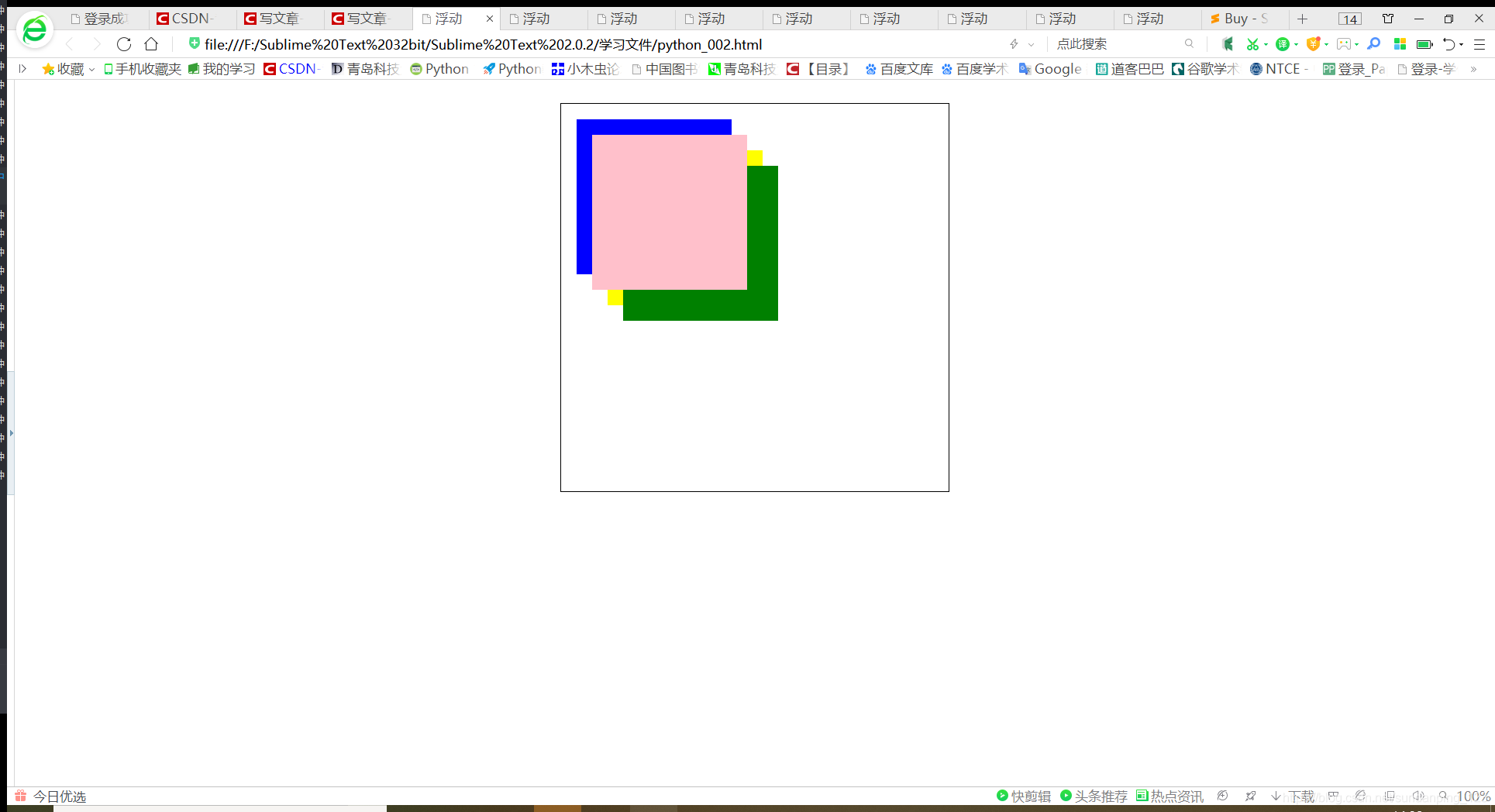






 本文探讨了前端开发中CSS的定位技术,分析了不同层级元素的关系,指出最后定义的块元素通常会位于最上方。内容涉及如何自定义元素定位以优化布局。
本文探讨了前端开发中CSS的定位技术,分析了不同层级元素的关系,指出最后定义的块元素通常会位于最上方。内容涉及如何自定义元素定位以优化布局。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








