路径总和题目如下:

思路:这道题用递归的话,到底什么时候有返回值呢,什么时候返回呢,代码随想录给出了以下三种情况:
- 如果需要搜索整棵二叉树且不用处理递归返回值,递归函数就不要返回值。(这种情况就是本文下半部分介绍的113.路径总和ii)
- 如果需要搜索整棵二叉树且需要处理递归返回值,递归函数就需要返回值。 (这种情况我们在236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 (opens new window)中介绍)
- 如果要搜索其中一条符合条件的路径,那么递归一定需要返回值,因为遇到符合条件的路径了就要及时返回。(本题的情况)
这里要判断路径和是否与目标值相等,直接将目标值作为计数器,每遍历一个节点,就将其值减去,最后判断到达叶子节点时目标值是否已经为0,如果为0,说明该条路径和已经达到目标值了,如果不为0,则继续寻找下一条路径。代码如下:
(这里面的回溯包含在递归里面):
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root == null) return false;
//直接将目标值作为计数器,每经过一个节点就减值
targetSum -= root.val;
//判断是否到达叶子节点以及是否满足目标值
if(root.left==null && root.right==null){
return targetSum == 0;
}
//对左子树和右子树进行递归
if(root.left!=null){
boolean left = hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum);
if(left) return true;//如果有路径和达到目标值可提前返回
}
//回溯隐含在递归中
if(root.right!=null){
boolean right = hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum);
if(right) return true;
}
return false;
}
}升级版的路径总和II题目如下:

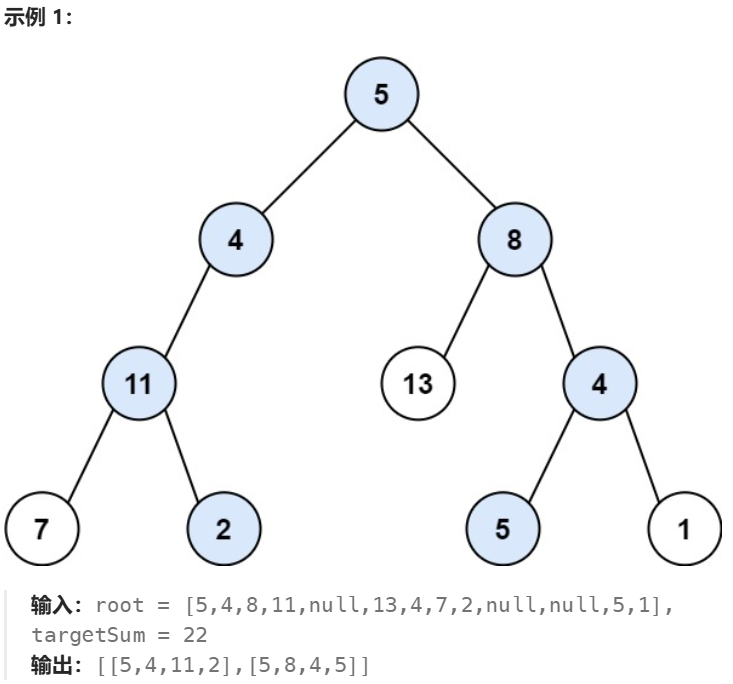
这个相当于求所有路径和路径和两道题的结合版
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
//这个相当于求所有路径和路径和两道题的结合版
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return result;//非空判断
List<Integer> path =new LinkedList<>();//存储路径
traversal(root,targetSum,result,path);
return result;
}
public void traversal(TreeNode root,int targetSum,List<List<Integer>> result,List<Integer> path){
path.add(root.val);
//遇到了叶子节点
if(root.left==null && root.right==null){
//判断该条路径是否满足目标值
if((targetSum-root.val) == 0){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
//如果和不为目标值,则一定也要返回
return;
}
if(root.left!=null){
traversal(root.left,targetSum-root.val,result,path);//递归
//回溯到上一级节点
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
if(root.right!=null){
traversal(root.right,targetSum-root.val,result,path);//递归
//回溯到上一级节点
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
}从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树题目如下:
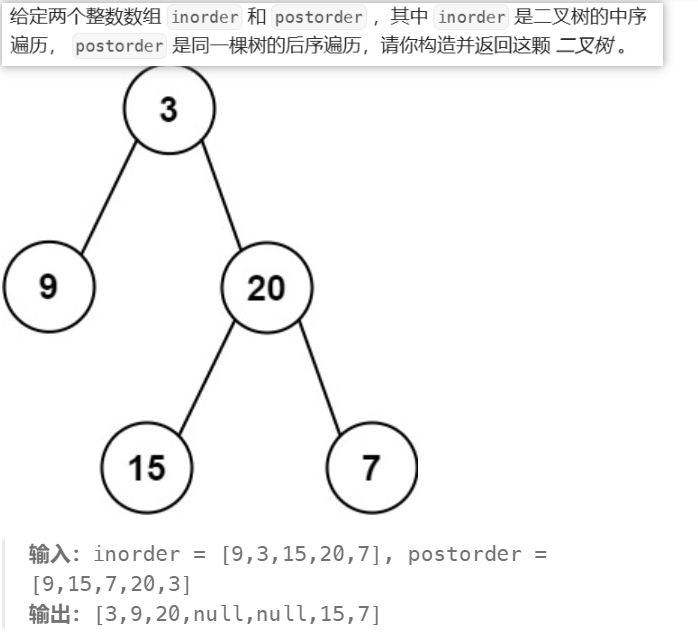
思路:主要难在每次从后序数组确认中节点后如何进行左右子树的分割并递归(重要!!)
class Solution {
Map<Integer, Integer> map;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
map = new HashMap<>();//用来存储中序序列的数值和对应位置
for(int i =0; i < inorder.length; i++){
map.put(inorder[i],i);
}
return findNode(inorder,0,inorder.length,postorder,0,postorder.length);
}
public TreeNode findNode(int[] inorder, int inBegin,int inEnd,int[] postorder, int postBegin, int postEnd){
//遵循左闭右开准则
if(inBegin >= inEnd || postBegin >= postEnd){//不满足左闭右开,说明没有元素
return null;
}
//1.找到后序遍历数组的最后一个元素在中序数组的位置
int rootIndex=map.get(postorder[postEnd-1]);
//2.构造树的节点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[rootIndex]);
//3.保存中序左子树个数,用来确定后序数列的个数
int lenOfLeft = rootIndex - inBegin;
//4.分割中序数组和后序数组的左子树部分
root.left = findNode(inorder,inBegin,rootIndex,
postorder,postBegin,postBegin+lenOfLeft);
//5.分割中序数组和后序数组的右子树部分
root.right = findNode(inorder,rootIndex+1,inEnd,
postorder,postBegin+lenOfLeft,postEnd-1);
return root;
}
}从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树与上面这道题是一模一样的思路,代码完全一样,不在赘述。




















 285
285

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








