目录
1.let
(一)变量不能重复声明
let a = '熊大';
let a = '熊二';
//会报错(二)块级作用域
只在{ } 里面起作用
{
let a = '熊大'
}
console.log(a) //报错(三)不存在变量提升
console.log(a); // 报错而不是undefined
let a = 'xiong';(四) 不影响作用域链
{
let a = 'xiong';
function fn(){
console.log(a) //xiong
}
}2.const
(一)一一定要赋初始值
(二)声明常量一般用大写-------潜规则
(三)常量的值不能修改
(四)块级作用域
(五)对于数组和对象的元素修改,不算做对常量的修改,不会报错
3.解构赋值
按照一定模式从数组和对象中提取值,对变量进行赋值
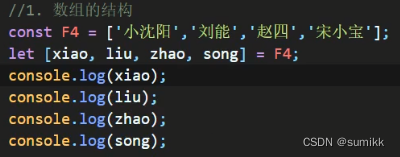
(一)数组的解构
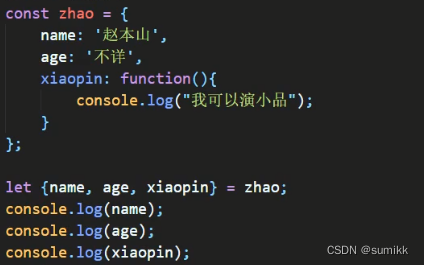
(二)对象的结构
4.ES6引入新的声明字符串的方式——``
(一)声明
let str = `我是字符串`;
(二)内容中可以直接出现换行符
(三)变量拼接
let name = 'xionger'
let he = `${name}是老二`
console。log(he) //xionger是老二5.变量和函数的简洁写法
{
name: name,
//简化为
name,
}
{
fn:function(){
console.log()
}
//可以简写为
fn(){
console.log()
}
}6.箭头函数
(一)this是静态的。this始终指向函数声明时所在作用域下的this的值
function fn() {
console.log(this.name)
}
let fn2 = () => {
console.log(this.name)
}
// 设置window对象的name属性
window.name = 'xiong';
const chan = {
name: "dog"
}
//直接调用
fn() //xiong
fn2() //xiong
//call方法调用
fn().call(chan); //dog
fn1().call(chan); //dog(二)不能作为构造实例化对象
let fn = (name) => {
this.name = name
}
let me = new fn('xiong') //报错
console.log(me);(三) 不能使用arguments变量
(四)简写
当形参只有一个时可以省略括号
当代码体只有一条语句时,return必须省略。而且执行结果就是函数的返回值
7.允许函数参数赋值初始值
function add(a, b, c = 5) {
return a + b + c;
}
let result = add(1, 2) //8
let result2 = add(1, 2, 3) //6(一)有默认值的参数一般放后
(二)与解构赋值结合
8.rest参数,代替arguments
function fn(...a){
console.log(a) //a打印出来是一个数组,可以使用数组的方法 filter some every map
}
fn(1,2,3,4)rest参数必须放在所有形参最后面
9.扩展运算符(...)
能将数组转化为逗号分隔的参数序列
arr = [1,2,3,4]
function fn(){
console.log(arguments)
}
fn(arr)
fn(...arr)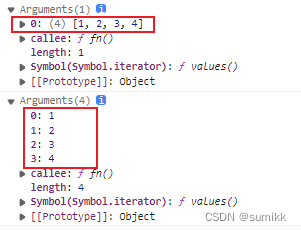
运用
(一)数组合并
const arr1 = [1,2]
const arr2 = [3,4]
const newarr = [...arr1 , ...arr2]
console.log(newarr) // 1,2,3,4(二)数组克隆
const arr1 = [1,2]
const arr2 = [...arr1](三)将为数组转化为真正的数组
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
var divs = document.querySelectorAll('div')
var arr = [...divs]
console.log(divs)
console.log(arr)
10.新数据类型Symbol
特点:
- Symbol的值是唯一的,用来解决命名冲突的问题
- Symbol值不能与其他数据类型进行运算
- Symbol定义的对象属性不能使用for...in 循环遍历,但是可以使用Reflect.ownKeys来获取对象的所有键名
//创建 Symbol
let s = Symbol();
let s1 = Symbol('张三');
let s2 = Symbol('张三');
console.log(s1 == s2) //false
// Symbol.for 创建
let s3 = Symbol.for('李四')
let s4 = Symbol.for('李四')
console.log(s3 == s4) //true给对象添加Symbol属性
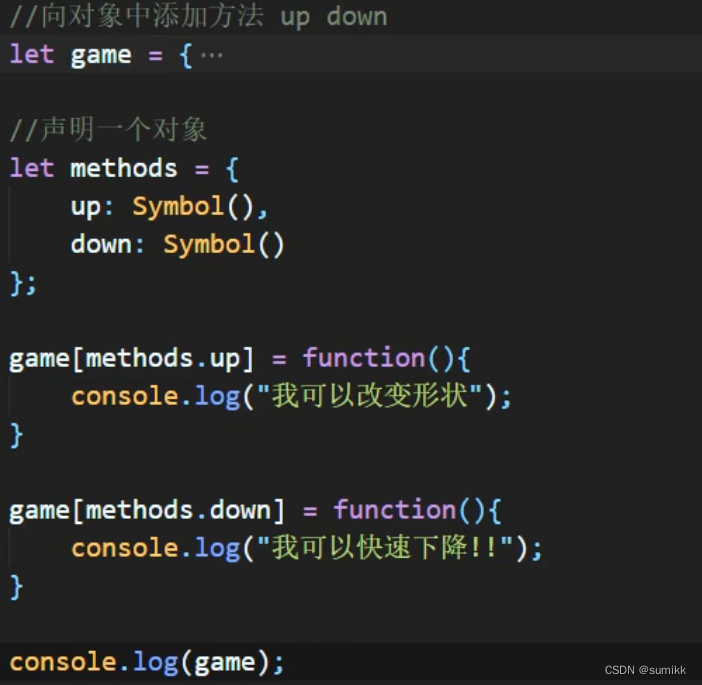
Symbol自己有11个内置属性
11.迭代器
迭代器(Iterator)是一种接口,为各种不同的数据结构提供统一的访问机制。任何数据结构只要部署Iterator接口,就可以完成遍历操作。
ES6创造了一种新的遍历命令for…of循环,Iterator接口主要供for…of消费
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
for (let v of arr) {
console.log(v) //a,b,c,d
}
for (let v in arr) {
console.log(v) //0,1,2,3
}工作原理:
a)创建一个指针对象,指向当前数据结构的起始位置
b)第一次调用对象的next方法,指针自动指向数据结构的第一个成员
c)接下来不断调用next方法,指针一直往后移动,知道指向最后一个成员
d)每次调用next方法返回一个包含value和done属性的对象
迭代器自定义遍历对象
//声明一个对象
const names = {
stus: [
'xiaoming',
'xiaotian',
'xiaoning',
'xiaohong'
],
[Symbol.iterator]() {
let index = 0;
let _this = this
return {
next: function () {
if (index < _this.stus.length) {
const result = {
value: _this.stus[index],
done: false
}
index++;
return result;
}
else {
return { value: undefined, done: true };
}
}
}
}
}
//遍历对象
for (let v of names) {
console.log(v)
}12.生成器
生成器其实就是一个含函数
(一)函数的声明
function * fun() {
console.log('xiong')
}与普通函数不同的是:声明的时候需要加“ * ”
(二)函数调用是一个迭代器对象,需要用next方法执行,也可以用for...of遍历
function* fun() {
console.log('aa')
}
let gofun = fun()
gofun.next()如果调用next方法时传入参数,则传入的参数将作为那一段yield的返回结果。第n次调用next传参数,等于第n-1次yield返回的结果。
function* fun() {
let one = yield 111;
console.log(one);
let two = yield 222;
console.log(two);
}
let gofun = fun()
console.log(gofun.next());
console.log(gofun.next(1));
console.log(gofun.next(2));(三)yield分割符
作用是将函数分隔成几段,以yield结束
function* fun() {
console.log('第一段')
yield 'aa'
console.log('第二段')
yield 'bb'
console.log('第三段')
}13.Promise
const p = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function{
let data = '成功'
resolve(data);
let eer = '失败';
reject(eer);
}, 1000)
})
//调用Promise 对象的then方法
p.then(function (res) {
console.log(res)
}), function (eer) {
console.log(eer)
}未完
14.集合和API
set
let s = new Set();
let s2 = new Set(['大事儿', '小事儿','好事儿','坏事儿','小事儿']);
//元素个数
console.log(s2.size)
//添加新的元素
s2.add('喜事儿');
//删除元素
s2.delete('坏事儿');
//检测
console.log(s2.has('糟心事'));
//清空
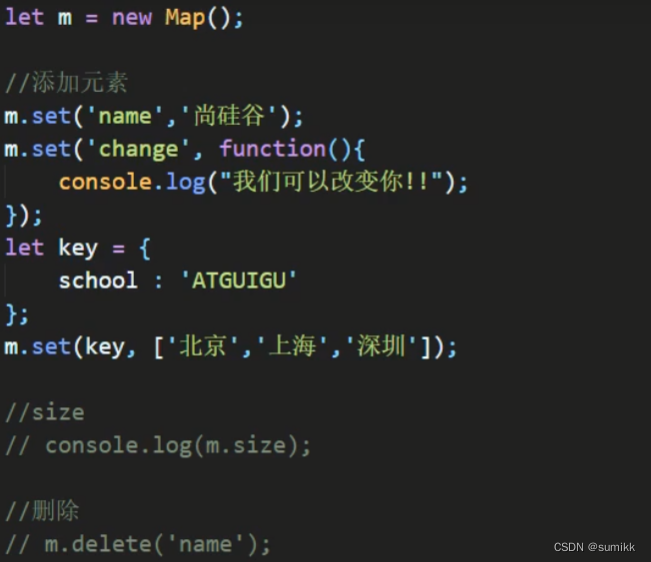
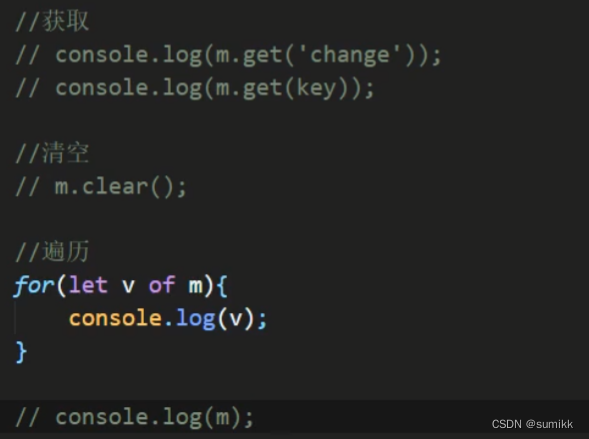
s2.clear()15.Map
类似于对象,也是键值对的集合。但是“键”的范围不限于字符串,各种类型的值(包括对象)都可以当作键。Map也可以实现iterator接口,所以可以使用扩展运算符和for...of进行遍历。
Map的属性和方法:
1)size 返回Map的元素个数
2)set 增加一个新元素,返回当前Map
3)get 返回个键名对象的键值
4)has 检测Map中是否包含某个元素,返回boolean值
5)clear 清空集合,返回underfined
参考例子:
16.class类
class作为对象的模板。通过class关键字,可以定义类。基本上,ES6的class可以只是一个语法糖,它的绝大部分功能,ES5都可以做到,新的class写法只是让对象原型的写法更加清晰、更像面向对象编程的语法而已
ES5
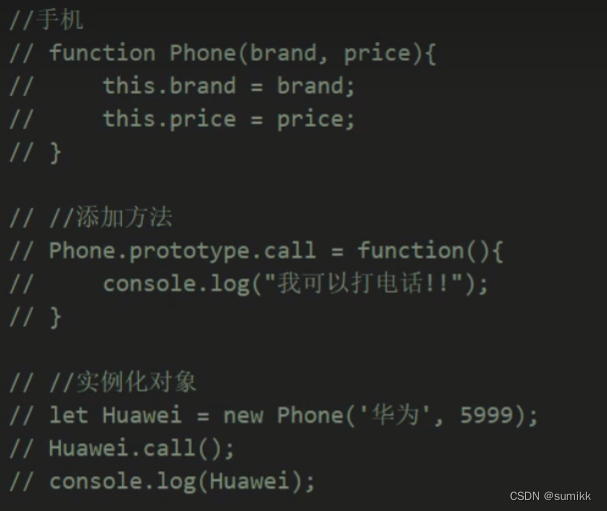
用class
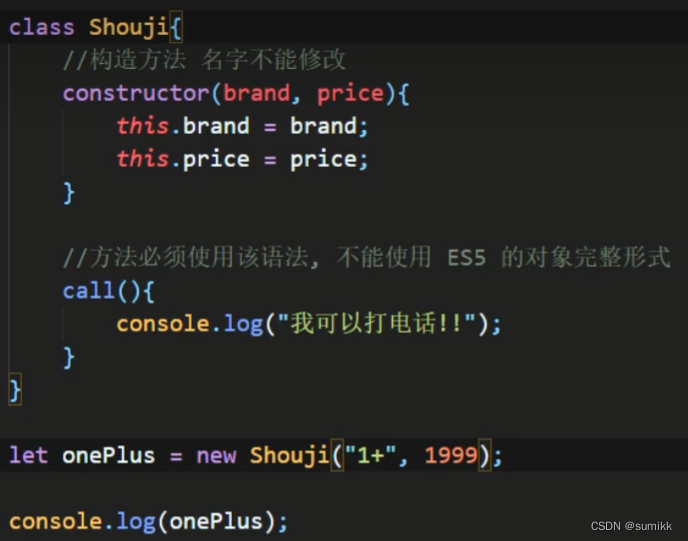
类的静态成员
class Phone {
//静态属性
static name = '手机';
static change() {
console.log('我可以改变世界')
}
}
let nokia = new Phone();
console.log(nokia.name) //undefined
console.log(Phone.name) //手机未完待续




















 2057
2057

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








