一. 关系图概览
二. 各层级概述
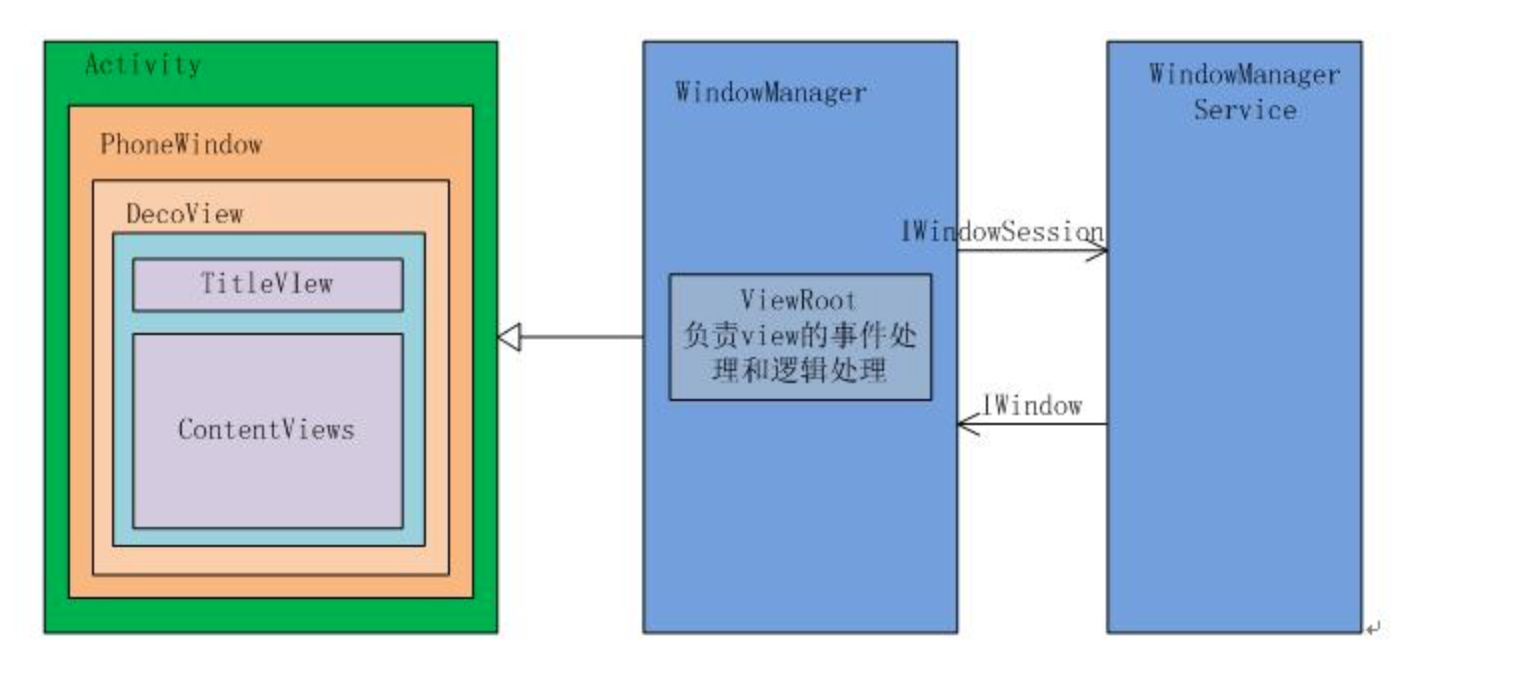
1. Activity
- Activity并不负责视图控制,它只是控制生命周期和处理事件。真正控制视图的是Window。
- 一个Activity包含了一个Window,Window才是真正代表一个窗口。
- Activity就像一个控制器,统筹视图的添加与显示,以及通过其他回调方法,来与Window、以及View进行交互。
2. Window
- Window是视图的承载器,内部持有一个 DecorView,而这个DecorView才是 view 的根布局。
- Window是一个抽象类,实际在Activity中持有的是其子类PhoneWindow。
- PhoneWindow中有个内部类DecorView,通过创建DecorView来加载Activity中设置的布局R.layout.activity_main。
- Window 通过WindowManager将DecorView加载其中,并将DecorView交给ViewRoot,进行视图绘制以及其他交互。
3. PhoneWindow
- 将Decoriew设置为整个应用窗口的根View,是Window的实现类。
- 它是Android中的最基本的窗口系统,每个Activity均会创建一个PhoneWindow对象,是Activity和整个View系统交互的接口。
4. DecorView
- DecorView是FrameLayout的子类,它可以被认为是Android视图树的根节点视图。
- DecorView作为顶级View,一般情况下它内部包含一个竖直方向的LinearLayout,在这个LinearLayout里面有上下三个部分,上面是个ViewStub,延迟加载的视图(应该是设置ActionBar,根据Theme设置),中间的是标题栏(根据Theme设置,有的布局没有),下面的是内容栏。 具体情况和Android版本及主体有关。
5. ViewRoot
- ViewRoot对应ViewRootImpl类,它是连接WindowManagerService和DecorView的纽带,View的三大流程(测量,布局,绘制)均通过ViewRoot来完成。
- ViewRoot并不属于View树的一份子。从源码实现上来看,它既非View的子类,也非View的父类,但是,它实现了ViewParent接口,这让它可以作为View的名义上的父视图。ViewRoot继承了Handler类,可以接收事件并分发,Android的所有触屏事件、按键事件、界面刷新等事件都是通过ViewRoot进行分发的。
6. WindowManager
- WindowManager 是 Android提供的一个接口,用于管理应用窗口的显示。它允许应用程序与系统窗口管理器交互,添加、更新或移除窗口。
- 开发者通常通过 Context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE) 获取其实例。
- WindowManager 是客户端(应用)用来与 WindowManagerService 通信的代理。
- 应用通过 WindowManager 提交窗口请求,最终由 WindowManagerService 统一调度和管理。
7. WindowManagerService
- WindowManagerService(简称 WMS)是 Android 系统的核心服务之一,运行在 System Server 进程中。
- 它负责管理所有窗口的布局、显示顺序、焦点控制、输入事件分发等核心功能。
- 它与底层的 SurfaceFlinger 交互,将窗口内容渲染到屏幕上。
三. 基于源码的深入分析
1. PhoneWindow,DecorView,setContentView源码理解
- Window
抽象基类,它提供了一系列窗口的方法,比如背景,标题等等,而它的唯一实现类则是PhoneWindow
/**
* Abstract base class for a top-level window look and behavior policy. An
* instance of this class should be used as the top-level view added to the
* window manager. It provides standard UI policies such as a background, title
* area, default key processing, etc.
*
* <p>The only existing implementation of this abstract class is
* android.view.PhoneWindow, which you should instantiate when needing a
* Window.
*/
public abstract class Window {
...
@Nullable
public View findViewById(@IdRes int id) {
return getDecorView().findViewById(id);
}
/**
* Convenience for * {@link #setContentView(View, android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams)}
* to set the screen content from a layout resource. The resource will be * inflated, adding all top-level views to the screen. * * @param layoutResID Resource ID to be inflated.
* @see #setContentView(View, android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams)
*/
public abstract void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID);
...
}
- PhoneWindow
Window的唯一实现类
public class PhoneWindow extends Window implements MenuBuilder.Callback {
private final static String TAG = "PhoneWindow";
...
// This is the top-level view of the window, containing the window decor.
private DecorView mDecor;
// This is the view in which the window contents are placed. It is either
// mDecor itself, or a child of mDecor where the contents go.
private ViewGroup mContentParent;
private ViewGroup mContentRoot;
...
}
在PhoneWindow里面,出现了成员变量DecorView的而这里,
- DecorView则是PhoneWindow里面的一个内部类,它是继承与FrameLayout
// 既然是FrameLayout,也就可以加载布局文件,也就是说,我们那些标题栏,内容栏,
/ 顶级上看是加载在DecorView上的。而DecorView则是由PhoneWindow负责添加
private final class DecorView extends FrameLayout implements RootViewSurfaceTaker {
/* package */int mDefaultOpacity = PixelFormat.OPAQUE;
/** The feature ID of the panel, or -1 if this is the application's DecorView */
private final int mFeatureId;
private final Rect mDrawingBounds = new Rect();
private final Rect mBackgroundPadding = new Rect();
private final Rect mFramePadding = new Rect();
private final Rect mFrameOffsets = new Rect();
....
}
- setContentView源码流程
activity.setContentView,实际上调用到的是它的实现类方法phoneWindow.setContentView
@Override
public void setContentView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
// 如果没有创建 mContentParent,则初始化 DecorView 和内容父布局
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
} else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
// 如果不使用过渡动画,直接移除旧内容
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
// 使用过渡动画时,将新 View 作为过渡内容添加
final Scene newScene = Scene.getSceneForLayout(mContentParent, view, mContext);
transitionTo(newScene);
} else {
// 否则直接添加 View 到内容父布局中
mContentParent.addView(view, params);
}
}
2. Activity启动到DecorView显示的流程
前置知识:
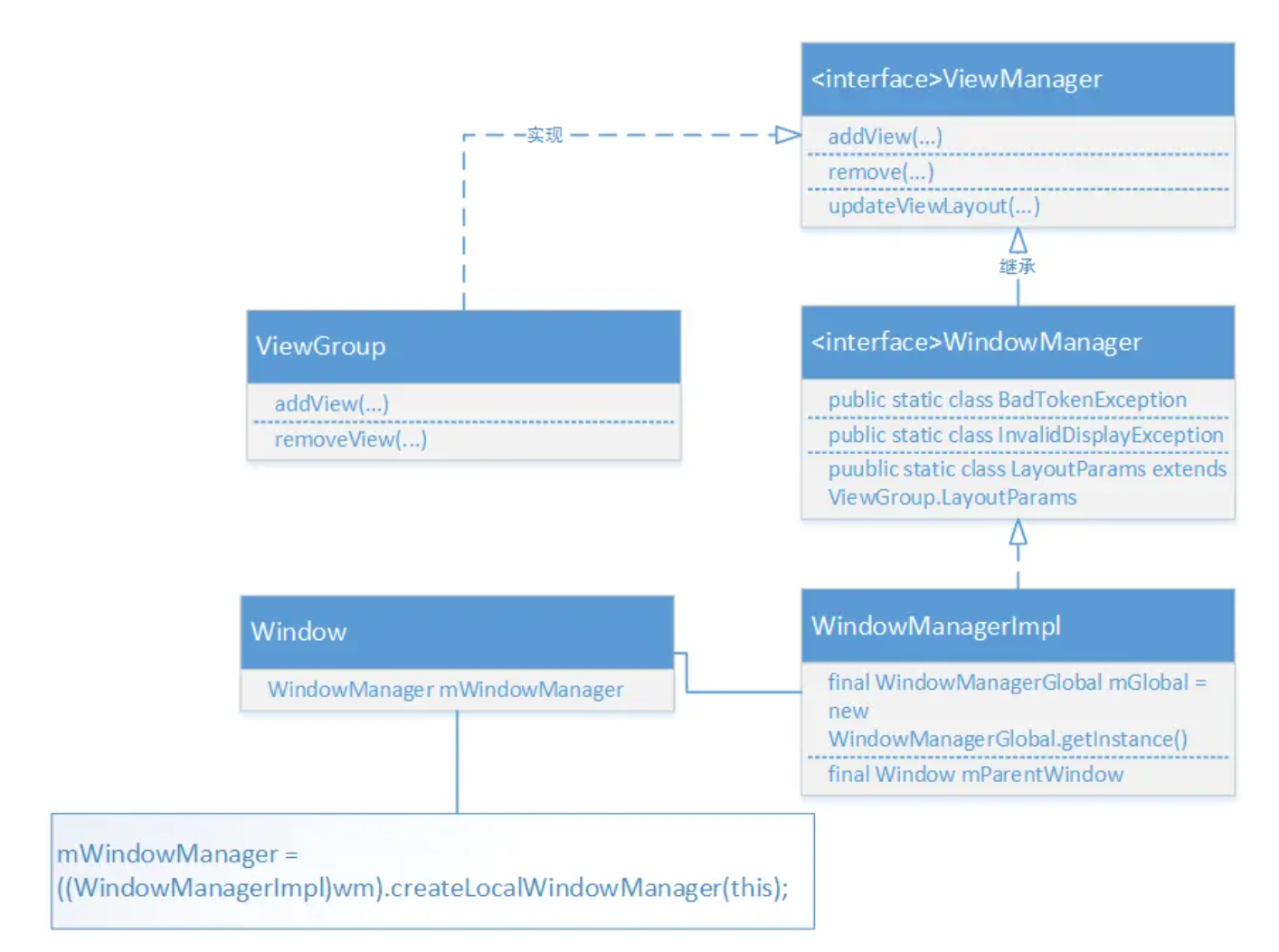
- ViewManager
- WindowManager
- WindowManagerImpl
2.1 ViewManager
- ViewManager接口定义了一组规则,也就是add、update、remove的操作View接口。
- ViewManager是用来添加和移除activity中View的接口,可以通过Context.getSystemService()获取实例。
/** Interface to let you add and remove child views to an Activity. To get an instance
- of this class, call {@link android.content.Context#getSystemService(java.lang.String) Context.getSystemService()}.
*/
public interface ViewManager
{
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params);
public void updateViewLayout(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params);
public void removeView(View view);
}
- ViewManager实现类ViewGroup
public abstract class ViewGroup extends View implements ViewParent, ViewManager {
private static final String TAG = "ViewGroup";
...
public void addView(View child, LayoutParams params) {
addView(child, -1, params);
}
/*
* @param child the child view to add
* @param index the position at which to add the child or -1 to add last
* @param params the layout parameters to set on the child
*/
public void addView(View child, int index, LayoutParams params) {
// addViewInner() will call child.requestLayout() when setting the new LayoutParams
// therefore, we call requestLayout() on ourselves before, so that the child's request
// will be blocked at our level
requestLayout();
invalidate(true);
addViewInner(child, index, params, false);
}
...
可以看到ViewGroup里面实现了ViewManager接口,View通过ViewGroup的addView方法添加到ViewGroup中,而ViewGroup层层嵌套到最顶级都会显示在在一个窗口Window中
2.2 WindowManager
- WindowManager是一个接口,而且它继承与ViewManager。WindowManager字面理解就是窗口管理器,每一个窗口管理器都与一个的窗口显示绑定
- 获取实例可以通过Context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE)获取。既然继承了ViewManager,那么它也就可以进行添加删除View的操作了,不过它的操作放在它的实现类WindowManagerImpl里面。
- BadTokenException:则是addView时它的LayoutParams无效则会被抛出,或是添加第二个View的时候没有移除第一个View则会被抛出
- InvalidDisplayException:如果一个窗口是在一个二级的显示上而指定的显示找不到则会被抛出
getDefaultDisplay:返回当前WindowManager管理的显示Display - removeViewImmediate:表示从窗口上移除View,一般是当View调用了onDetachedFromWindow也就是从Window上分开后,把它移除。
- LayoutParams:静态内部类。显然是Window的布局参数,里面定义了一系列的窗口属性
/* The interface that apps use to talk to the window manager.
Use Context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE) to get one of these.
*/
public interface WindowManager extends ViewManager {
public static class BadTokenException extends RuntimeException{...}
public static class InvalidDisplayException extends RuntimeException{...}
public Display getDefaultDisplay();
public void removeViewImmediate(View view);
public static class LayoutParams extends ViewGroup.LayoutParams
implements Parcelable
2.3 WindowManagerImpl
WindowManagerImpl里面有一个成员变量WindowManagerGlobal,而真正的实现则是在WindowManagerGlobal了,类似代理,只不过WindowManagerGlobal是个没有实现WindowManager的类的,自己定义了套实现。
public final class WindowManagerImpl implements WindowManager {
private final WindowManagerGlobal mGlobal = WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance();
private final Display mDisplay;
private final Window mParentWindow;
@Override
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mDisplay, mParentWindow);
}
...
@Override
public void removeView(View view) {
mGlobal.removeView(view, false);
}
}
- WindowManagerGlobal
public final class WindowManagerGlobal {
private static final String TAG = "WindowManager";
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
...
}
}
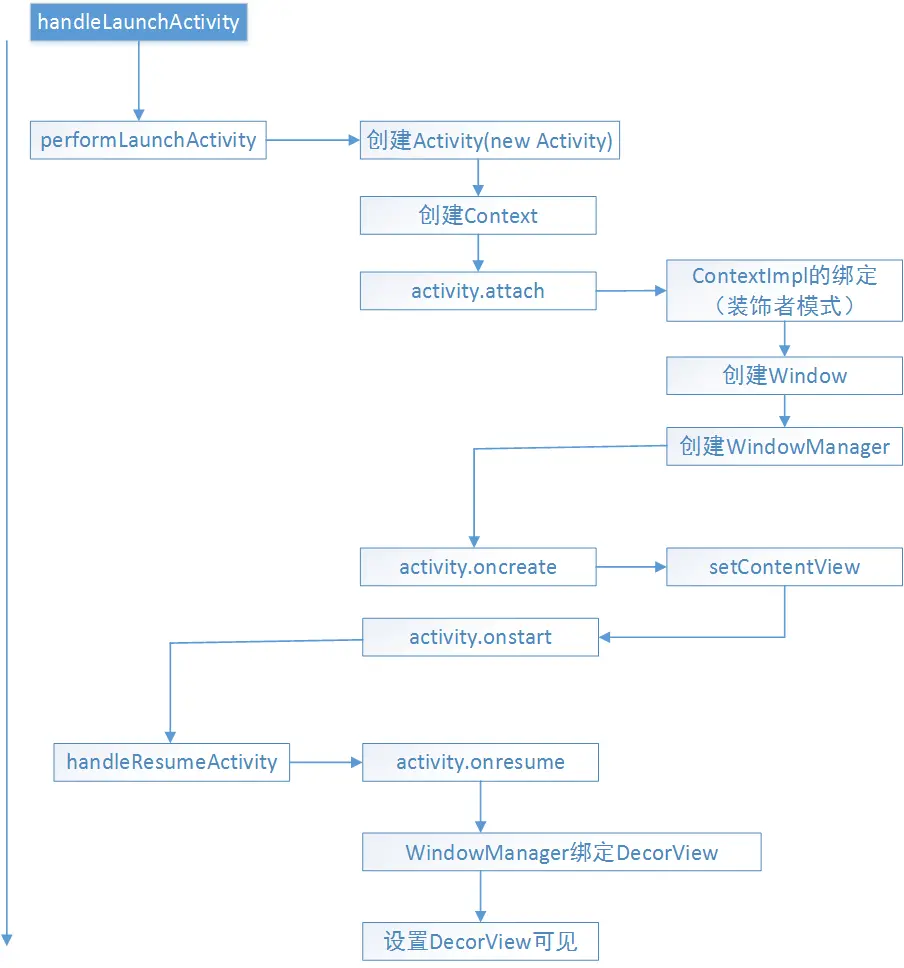
2.4 Activity启动到DecorView显示的流程
- Window,WindowManager,DecorView,WindowManagerGlobal的关系概念
- DecorView什么时候初始化?
setContentView() 是开发者在 Activity 中调用的方法,用于设置界面布局。
第一次调用该方法时,会触发 PhoneWindow 的初始化,并创建 DecorView。 - DecorView什么时候被添加
在DecorView在handleResumeActivity方法中被绑定到了WindowManager,也就是调用了windowManager.addView(decorView)
-
WindowManager 与 DecorView 的关系
Activity.setContentView()
↓
创建 PhoneWindow 和 DecorView
↓
Activity.onResume()
↓
WindowManager.addView(DecorView)
↓
创建 ViewRootImpl
↓
ViewRootImpl.setView(DecorView)
↓
与 WindowManagerService 通信,完成窗口显示 -
窗口添加流程调用关系链
WindowManager.addView()
↓
WindowManagerGlobal.addView()
↓
创建 ViewRootImpl
↓
ViewRootImpl.setView()
↓
与 WindowManagerService 通信注册窗口
本质是调用ViewRootImpl.setView
3. ViewRootImpl与View关系深入理解
3.1 基础概念理解
- ViewRootImpl,ViewRoot:ViewRoot类在Android2.2之后就被ViewRootImpl替换了。
- ViewRootImpl是一个视图层次结构的顶部,它实现了View与WindowManager之间所需要的协议,作为WindowManagerGlobal中大部分的内部实现。
- addView,removeView,update调用顺序:WindowManagerImpl -> WindowManagerGlobal -> ViewRootImp
3.2 源码理解
- ViewRootImp的setView方法
实际是一次IPC过程
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
...
// Schedule the first layout -before- adding to the window
// manager, to make sure we do the relayout before receiving
// any other events from the system.
requestLayout();
...
try {
...
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(),
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mInputChannel);
}
}
首先会调用到requestLayout(),表示添加Window之前先完成第一次layout布局过程,以确保在收到任何系统事件后面重新布局。requestLayout最终会调用performTraversals方法来完成View的绘制。
接着会通过WindowSession最终来完成Window的添加过程。在下面的代码中mWindowSession类型是IWindowSession,它是一个Binder对象,真正的实现类是Session,也就是说这其实是一次IPC过程,远程调用了Session中的addToDisPlay方法。
- requestLayout方法解读 (重点)
- checkThread 这里就是为什么子线程无法更新ui的原因所在
- scheduleTraversals最终调用的是performTraversals,经过measure、layout和draw三个过程才能将一个View绘制出来
@Override
public void requestLayout() {
if (!mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest) {
checkThread();
mLayoutRequested = true;
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
void checkThread() {
if (mThread != Thread.currentThread()) {
throw new CalledFromWrongThreadException(
"Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.");
}
}
3.3 重要结论
- DecorView真正的绘制在什么时候
DecorView真正的绘制显示是在activity.handleResumeActivity方法中DecorView被添加到WindowManager时候,也就是调用到windowManager.addView(decorView)。而在windowManager.addView方法中调用到windowManagerGlobal.addView,开始创建初始化ViewRootImpl,再调用到viewRootImpl.setView,最后是调用到viewRootImpl的performTraversals来进行view的绘制(measure,layout,draw),这个时候View才真正被绘制出来。
- 如何获取view的实际高度,在哪个时机
onCreate不可以:实际调用时机activity.handleResumeActivity最后调用到的是activity的onResume方法
onResume不可以:原因在于绘制是异步的
- 为什么在onCreate里面的子线程去更新UI的不报错(如果放置个button再去点击就报错)
ViewRootImpl的初始化有关,因为在onCreate的时候此时View还没被绘制出来,ViewRootImpl还未创建出来,它的创建是在activity.handleResumeActivity的调用到windowManager.addView(decorView)时候,如前面说的ViewRootImpl才被创建起来
- 每一个View对应一个ViewRoot
四. Dialog,PopupWindow,Toast窗口机制
仅介绍部分知识,更加详细的见 添加链接描述
1. WindowManager.LayoutParams
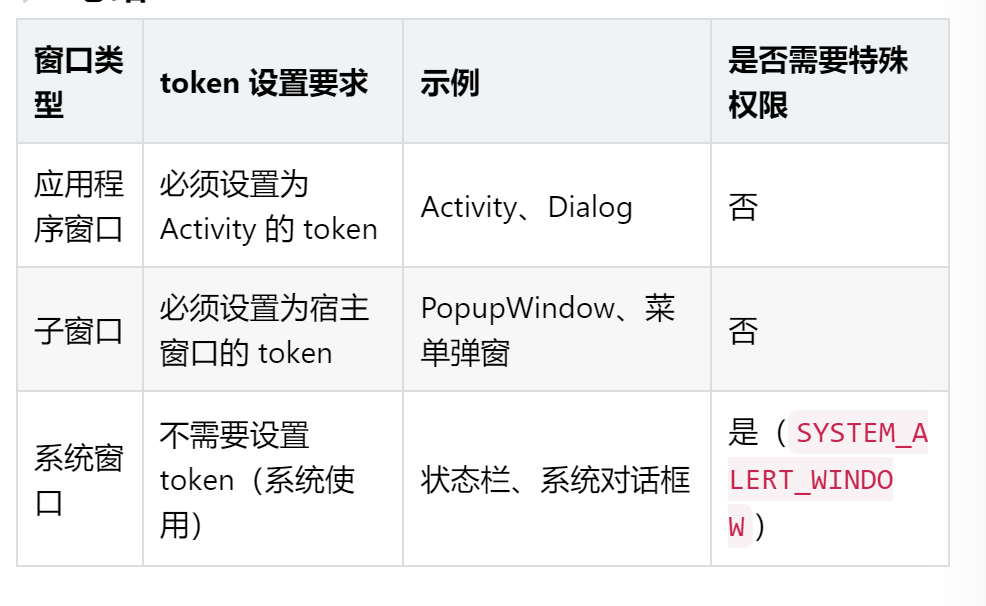
有三种窗口类型Type
- 应用程序窗口 : type值在 FIRST_APPLICATION_WINDOW ~ LAST_APPLICATION_WINDOW
须将token设置成Activity的token。
eg: 前面介绍的Activity窗口,Dialog - 子窗口: type值在 FIRST_SUB_WINDOW ~ LAST_SUB_WINDOW SubWindows与顶层窗口相关联,需将token设置成它所附着宿主窗口的token。
eg: PopupWindow(想要依附在Activity上需要将token设置成Activity的token) - 系统窗口: type值在 FIRST_SYSTEM_WINDOW ~ LAST_SYSTEM_WINDOW SystemWindows不能用于应用程序,使用时需要有特殊权限,它是特定的系统功能才能使用。
eg: Toast,输入法等。
public static class LayoutParams extends ViewGroup.LayoutParams
implements Parcelable {
//窗口的绝对XY位置,需要考虑gravity属性
public int x;
public int y;
//在横纵方向上为相关的View预留多少扩展像素,如果是0则此view不能被拉伸,其他情况下扩展像素被widget均分
public float horizontalWeight;
public float verticalWeight;
//窗口类型
//有3种主要类型如下:
//ApplicationWindows取值在FIRST_APPLICATION_WINDOW与LAST_APPLICATION_WINDOW之间,是常用的顶层应用程序窗口,须将token设置成Activity的token;
//SubWindows取值在FIRST_SUB_WINDOW和LAST_SUB_WINDOW之间,与顶层窗口相关联,需将token设置成它所附着宿主窗口的token;
//SystemWindows取值在FIRST_SYSTEM_WINDOW和LAST_SYSTEM_WINDOW之间,不能用于应用程序,使用时需要有特殊权限,它是特定的系统功能才能使用;
public int type;
//WindowType:开始应用程序窗口
public static final int FIRST_APPLICATION_WINDOW = 1;
//WindowType:所有程序窗口的base窗口,其他应用程序窗口都显示在它上面
public static final int TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION = 1;
//WindowType:普通应用程序窗口,token必须设置为Activity的token来指定窗口属于谁
public static final int TYPE_APPLICATION = 2;
//WindowType:应用程序启动时所显示的窗口,应用自己不要使用这种类型,它被系统用来显示一些信息,直到应用程序可以开启自己的窗口为止
public static final int TYPE_APPLICATION_STARTING = 3;
//WindowType:结束应用程序窗口
public static final int LAST_APPLICATION_WINDOW = 99;
//WindowType:SubWindows子窗口,子窗口的Z序和坐标空间都依赖于他们的宿主窗口
public static final int FIRST_SUB_WINDOW = 1000;
//WindowType: 面板窗口,显示于宿主窗口的上层
......
public final int copyFrom(LayoutParams o) {
......
}
......
public void scale(float scale) {
......
}
......
}
2. token
- token是用来表示窗口的一个令牌,只有符合条件的token才能被WMS通过添加到应用上。
- 首先对于Activity里面的token,它的创建则是在AMS启动Activity开始的,之后保存在ActivityRecord.appToken中。而对于Activity中的token绑定到对应的Window上(具体是在activity.attach方法中创建的)
五. 思维导图























 665
665

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








