Leakcanary是square推出的内存泄露分析工具,使用很简单,可谓“傻瓜式”应用。
但其内部原理实现直的深究学习,今天我们就层层剖析其使用方式、源码实现,了解一下大牛是如何写代码的。
前期知识点准备:内存泄漏 GC回收原理 java四种引用等等。
一、使用方法
1、gradle中添加依赖,目前最新版本为1.6.1
debugImplementation 'com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android:1.6.1'//debug版本
releaseImplementation 'com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android-no-op:1.6.1'//发布版本,将该工具失效,避免影响线上业务2、Application类中调用 LeakCanary.install(this);即可以开启该工具监控Activity内存泄漏,其他对象fragmen、service等其他对象的监控需要在对应类的中调用refWatcher.watch(this);
public class MyApplacition extends Application {
static MyApplacition instance;
private RefWatcher refWatcher;
public static RefWatcher getRefWatcher(Context context) {
return instance.refWatcher;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
if (LeakCanary.isInAnalyzerProcess(this)) {
// This process is dedicated to LeakCanary for heap analysis.
// You should not init your app in this process.
return;
}
LeakCanary.install(this);
public class MyFragment extends Fragment {
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
RefWatcher refWatcher = Myapplacition.getRefWatcher(getActivity());
refWatcher.watch(this);
// RefWatcher refWatcher = LeakCanary.installedRefWatcher();//1.6.1版本中提供该方法获取refWatcher对象,之前的版本需要按上面方法自行获取。另,android8.0以上工具中添加了fragment的生命周期监测,不需要再添加此处代码。
}二、源码分析
在讲源码之前,先上一段栗子,
void refTest(){
A a = new A();//a为强引用
ReferenceQueue queue = new ReferenceQueue();
WeakReference aa = new WeakReference(a, queue);//aa为弱引用
a = null;
Runtime.getRuntime().gc();//通知系统GC
System.runFinalization();//强制系统回收已经没有强引用的对象
Reference poll = null;
while ((poll = queue.poll()) != null) {
Log.i(TAG,"Reference"+poll.toString());
}
}以上这段代码中,强引用a置为null,则A对象只有aa这个弱引用存在。之后手动触发GC,log中可以看到aa的弱引用已经放到了引用队列中,说明A对象已经被回收。Leakcanary就是(1)利用此原理初步定位内存泄漏对象后,(2)再调用系统接口dump出堆转储文件快照.hprof,(3)调用haha库分析该文件解析出最短引用路径,(4)提示给用户的。
如图所示
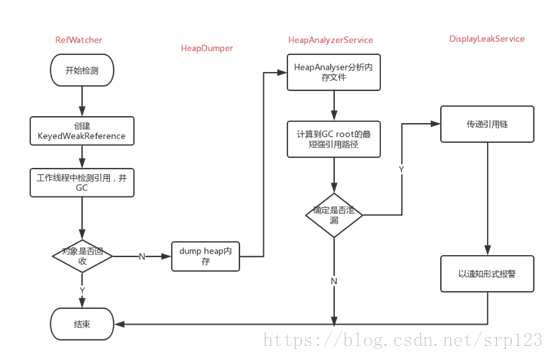
1、初步定位内存泄漏对象
(1)//在调用LeakCanary的intsall方法之后,会调用buildAndInstall()生成refWatcher对象
public RefWatcher buildAndInstall() {
if (LeakCanaryInternals.installedRefWatcher != null) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("buildAndInstall() should only be called once.");
}
RefWatcher refWatcher = build();//构造模式,获取RefWatcher对象
if (refWatcher != DISABLED) {
if (watchActivities) {//监控activity,默认为true
ActivityRefWatcher.install(context, refWatcher);
}
if (watchFragments) {//监控fragment,默认为true
FragmentRefWatcher.Helper.install(context, refWatcher);
}
}
LeakCanaryInternals.installedRefWatcher = refWatcher;
return refWatcher;
}(2)//refWatcher开始监控Activity、Fragment等对象
public final class ActivityRefWatcher {
public static void installOnIcsPlus(Application application, RefWatcher refWatcher) {
install(application, refWatcher);
}
public static void install(Context context, RefWatcher refWatcher) {
Application application = (Application) context.getApplicationContext();
ActivityRefWatcher activityRefWatcher = new ActivityRefWatcher(application, refWatcher);
application.registerActivityLifecycleCallbacks(activityRefWatcher.lifecycleCallbacks);
}
private final Application.ActivityLifecycleCallbacks lifecycleCallbacks =
new ActivityLifecycleCallbacksAdapter() {
@Override public void onActivityDestroyed(Activity activity) {
refWatcher.watch(activity);
}
};public interface FragmentRefWatcher {
void watchFragments(Activity activity);
final class Helper {
private static final String SUPPORT_FRAGMENT_REF_WATCHER_CLASS_NAME =
"com.squareup.leakcanary.internal.SupportFragmentRefWatcher";
public static void install(Context context, RefWatcher refWatcher) {
List<FragmentRefWatcher> fragmentRefWatchers = new ArrayList<>();
if (SDK_INT >= O) {
fragmentRefWatchers.add(new AndroidOFragmentRefWatcher(refWatcher));
}(3)//Android8.0以上引入了fragment的生命周期,用户不需要在onDestroy中自行调用
@RequiresApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.O) //
class AndroidOFragmentRefWatcher implements FragmentRefWatcher {
private final RefWatcher refWatcher;
AndroidOFragmentRefWatcher(RefWatcher refWatcher) {
this.refWatcher = refWatcher;
}
private final FragmentManager.FragmentLifecycleCallbacks fragmentLifecycleCallbacks =
new FragmentManager.FragmentLifecycleCallbacks() {
@Override
public void onFragmentDestroyed(FragmentManager fm, Fragment fragment) {
refWatcher.watch(fragment);
}
};
(4)//生成唯一key标识对象,并建立该对象的弱引用关联到引用队列,如上述栗子中所示。
//其中retainedKeys为CopyOnWriteArraySet类型,解决并发读写问题
public void watch(Object watchedReference, String referenceName) {
if (this == DISABLED) {
return;
}
checkNotNull(watchedReference, "watchedReference");
checkNotNull(referenceName, "referenceName");
final long watchStartNanoTime = System.nanoTime();
String key = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
retainedKeys.add(key);
final KeyedWeakReference reference =
new KeyedWeakReference(watchedReference, key, referenceName, queue);
ensureGoneAsync(watchStartNanoTime, reference);
}(5)//watchExecutor子线程中进行分析
private void ensureGoneAsync(final long watchStartNanoTime, final KeyedWeakReference reference) {
watchExecutor.execute(new Retryable() {
@Override public Retryable.Result run() {
return ensureGone(reference, watchStartNanoTime);
}
});
}
(6)//初步分析定位出泄漏对象
@SuppressWarnings("ReferenceEquality") // Explicitly checking for named null.
Retryable.Result ensureGone(final KeyedWeakReference reference, final long watchStartNanoTime) {
long gcStartNanoTime = System.nanoTime();
long watchDurationMs = NANOSECONDS.toMillis(gcStartNanoTime - watchStartNanoTime);
removeWeaklyReachableReferences();//retainedKeys中,移除未泄露的对象(弱引用已被GC添加到引用队列的对象)
if (debuggerControl.isDebuggerAttached()) {
// The debugger can create false leaks.
return RETRY;
}
if (gone(reference)) {//未泄露则返回,结束此次分析
return DONE;
}
gcTrigger.runGc();//手动GC
removeWeaklyReachableReferences();//再次移除未泄漏对象
if (!gone(reference)) {//初步确认该对象内存泄漏
long startDumpHeap = System.nanoTime();
long gcDurationMs = NANOSECONDS.toMillis(startDumpHeap - gcStartNanoTime);
File heapDumpFile = heapDumper.dumpHeap();//生成hprof文件
if (heapDumpFile == RETRY_LATER) {
// Could not dump the heap.
return RETRY;
}
long heapDumpDurationMs = NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - startDumpHeap);
HeapDump heapDump = heapDumpBuilder.heapDumpFile(heapDumpFile).referenceKey(reference.key)
.referenceName(reference.name)
.watchDurationMs(watchDurationMs)
.gcDurationMs(gcDurationMs)
.heapDumpDurationMs(heapDumpDurationMs)
.build();
heapdumpListener.analyze(heapDump);//分析hprof文件
}
return DONE;
}
private boolean gone(KeyedWeakReference reference) {
return !retainedKeys.contains(reference.key);
}
private void removeWeaklyReachableReferences() {
// WeakReferences are enqueued as soon as the object to which they point to becomes weakly
// reachable. This is before finalization or garbage collection has actually happened.
KeyedWeakReference ref;
while ((ref = (KeyedWeakReference) queue.poll()) != null) {
retainedKeys.remove(ref.key);
}
}2、调用系统接口dump出堆转储文件快照.hprof
@SuppressWarnings("ReferenceEquality") // Explicitly checking for named null.
@Override public File dumpHeap() {
File heapDumpFile = leakDirectoryProvider.newHeapDumpFile();
if (heapDumpFile == RETRY_LATER) {
return RETRY_LATER;
}
FutureResult<Toast> waitingForToast = new FutureResult<>();
showToast(waitingForToast);//在开始生成hprof文件之前,在主线程中显示toast,如附图
if (!waitingForToast.wait(5, SECONDS)) {//等待主线程完成toast的展示
CanaryLog.d("Did not dump heap, too much time waiting for Toast.");
return RETRY_LATER;
}
Notification.Builder builder = new Notification.Builder(context)
.setContentTitle(context.getString(R.string.leak_canary_notification_dumping));
Notification notification = LeakCanaryInternals.buildNotification(context, builder);
NotificationManager notificationManager =
(NotificationManager) context.getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
int notificationId = (int) SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
notificationManager.notify(notificationId, notification);
Toast toast = waitingForToast.get();
try {
Debug.dumpHprofData(heapDumpFile.getAbsolutePath());//调用系统方法生成.hprof文件
cancelToast(toast);
notificationManager.cancel(notificationId);
return heapDumpFile;
} catch (Exception e) {
CanaryLog.d(e, "Could not dump heap");
// Abort heap dump
return RETRY_LATER;
}
}
private void showToast(final FutureResult<Toast> waitingForToast) {
mainHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
final Toast toast = new Toast(context);
toast.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL, 0, 0);
toast.setDuration(Toast.LENGTH_LONG);
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
toast.setView(inflater.inflate(R.layout.leak_canary_heap_dump_toast, null));
show(toast);
// Waiting for Idle to make sure Toast gets rendered.
Looper.myQueue().addIdleHandler(new MessageQueue.IdleHandler() {
@Override public boolean queueIdle() {
waitingForToast.set(toast);
return false;
}
});
}
});
}
3、调用haha库分析该文件解析出最短引用路径
和MAT分析.hprof文件类似,此处调用haha开源库分析出最短引用路径。
haha库的github路径https://github.com/square/haha。
4、提示用户
将分析出的结果最终通过DisplayLeakService在状态栏提示展示出来,通知用户。点击通知调起DisplayLeakActivity显示泄露信息,即最短引用路径。这两给类是另开进程的,在桌面上可以看到leakcanry的图标就是在DisplayLeakActivity中配置的,至于另开进程的原因,应该是为了避免占用主应用的内存。
三、示例
1、线程泄露
在ativity中调用此方法,然后按返回键结束activity。
void startAsyncWork() {
// This runnable is an anonymous class and therefore has a hidden reference to the outer
// class MainActivity. If the activity gets destroyed before the thread finishes (e.g. rotation),
// the activity instance will leak.
Runnable work = new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
// Do some slow work in background
SystemClock.sleep(20000);
}
};
Thread thread=new Thread(work);
thread.start();
}测试结果如下:
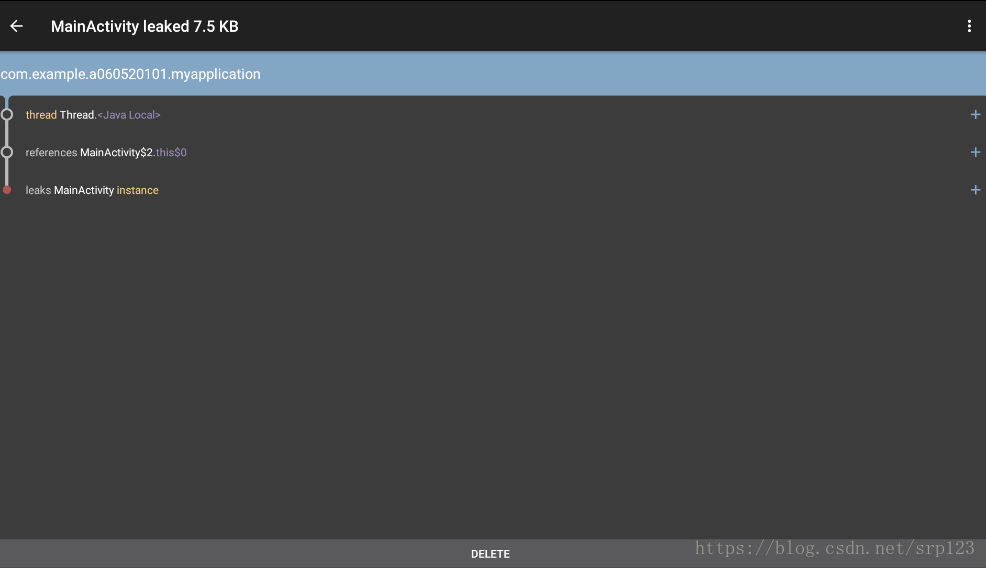
结果中显示MainActivity存在泄漏,原因是被this指针引用,this指针就是java中非静态内部类对外部类默认的引用,this指针被thread持有,而thread里面有耗时任务。所以在Activity结束的时候,因为thread的耗时任务没有执行完,导致Activity不能销毁,出现泄漏。
2、handler泄露
Activity中,直接new handler发送延迟消息,出现泄漏。改为弱引用,则不出现泄漏,原理同上面栗子。
public class HandlerActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.handlerac_layout);
handler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(0, 10 * 60 * 1000);
// new WeakHandler(this).sendEmptyMessageDelayed(0, 10 * 60 * 1000);
findViewById(R.id.gc).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
finish();
}
});
}
Handler handler = new Handler(){
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
Log.i("HandlerActivity","接收消息") ;
}
};
private static class WeakHandler extends Handler {
WeakReference<HandlerActivity> weakReference;
public WeakHandler(HandlerActivity activity) {
weakReference = new WeakReference<HandlerActivity>(activity);
}
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
HandlerActivity activity = weakReference.get();
if (activity != null && activity.tvHandler != null) {
Log.i("HandlerActivity","接收消息") ;
}
}
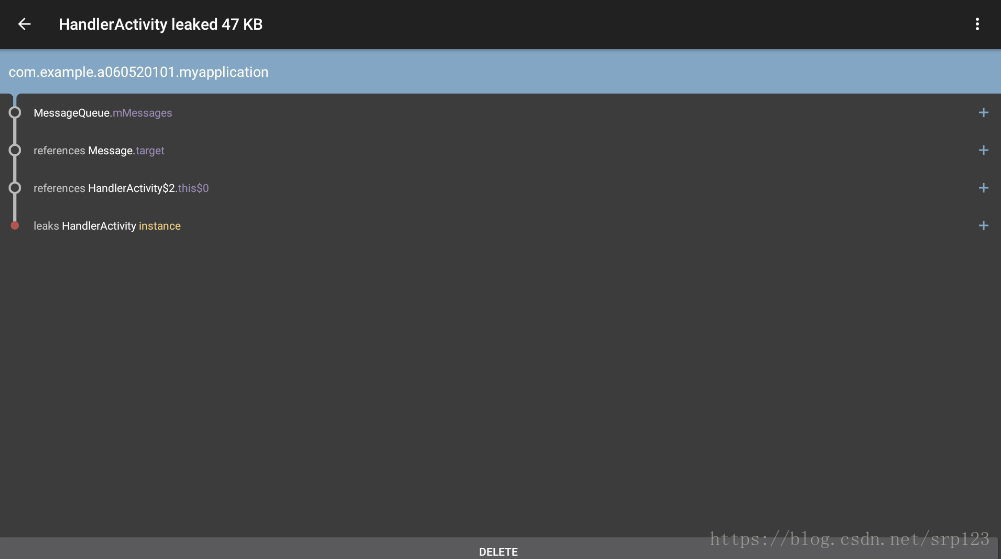
}测试结果如下:
this指针被Message.target即handler对象持有,在new handler时会关联到当前线程的looper,而looper创建了messagequeue对象,所以handler最终被messagequeue持有。栗子中发送了延时任务,所以Activity结束时,因为MessageQueue队列中的消息没有结束,导致Activity泄漏。
3、单例泄漏
4、io资源未关闭
5、注册未反注册
6、静态activity、静态view等
其他栗子类似,也是常见的一些泄漏问题。
四、其他
leakcanar中一些比较好的用法,也值得我们借鉴一下
1、自定义结果处理
使用中可以继承DisplayLeakService 自定义分析结果处理方式,比如上传服务器等,只需要将自定义的sevice传到rewatcher对象中,因为其参数类型设计为边界上限的泛型Class<? extends AbstractAnalysisResultService> listenerServiceClass,在开发中可以借鉴这种方式,提升代码的扩展性。
//继承类
public class LeakUploadService extends DisplayLeakService {
static final String TAG="ReferenceQueue";
@Override
protected void afterDefaultHandling(HeapDump heapDump, AnalysisResult result, String leakInfo) {
if (!result.leakFound || result.excludedLeak) {
return;
}
Log.i(TAG,"leakInfo"+leakInfo);//传参
RefWatcher refWatcher = LeakCanary.refWatcher(this)
.listenerServiceClass(LeakUploadService.class)
.buildAndInstall();2、多线程同步
源码中的showtoast方法,使用了CountDownLatch实现主线程和子线程之间的同步。
public final class FutureResult<T> {
private final AtomicReference<T> resultHolder;
private final CountDownLatch latch;
public FutureResult() {
resultHolder = new AtomicReference<>();
latch = new CountDownLatch(1);//子线程等待主线程展示toast,计数为1
}
public boolean wait(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
try {
return latch.await(timeout, unit);//计数结束
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Did not expect thread to be interrupted", e);
}
}
public T get() {
if (latch.getCount() > 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Call wait() and check its result");
}
return resultHolder.get();
}
public void set(T result) {
resultHolder.set(result);
latch.countDown();
}
}3、并发读写
CopyOnWrite的读写数据,解决并发读写问题
retainedKeys = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>();
4、当前进程判断
因为heap文件的分析服务、结果处理服务、结果展示activity都是新开进程的,二新的进程会触发application的oncreate,所以调用该方法判断当前进程是否为leakcanary新开的进程。
public static boolean isInServiceProcess(Context context, Class<? extends Service> serviceClass) {
PackageManager packageManager = context.getPackageManager();
PackageInfo packageInfo;
try {
packageInfo = packageManager.getPackageInfo(context.getPackageName(), GET_SERVICES);
} catch (Exception e) {
CanaryLog.d(e, "Could not get package info for %s", context.getPackageName());
return false;
}
String mainProcess = packageInfo.applicationInfo.processName;
ComponentName component = new ComponentName(context, serviceClass);
ServiceInfo serviceInfo;
try {
serviceInfo = packageManager.getServiceInfo(component, 0);
} catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException ignored) {
// Service is disabled.
return false;
}
if (serviceInfo.processName.equals(mainProcess)) {
CanaryLog.d("Did not expect service %s to run in main process %s", serviceClass, mainProcess);
// Technically we are in the service process, but we're not in the service dedicated process.
return false;
}
int myPid = android.os.Process.myPid();
ActivityManager activityManager =
(ActivityManager) context.getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
ActivityManager.RunningAppProcessInfo myProcess = null;
List<ActivityManager.RunningAppProcessInfo> runningProcesses;
try {
runningProcesses = activityManager.getRunningAppProcesses();
} catch (SecurityException exception) {
// https://github.com/square/leakcanary/issues/948
CanaryLog.d("Could not get running app processes %d", exception);
return false;
}
if (runningProcesses != null) {
for (ActivityManager.RunningAppProcessInfo process : runningProcesses) {
if (process.pid == myPid) {
myProcess = process;
break;
}
}
}
if (myProcess == null) {
CanaryLog.d("Could not find running process for %d", myPid);
return false;
}
return myProcess.processName.equals(serviceInfo.processName);
}5、构造模式
类似dialog的builder,rewatcher对象采用了构造模式,通过rewatcherbuilder生成。

6、IdleHandler
源码中多处使用idlehandler,是一种很巧妙的用法,首先触发UI更新操作,然后等待主线程空闲,则说明主线程已经完成UI更新操作,继而执行下一步操作。
// Waiting for Idle to make sure Toast gets rendered.
Looper.myQueue().addIdleHandler(new MessageQueue.IdleHandler() {
@Override public boolean queueIdle() {
waitingForToast.set(toast);
return false;
}
});7、手动gc
源码中使用该方法保证只有弱引用的对象被回收,即首先调用Runtime.gc(),等待100ms后,再调用System.runFinalization()强制系统回收已经没有强引用的对象释放内存,并确保该对象的弱引用被添加到引用队列。
public interface GcTrigger {
GcTrigger DEFAULT = new GcTrigger() {
@Override public void runGc() {
// Code taken from AOSP FinalizationTest:
// https://android.googlesource.com/platform/libcore/+/master/support/src/test/java/libcore/
// java/lang/ref/FinalizationTester.java
// System.gc() does not garbage collect every time. Runtime.gc() is
// more likely to perfom a gc.
Runtime.getRuntime().gc();
enqueueReferences();
System.runFinalization();
}8、 监控对象类型
rewatcher的watch方法入参是object类型,所以本质上是可以监控任意对象类型的,关键在于监控的时机,像activity、service、fragmen是有生命周期的,可以在ondestroy时开始监控,其他的对象类型用户可以选择合适的时机调用该方法进行监控,所以网上一般说的leakcanary只能监控activity是不准确的。
public void watch(Object watchedReference) {







 本文深入剖析LeakCanary内存泄漏分析工具。先介绍使用方法,包括gradle添加依赖和在特定类中调用监控方法;接着分析源码,阐述其定位内存泄漏对象、生成堆转储文件、解析最短引用路径及提示用户的原理;还给出线程、handler等泄漏示例;最后介绍其一些优秀用法。
本文深入剖析LeakCanary内存泄漏分析工具。先介绍使用方法,包括gradle添加依赖和在特定类中调用监控方法;接着分析源码,阐述其定位内存泄漏对象、生成堆转储文件、解析最短引用路径及提示用户的原理;还给出线程、handler等泄漏示例;最后介绍其一些优秀用法。
















 4万+
4万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








