遍历时删除
在遍历List的时时候对List进行remove()后,出现ConcurrentModificationException的问题分析和解决
代码1:
@Test
public void test02(){
List<People> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new People("张三",21,"男"));
list.add(new People("小红",20,"女"));
for (People p:
list) {
System.out.println(p);
if("张三".equals(p.name)) list.remove(p);
}
}
代码1的执行结果
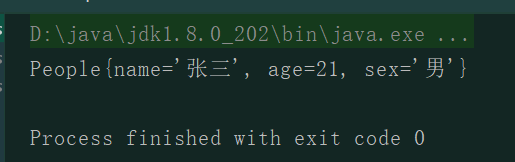
这里并没有出现ConcurrentModificationException
代码2:
@Test
public void test02(){
List<People> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new People("张三",21,"男"));
list.add(new People("小红",20,"女"));
list.add(new People("李四",21,"男"));
for (People p:
list) {
System.out.println(p);
if("张三".equals(p.name)) list.remove(p);
}
}
代码2的执行结果:
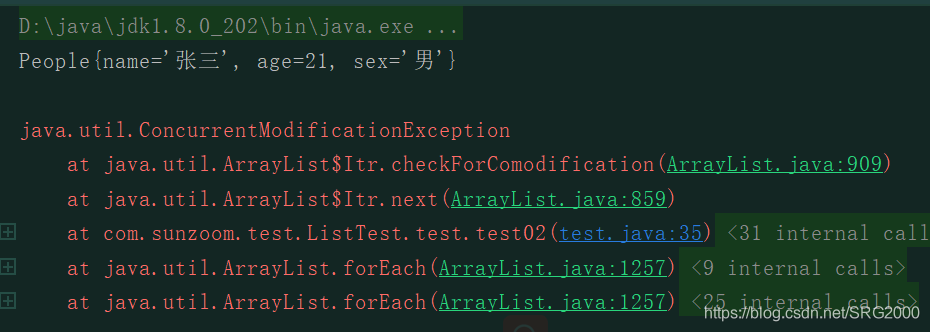
这里出现了ConcurrentModificationException
分析
我们这里采用的是foreach遍历,foreach 最终会被转换成迭代器遍历的形式。让我们看看ArrayList里的源码中的next() 和hasNext()
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
next()中的checkForComodification()方法如下
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
在代码1中,我们的list只有2个People实例
- 开始第一次遍历的时候,迭代器的cursor为0,ArrayList的size为2,此时hasNext()为True
- 然后我们在删除第一个People实例,在第二次遍历的时候,迭代器的cursor为1,ArrayList的size为1
- 此时hasNext()为false,退出遍历。所以代码1的执行结果为一行输出people实例。
在代码2中,我们的list有3个People实例
- 开始第一次遍历的时候,迭代器的cursor为0,ArrayList的size为2,此时hasNext()为True;
- 然后我们删除第一个People实例,在第二次遍历的时候,迭代器的cursor为1,ArrayList的size为2,此时hasNext()仍为true,并没有退出遍历
- 而这时在去调用next()的的时候,next()会去调用checkForComodification()而这时的modCount为4,expectedModCount为3,所以抛出ConcurrentModificationException。
而modCount和expectedModCount是如何计算?
在获取迭代器的时候,迭代器的expectedModCount赋值为list的modCount,如代码2中为3,而往后的list进行remove或者是add等操作时modCount都会进行++操作,这就导致了checkForComodification()时抛出异常。
**解决方法**
1、不要在 foreach 循环里进行元素的 remove/add 操作,remove 元素使用 Iterator 方式
@Test
public void test03(){
List<People> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new People("张三",21,"男"));
list.add(new People("小红",20,"女"));
list.add(new People("李四",21,"男"));
Iterator<People> itr = list.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
People p = itr.next();
if("小红".equals(p.name)){
itr.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(list);
}
2、使用下标来进行删除
@Test
public void test04(){
List<People> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new People("张三",21,"男"));
list.add(new People("小红",20,"女"));
list.add(new People("李四",21,"男"));
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
if ("张三".equals(list.get(i).name)) {
list.remove(i);
}
}
System.out.println(list);
}







 本文解析了在遍历List过程中进行元素删除时出现ConcurrentModificationException的原因,并提供了两种有效的解决方案。
本文解析了在遍历List过程中进行元素删除时出现ConcurrentModificationException的原因,并提供了两种有效的解决方案。

















 680
680

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










