作者简介:大家好,我是码炫码哥,前中兴通讯、美团架构师,现任某互联网公司CTO,兼职码炫课堂主讲源码系列专题
代表作:《jdk源码&多线程&高并发》,《深入tomcat源码解析》,《深入netty源码解析》,《深入dubbo源码解析》,《深入springboot源码解析》,《深入spring源码解析》,《深入redis源码解析》等
联系qq:184480602,加我进群,大家一起学习,一起进步,一起对抗互联网寒冬。码炫课堂的个人空间-码炫码哥个人主页-面试,源码等
回答
以注解为例。
Spring 容器在启动时会扫描 @Controller 或 @RestController,然后解析类和方法上面的注解,将路径和处理器方法(handler method)之间的映射关系存储起来。当请求到达时,我们只需要根据 request 从注册表中匹配对应的 handler method 即可。
详解
原理很简单,其实内部实现并不简单。我们直接看源码。
DispatcherServlet 中的 doDispatch() 是处理请求的核心逻辑,其中的 getHandler() 就是根据 request 获取对应的 Handler:
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
HandlerMapping 是来将请求 URL 映射到具体的 Handler 的核心组件,它内部包含了 url 和 Controller&Method 的映射关系。Spring MVC 内置了多种实现:
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping:根据 Bean 的名称来匹配 URL。ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping:已废弃。RequestMappingHandlerMapping:Spring MVC 默认使用的HandlerMapping实现。通过注解@RequestMapping或其他请求映射注解(如@GetMapping,@PostMapping)来映射处理器。SimpleUrlHandlerMapping:使用配置文件中的 URL 映射,例如通过 bean 的配置来手动指定 URL 和 Handler 的对应关系。DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping:已废弃。RouterFunctionMapping:使用函数式风格定义路由。Spring 5 引入,用于响应式 Web 应用(WebFlux)。SimpleServletHandlerAdapter:辅助映射 Servlet 类型的 Bean。一般用于兼容传统的 Servlet 组件。
码哥的应用中主要有四种,如下:
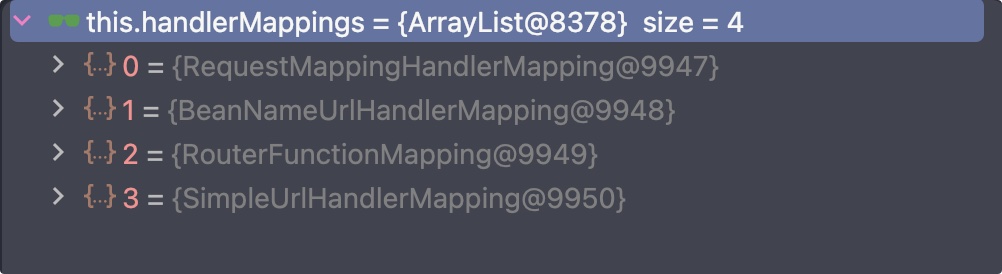
我们目前主要是使用 RequestMappingHandlerMapping,所以我们直接看它的 getHandler():
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
// 省略很多代码....
}
调用 getHandlerInternal() ,该方法由子类实现,我们直接看 RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping 就可以了:
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
request.removeAttribute(PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE);
try {
return super.getHandlerInternal(request);
}
finally {
ProducesRequestCondition.clearMediaTypesAttribute(request);
}
}
委托给父类的 getHandlerInternal():
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String lookupPath = initLookupPath(request);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
首先调用 initLookupPath() 根据 request 获取 lookupPath ,其实就是提取出 url,比如我们前端请求的是 http://localhost:9901/mianshi/baodian/detail/1077120523 ,则 lookupPath就是 /mianshi/baodian/detail/1077120523。
提取 lookupPath 后,调用 lookupHandlerMethod() 获取HandlerMethod :
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
// 根据 lookupPath 获取所有的 RequestMappingInfo
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
// 通过条件进行筛选,并把结果放到matches里
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
// 如果还为空,则兜底遍历所有接口
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
/*
* 如果有多个,则进行优先级排序,寻找最优的
*/
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
matches.sort(comparator);
bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
for (Match match : matches) {
if (match.hasCorsConfig()) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
}
}
else {
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
}
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.getHandlerMethod());
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.getHandlerMethod();
}
else {
// 没有找到
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
this.mappingRegistry 是 Spring MVC 中的注册表,用于存储和管理各种请求 URL(或其他匹配条件)到处理方法(handler method)之间的映射关系。它内部有四个映射关系:
private final Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> registry = new HashMap<>();
private final MultiValueMap<String, T> pathLookup = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
private final Map<String, List<HandlerMethod>> nameLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Map<HandlerMethod, CorsConfiguration> corsLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
- registry:用于将某种类型
T(可能是请求路径或其他匹配条件)与MappingRegistration<T>关联。MappingRegistration<T>是一个包含注册信息的对象,可能包括 URL、HTTP 方法、处理方法、优先级等信息。当我们注册一个@RequestMapping注解时,Spring MVC 会将请求路径及其相关属性存储在这个registry中。 - pathLookup:存储了每个请求路径(作为
String)与多个映射目标T之间的关系。MultiValueMap允许每个请求路径关联多个映射目标。 - nameLookup:存储了每个方法名称(
String)与多个处理方法(HandlerMethod)的对应关系。通常是根据方法的名称或标识来查找所有匹配的处理方法。 - corsLookup:用于存储每个处理方法(
HandlerMethod)的 CORS 配置信息(CorsConfiguration)。
首先调用 getMappingsByDirectPath() 从 pathLookup 注册表中获取:
public List<T> getMappingsByDirectPath(String urlPath) {
return this.pathLookup.get(urlPath);
}
码哥个人网站 pathLookup 注册表内容如下:
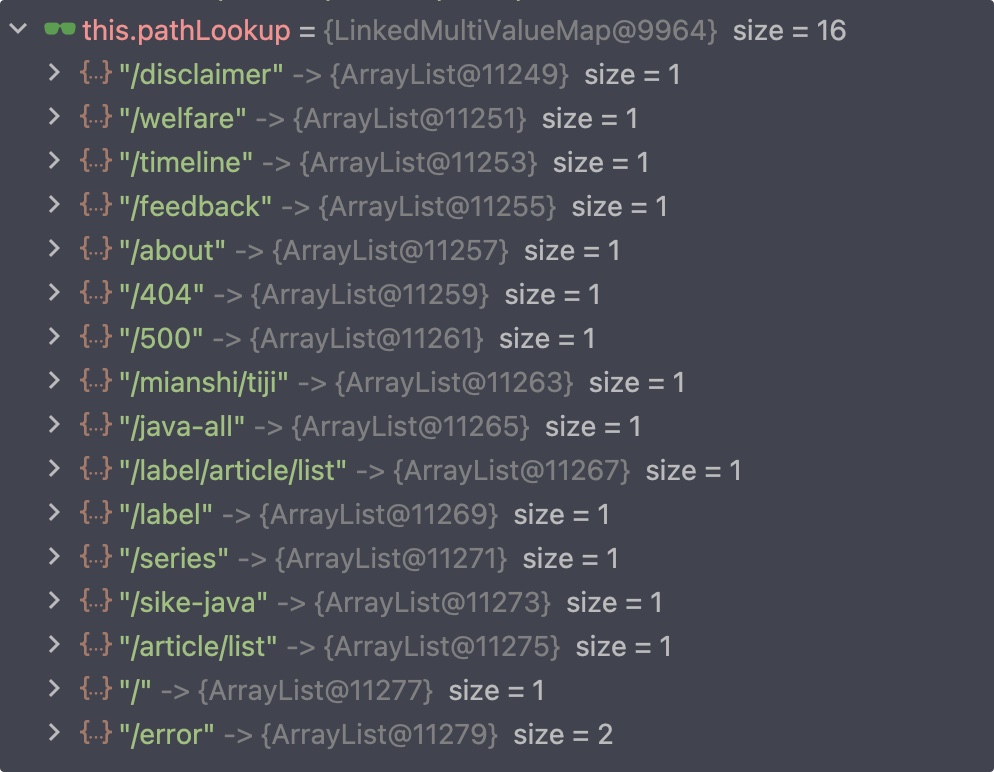
我们请求的 urlPath 为 /mianshi/baodian/detail/1077120523 ,所以这个注册表肯定取不到。则调用 addMatchingMappings() 从 registry 注册表中获取:
private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) {
for (T mapping : mappings) {
T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request);
if (match != null) {
matches.add(new Match(match, this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().get(mapping)));
}
}
}
这里是迭代 registry 注册表中的元素,一次调用 getMatchingMapping() 进行匹配:
public RequestMappingInfo getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
// 请求方法 requestMapping 是否匹配
RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods = this.methodsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (methods == null) {
return null;
}
// 请求参数是否匹配
ParamsRequestCondition params = this.paramsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (params == null) {
return null;
}
// header 是否匹配
HeadersRequestCondition headers = this.headersCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (headers == null) {
return null;
}
//consums Content-Type 是否匹配
ConsumesRequestCondition consumes = this.consumesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (consumes == null) {
return null;
}
// produces Content-Type 是否匹配
ProducesRequestCondition produces = this.producesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (produces == null) {
return null;
}
// 匹配 directPath 和通配符的请求映射匹配关系
PathPatternsRequestCondition pathPatterns = null;
if (this.pathPatternsCondition != null) {
pathPatterns = this.pathPatternsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (pathPatterns == null) {
return null;
}
}
// 匹配 ant 风格的请求
PatternsRequestCondition patterns = null;
if (this.patternsCondition != null) {
patterns = this.patternsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (patterns == null) {
return null;
}
}
// 匹配自定义
RequestConditionHolder custom = this.customConditionHolder.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (custom == null) {
return null;
}
return new RequestMappingInfo(this.name, pathPatterns, patterns,
methods, params, headers, consumes, produces, custom, this.options);
}
我们看 registry 注册表中的内容:
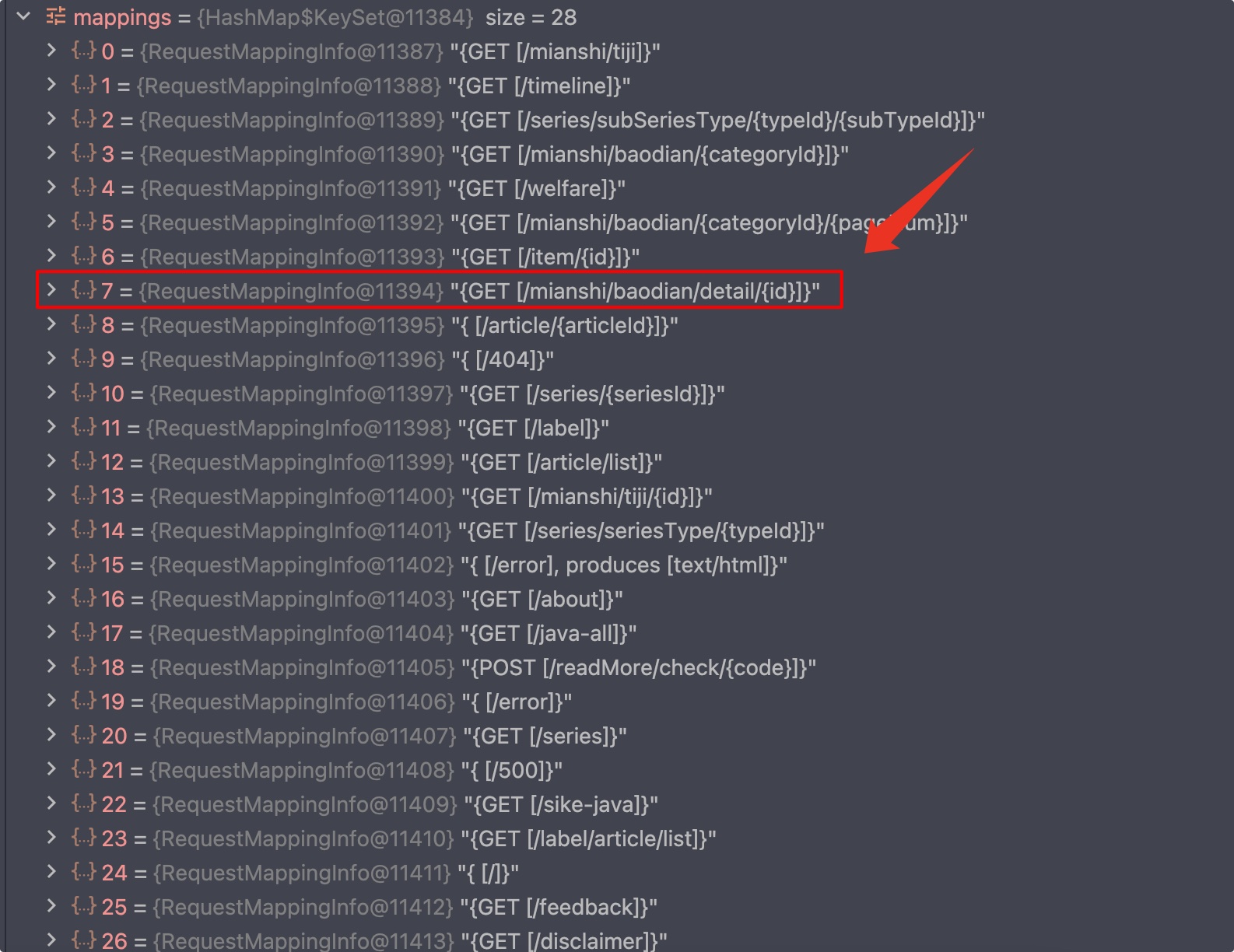
经过 getMatchingCondition() 对比我们就可以找到上图的 RequestMappingInfo。但是我们有可能会找到多个,则先进行排序,然后获取第 1 、2 个,对比两个优先级是否是一样的,如果一样则抛出异常,否则获取第一个。对比条件:
public int compareTo(RequestMappingInfo other, HttpServletRequest request) {
int result;
// Automatic vs explicit HTTP HEAD mapping
if (HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(request.getMethod())) {
result = this.methodsCondition.compareTo(other.getMethodsCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
}
result = getActivePatternsCondition().compareTo(other.getActivePatternsCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
result = this.paramsCondition.compareTo(other.getParamsCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
result = this.headersCondition.compareTo(other.getHeadersCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
result = this.consumesCondition.compareTo(other.getConsumesCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
result = this.producesCondition.compareTo(other.getProducesCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
// Implicit (no method) vs explicit HTTP method mappings
result = this.methodsCondition.compareTo(other.getMethodsCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
result = this.customConditionHolder.compareTo(other.customConditionHolder, request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
return 0;
}






















 630
630

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








