作者简介:大家好,我是码炫码哥,前中兴通讯、美团架构师,现任某互联网公司CTO,兼职码炫课堂主讲源码系列专题
代表作:《jdk源码&多线程&高并发》,《深入tomcat源码解析》,《深入netty源码解析》,《深入dubbo源码解析》,《深入springboot源码解析》,《深入spring源码解析》,《深入redis源码解析》等
联系qq:184480602,加我进群,大家一起学习,一起进步,一起对抗互联网寒冬。码炫课堂的个人空间-码炫码哥个人主页-面试,源码等
“请你描述下 Spring Bean 的生命周期?”,这是 Spring 中一个很常见的面试题。Spring Bean 从出生到销毁的全过程就是它的整个生命周期,它一共会经历以下四个阶段:
- 实例化 Instantiation
- 属性赋值 Populate
- 初始化 Initialization
- 销毁 Destruction
如下:

四个阶段共分为 10 个小步骤:
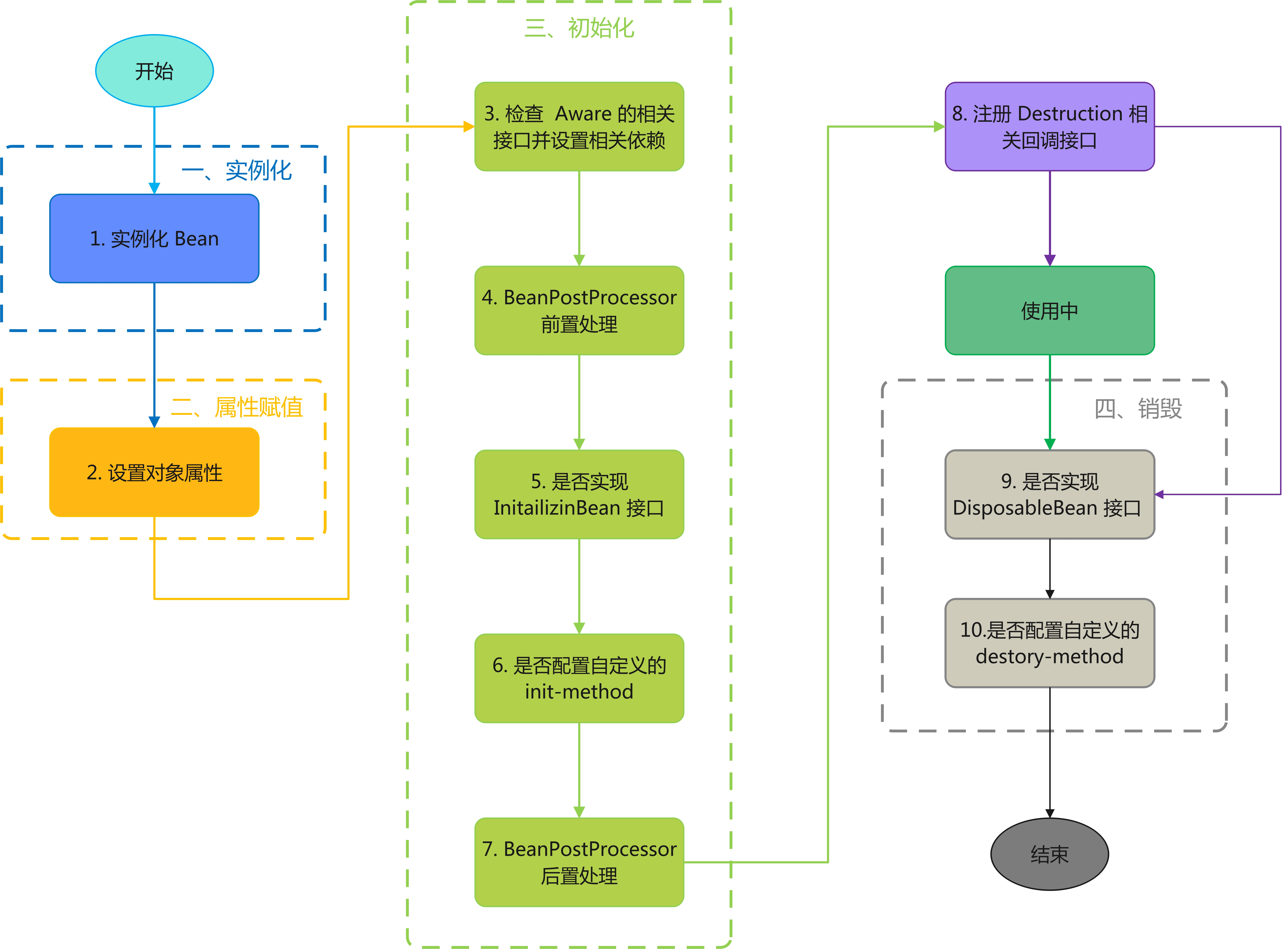
- 实例化:第 1 步,实例化一个 Bean 对象。
- 属性赋值:第2 步,为该 Bean 对象设置属性并注入依赖。
- 初始化:这步骤要处理的事情比较多:
- 检查 Aware 的相关接口并设置相关依赖:当一个Bean实现了
Aware的相关接口,Spring容器会在初始化过程中自动调用相应的方法,为Bean注入特定的对象或信息。这些接口允许Bean获取到Spring容器的一些内部工作情况,比如环境配置、文件资源、应用上下文等。 - BeanPostProcessor 前后置处理:
- 在Bean的自定义初始化方法执行之前,Spring容器会调用
BeanPostProcessors的postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法,它允许在Bean初始化前进行一些自定义的操作。 - 在Bean的自定义初始化方法执行之后,Spring容器会调用
BeanPostProcessors的postProcessAfterInitialization(),它允许在Bean初始化后进行一些自定义的操作。
- 在Bean的自定义初始化方法执行之前,Spring容器会调用
- 步骤 5、6 是真正的初始化操作,它主要分为三个部分:
- 如果在XML配置中使用了
init-method属性,Spring会调用指定的方法作为Bean的初始化方法。 - 如果使用了
@PostConstruct注解,Spring会在依赖注入完成后调用被该注解标记的方法。 - 如果Bean实现了
InitializingBean接口,那么Spring将会在设置所有属性后调用afterPropertiesSet()。
- 如果在XML配置中使用了
- 检查 Aware 的相关接口并设置相关依赖:当一个Bean实现了
- 销毁:步骤 8 其实算不上真正的销毁操作,它这是在使用前注册了销毁的相关调用接口,为后面的第 9、10 步真正销毁 Bean 是在执行相应的方法。
我们再结合源码看下,AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean():
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
//阶段一:实例化 Bean
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 阶段二:属性赋值
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// 阶段三:初始化
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
//...
}
// 销毁-注册回调接口
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
其中初始化阶段又稍微复杂点,我们进入 initializeBean() 看下:
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
// 3. 检查 Aware 相关接口并设置相关依赖
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
// 4. BeanPostProcessor 前置处理
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
// 5. 若实现 InitializingBean 接口,调用 afterPropertiesSet() 方法
// 6. 若配置自定义的 init-method方法,则执行
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
// 7. BeanPostProceesor 后置处理
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
阶段四:销毁,源码如下:
// DisposableBeanAdapter.java
public void destroy() {
// 9. 若实现 DisposableBean 接口,则执行 destory()方法
if (this.invokeDisposableBean) {
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> {
((DisposableBean) this.bean).destroy();
return null;
}, this.acc);
}
else {
((DisposableBean) this.bean).destroy();
}
}
}
// 10. 若配置自定义的 detory-method 方法,则执行
if (this.destroyMethod != null) {
invokeCustomDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethod);
}
else if (this.destroyMethodName != null) {
Method methodToInvoke = determineDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethodName);
if (methodToInvoke != null) {
invokeCustomDestroyMethod(ClassUtils.getInterfaceMethodIfPossible(methodToInvoke));
}
}
}
下面我们来看一个例子,用这个例子来演示一个 Bean 的一生。
- 新建一个 Bean
public class SkSpringBeanLifeCycle implements InitializingBean, BeanFactoryAware, BeanNameAware, DisposableBean {
private String name;
private String website;
public SkSpringBeanLifeCycle(){
System.out.println("调用构造函数,实例化...");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("设置属性;name = " +name);
this.name = name;
}
public String getWebsite() {
return website;
}
public void display(){
System.out.println("调用方法.....");
}
public void setWebsite(String website) {
System.out.println("设置属性;website = " + website);
this.website = website;
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanFactoryAware 被调用...");
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("BeanNameAware 被调用...");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("DisposableBean destroy 被调用...");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("InitializingBean afterPropertiesSet 被调动...");
}
public void initMethod(){
System.out.println("init-method 被调用...");
}
public void destroyMethod(){
System.out.println("destroy-method 被调用...");
}
}
该 Bean 有两个属性:name 和 website。且实现了接口InitializingBean, BeanFactoryAware, BeanNameAware, DisposableBean,其中 InitializingBean 是初始化化接口,BeanFactoryAware, BeanNameAware 是两个 Aware 类接口,DisposableBean 是销毁时的接口。
- 再定义一个 Bean 实现 BeanPostProcessor 接口,进行 Bean 初始化阶段的前后置处理:
public class SkSpringBeanLifeCycleProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor postProcessBeforeInitialization 被调用...");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor postProcessAfterInitialization 被调用...");
return bean;
}
}
- 为了更容易地测试,我们使用 XML 配置文件:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean name="skSpringBeanLifeCycleProcessor" class="com.skjava.admin.dto.SkSpringBeanLifeCycleProcessor"/>
<bean name="skSpringBeanLifeCycle" class="com.skjava.admin.dto.SkSpringBeanLifeCycle"
init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod">
<property name="name" value= "死磕 Java"/>
<property name="website" value="https://skjava.com" />
</bean>
</beans>
- 测试类:
public class SkSpringBeanLifeCycleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
SkSpringBeanLifeCycle beanLifeCycle = (SkSpringBeanLifeCycle) context.getBean("skSpringBeanLifeCycle");
System.out.println("Bean 初始化完成,调用其方法...");
beanLifeCycle.display();
System.out.println("方法调用完成,容器开始关闭....");
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) context).destroy();
}
}
- 执行结果:
调用构造函数,实例化...
设置属性;name = 死磕 Java
设置属性;website = https://skjava.com
BeanNameAware 被调用...
BeanFactoryAware 被调用...
BeanPostProcessor postProcessBeforeInitialization 被调用...
InitializingBean afterPropertiesSet 被调动...
init-method 被调用...
BeanPostProcessor postProcessAfterInitialization 被调用...
Bean 初始化完成,调用其方法...
调用方法.....
方法调用完成,容器开始关闭....
DisposableBean destroy 被调用...
destroy-method 被调用...






















 628
628

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








