1.Spring Boot 简介
Spring Boot来简化Spring应用开发,约定大于配置, 去繁从简,just run就能创建一个独立的,产品级别的应用
背景:
J2EE笨重的开发、繁多的配置、低下的开发效率、 复杂的部署流程、第三方技术集成难度大。
解决:
“Spring全家桶”时代。
Spring Boot --> J2EE一站式解决方案
Spring Cloud --> 分布式整体解决方案
优点:
– 快速创建独立运行的Spring项目以及与主流框架集成
– 使用嵌入式的Servlet容器,应用无需打成WAR包
– starters自动依赖与版本控制
– 大量的自动配置,简化开发,也可修改默认值
– 无需配置XML,无代码生成,开箱即用
– 准生产环境的运行时应用监控
– 与云计算的天然集成
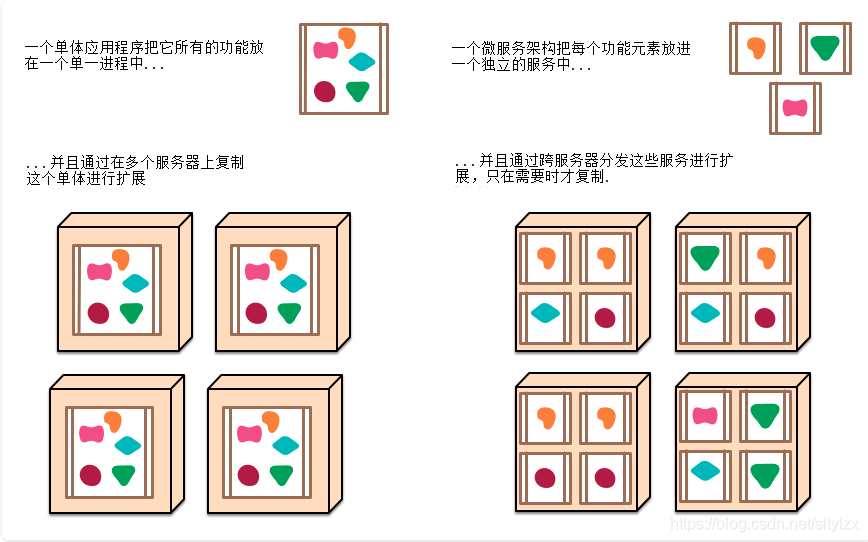
2.微服务
2014,martin fowler https://martinfowler.com/articles/microservices.html#MicroservicesAndSoa
微服务:架构风格(服务微化)
一个应用应该是一组小型服务;可以通过HTTP的方式进行互通;
单体应用:ALL IN ONE
微服务:每一个功能元素最终都是一个可独立替换和独立升级的软件单元;
3.环境准备
[1].环境约束
–jdk1.8:Spring Boot 推荐jdk1.7及以上;java version "1.8.0_112"
–maven3.x:maven 3.3以上版本;Apache Maven 3.3.9
–IntelliJIDEA2017:IntelliJ IDEA 2017.2.2 x64、STS
–SpringBoot 1.5.9.RELEASE:1.5.9;
统一环境;
[2].MAVEN设置;给maven 的settings.xml配置文件的profiles标签添加
<profile>
<id>jdk-1.8</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
<jdk>1.8</jdk>
</activation>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.8</maven.compiler.compilerVersion>
</properties>
</profile>[3].将idea的maven配置成自己下载的maven
4.Spring Boot HelloWorld
[1].创建一个maven工程;(jar)
[2].导入spring boot相关的依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>[3].编写一个主程序;启动Spring Boot应用
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//启动springboot应用
SpringApplication.run(MainApp.class, args);
}
}[4].编写controller
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello world";
}
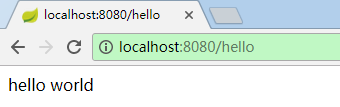
}[5].启动主程序的main方法,访问 http://localhost:8080/hello
[6].简化部署
①.在pom.xml文件中添加插件
<!--这个插件,可以将应用打包成一个可执行的jar包;-->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
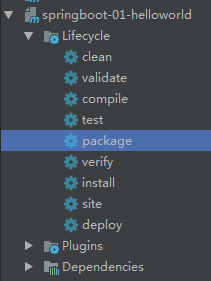
</build>②.点击maven的打包按钮
③.控制台输出打包的位置![]()
④.找到该jar包,双击运行,或者在命令行运行都可以,就部署完成了
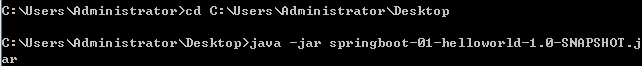
![]()
5.HelloWorld探究
[1.]pom文件
①.父项目
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version>
</parent>他的父项目是
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath>../../spring-boot-dependencies</relativePath>
</parent>它来真正管理springboot应用里面的所有仲裁版本
Springboot的版本仲裁中心,以后我们导入依赖默认不需要写版本(在dependencies 里面没有的也需要写版本)
②.导入的依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>spring-boot-starter-web
spring-boot-starter:springboot场景启动器, 帮我们导入web模块运行所依赖的组件(详见https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.0.0.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#getting-started-first-application-executable-jar)
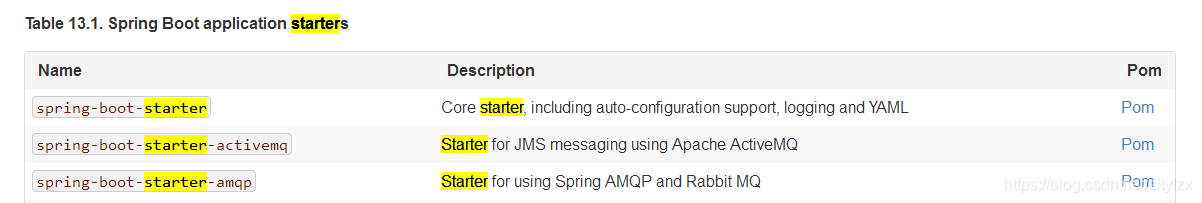
springboot将所有的功能场景都抽取出来,做成一个个的starter(启动器),只需要在项目里面引入这些starter,相关场景所有依赖都会导入进来,要用什么功能就导入什么场景启动器
[2].主程序类
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//启动springboot应用
SpringApplication.run(MainApp.class, args);
}
}@SpringBootApplication:说明这个类是springboot的主配置类,就应该启动这个类的main方法来启动springboot应用
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(
excludeFilters = {@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}
), @Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class}
)}
)
public @interface SpringBootApplication {@SpringBootConfiguration:springboot的配置类
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {@Configuration:配置类上来标注这个注解;配置类----配置文件;配置类也是容器的组件
@EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置功能;@EnableAutoConfiguration告诉SpringBoot开启自 动配置功能;这样自动配置才能生效;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {@AutoConfigurationPackage自动配置包
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import({Registrar.class})
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {@Import:spring底层注解;给容器中导入一个组件;导入的组件由 AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class; 将主配置类(@SpringBootApplication标注的类)的所在包及下面所有子包里面的所有组件扫描到Spring容器;
@Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class):
给容器中导入组件?
EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector:导入哪些组件的选择器;将所有需要导入的组件以全类名的方式返回;这些组件就会被添加到容器中; 会给容器中导入非常多的自动配置类(xxxAutoConfiguration);就是给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件, 并配置好这些组件;
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector, BeanClassLoaderAware, ResourceLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware, EnvironmentAware, Ordered {
private static final String[] NO_IMPORTS = new String[0];
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class);
private static final String PROPERTY_NAME_AUTOCONFIGURE_EXCLUDE = "spring.autoconfigure.exclude";
private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
private Environment environment;
private ClassLoader beanClassLoader;
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
public AutoConfigurationImportSelector() {
}
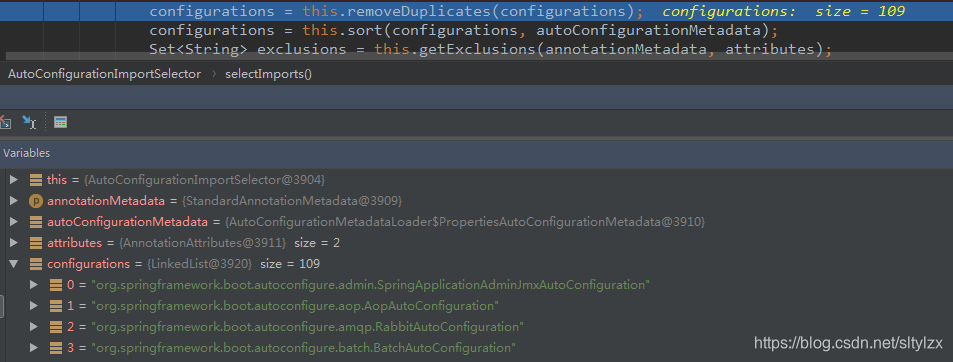
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!this.isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
} else {
try {
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
AnnotationAttributes attributes = this.getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List<String> configurations = this.getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = this.removeDuplicates(configurations);
configurations = this.sort(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
Set<String> exclusions = this.getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
this.checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = this.filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
this.fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(configurations);
} catch (IOException var6) {
throw new IllegalStateException(var6);
}
}
}
有了自动配置类,免去了我们手动编写配置注入功能组件等的工作;
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(EnableAutoConfiguration.class,classLoader)
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories") : ClassLoader.getSystemResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap();
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next();
List<String> factoryClassNames = Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue()));
result.addAll((String)entry.getKey(), factoryClassNames);
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
} catch (IOException var9) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var9);
}
}
}Spring Boot在启动的时候从类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories中获取EnableAutoConfiguration指定的值,将 这些值作为自动配置类导入到容器中,自动配置类就生效,帮我们进行自动配置工作;以前我们需要自己配置的东西,自动配置类都帮我们;
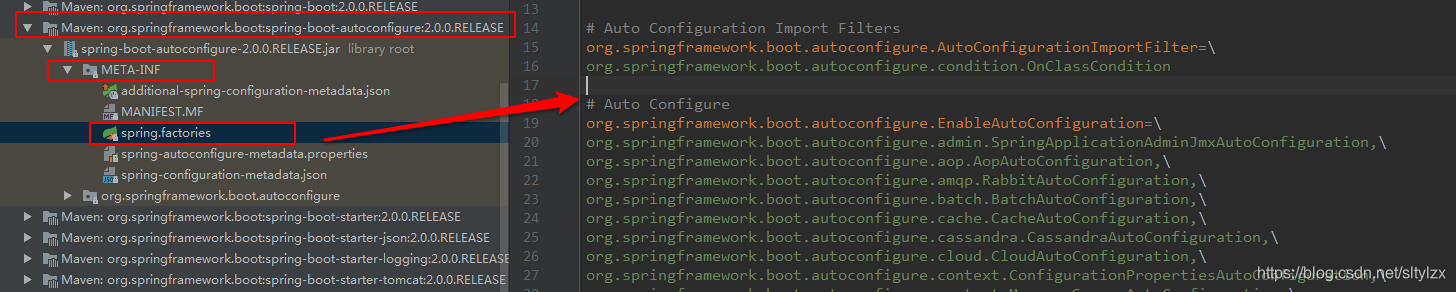
J2EE的整体整合解决方案和自动配置都在spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.0.0.RELEASE.jar
6.使用Spring Initializer快速创建Spring Boot项目(需联网)
[1].IDEA创建
①.选择Spring Initializer,选择对应的jdk/sdk,然后next
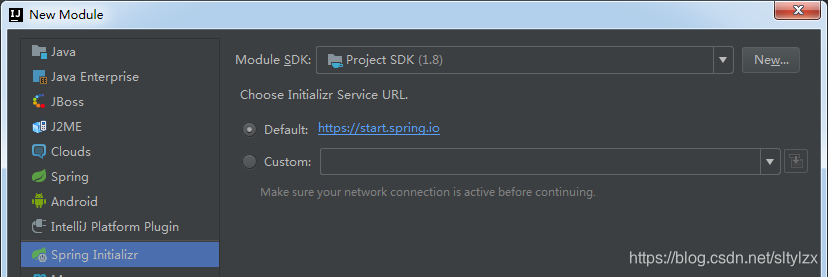
②.填入项目信息,点击next
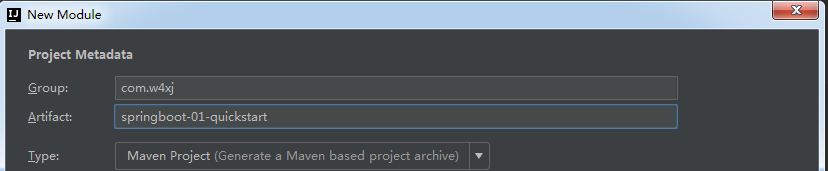
③.选择对以的模块,next
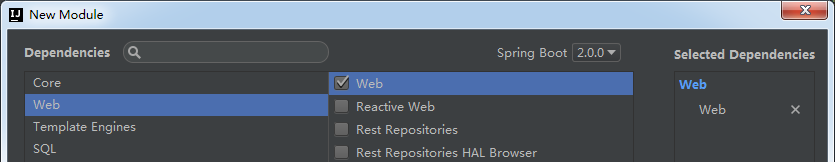
④.finish
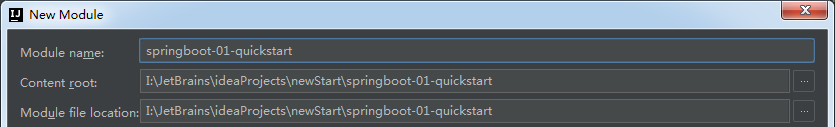
⑤.联网导包
IDE都支持使用Spring的项目创建向导快速创建一个Spring Boot项目;
选择我们需要的模块;向导会联网创建Spring Boot项目;
默认生成的Spring Boot项目;
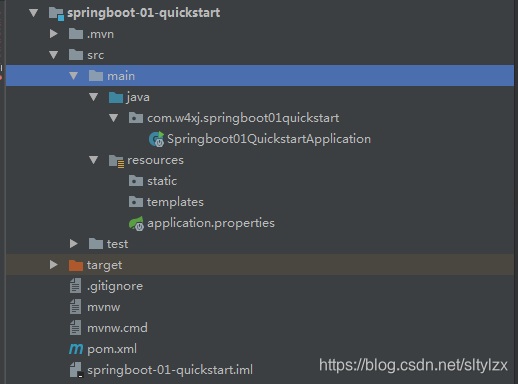
主程序已经生成好了,我们只需要我们自己的逻辑
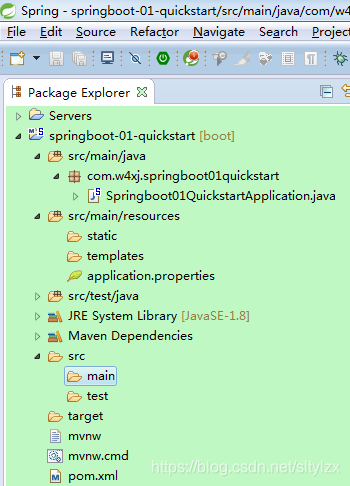
resources文件夹中目录结构
static:保存所有的静态资源; js css images;
templates:保存所有的模板页面;(Spring Boot默认jar包使用嵌入式的Tomcat,默认不支持JSP页面);可以使用模板引擎(freemarker、thymeleaf);
application.properties:Spring Boot应用的配置文件;可以修改一些默认设置;
[2].STS创建类似
①.new springboot starter project
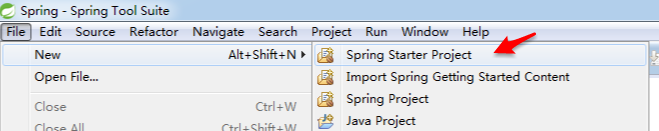
②.填入对应信息,next
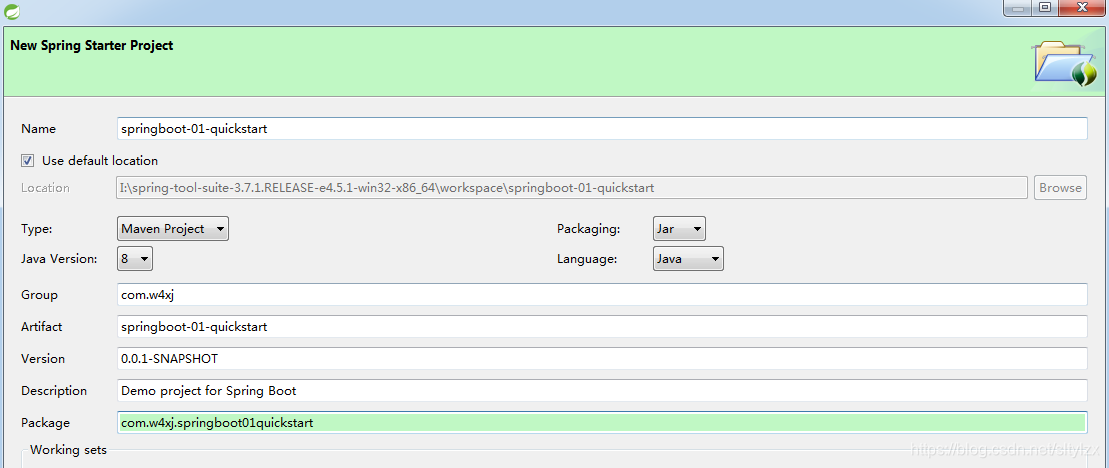
③.选择对应springboot版本和需要的模块,finish
④.联网生成

⑤.目录结构
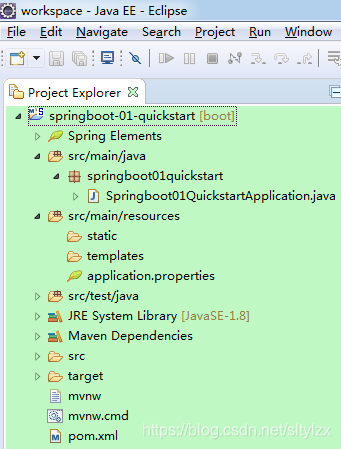
[3].Eclipse---先装较新的spring插件支持Springboot
①安装后和STS一样,新建过程略
②.结构





 本文介绍SpringBoot简化Spring应用开发的过程,包括快速创建独立运行的项目、使用嵌入式Servlet容器、自动依赖与版本控制等优势。同时,详细讲解了微服务概念及其与单体应用的区别,以及SpringBoot环境准备、Maven设置、HelloWorld示例的创建步骤。
本文介绍SpringBoot简化Spring应用开发的过程,包括快速创建独立运行的项目、使用嵌入式Servlet容器、自动依赖与版本控制等优势。同时,详细讲解了微服务概念及其与单体应用的区别,以及SpringBoot环境准备、Maven设置、HelloWorld示例的创建步骤。
















 1296
1296

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








