2.利用reshape改变 x 的shape以满足input的参数
convolution
官方文档
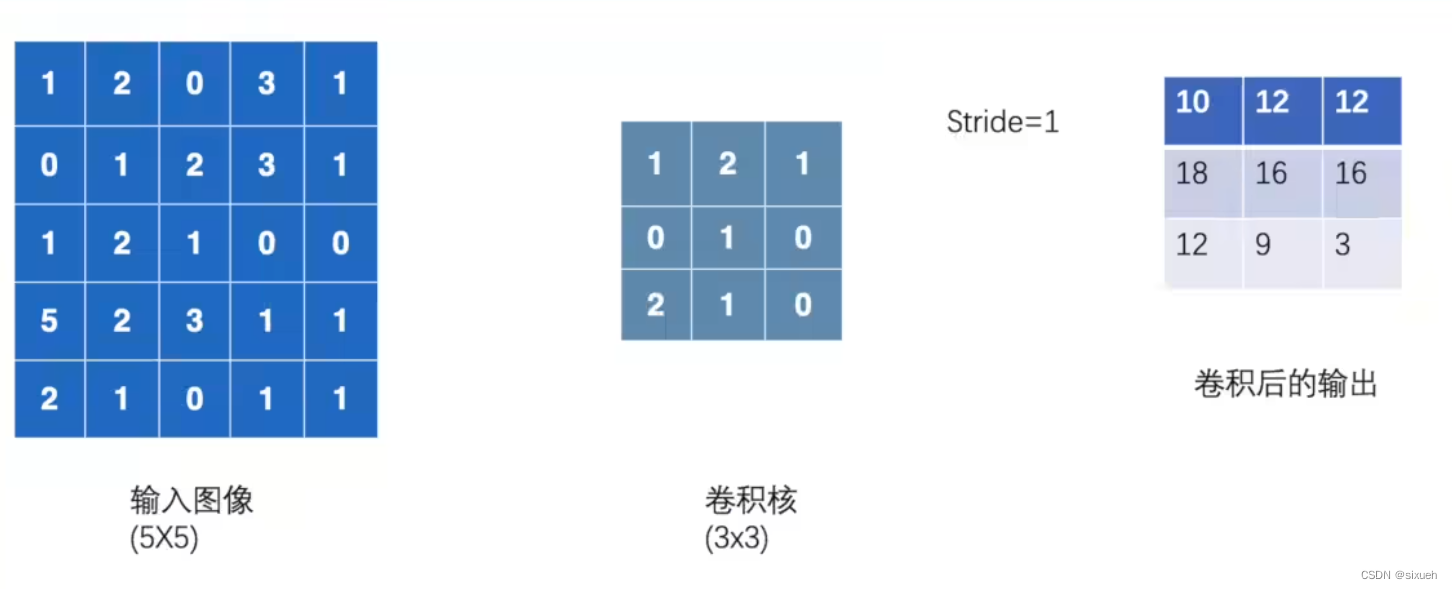
1.设置输入矩阵和卷积核
import torch
# 二维矩阵的输入
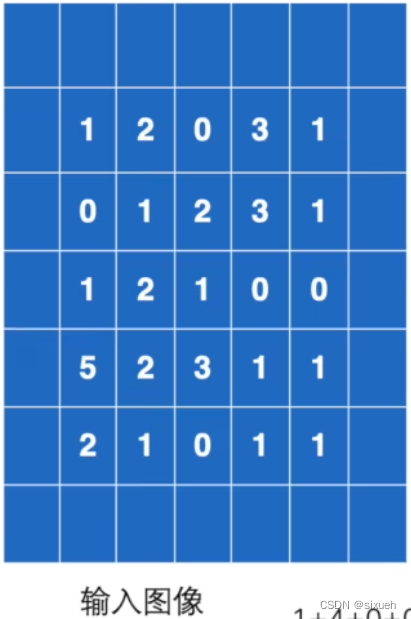
input = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 0, 3, 1],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 1],
[1, 2, 1, 0, 0],
[5, 2, 3, 1, 1],
[2, 1, 0, 1, 1]])
kernel = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[2, 1, 0]])input需要是这种shape

input:输入
weight:核
stride:核每次移动的步数
2.利用reshape改变 x 的shape以满足input的参数
input = torch.reshape(input, (1, 1, 5, 5))
kernel = torch.reshape(kernel, (1, 1, 3, 3))3.调用conv2d,并查看输出结果
import torch.nn.functional as F
output = F.conv2d(input1, kernel, stride=1)
print(output)输出
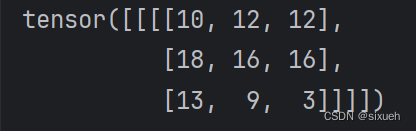
4.stride:核每次移动的步数
stride=1时: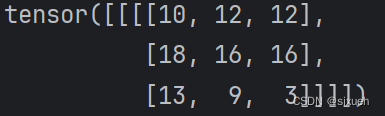
stride=2时: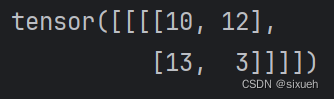
5.padding:在输入的边上填充数据
完整代码
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
# 二维矩阵的输入
input1 = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 0, 3, 1],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 1],
[1, 2, 1, 0, 0],
[5, 2, 3, 1, 1],
[2, 1, 0, 1, 1]])
kernel = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[2, 1, 0]])
input1 = torch.reshape(input1, (1, 1, 5, 5))
kernel = torch.reshape(kernel, (1, 1, 3, 3))
# print(input1.shape) # 输出input和kernel的shape
# print(kernel.shape) # 满足conv2d的参数要求
# stride=1
output = F.conv2d(input1, kernel, stride=1)
print(output)
# stride=2
output2 = F.conv2d(input1, kernel, stride=2)
print(output2)
# padding
output3 = F.conv2d(input1, kernel, stride=1, padding=1)
print(output3)



 本文介绍了如何使用PyTorch库中的convolution操作,包括设置输入矩阵、调整卷积核形状、设置stride和padding,以及演示了不同参数对输出结果的影响。
本文介绍了如何使用PyTorch库中的convolution操作,包括设置输入矩阵、调整卷积核形状、设置stride和padding,以及演示了不同参数对输出结果的影响。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








