fstream头文件定义了三种支持文件输入输出的类型:
(1)ifstream,由istream派生而来,提供读文件的功能;
(2)ofstream,由ostream派生而来,提供写文件的功能;
(3)fstream,由iostream派生而来,提供读写同一个文件的功能;
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
<span style="font-size:14px;">#include "stdafx.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::fstream;
using std::ofstream;
using std::ifstream;
using std::string;
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
string strFileName("1.txt");
//定义一个写文件流ofile,以out|app模式打开
ofstream ofile(strFileName.c_str(),ofstream::out |ofstream::app);
//向文件流中写入两个字符串
ofile<<"Hello World!\r\n";
ofile<<"Thank you!\r\n";
//关闭文件流
ofile.close();
//定义一个读文件流ifile,默认方式打开
ifstream ifile(strFileName.c_str());
string str1,str2;
//从文件流中读取数据到str1
ifile>>str1;
cout<<str1;
system("pause");
return 0;
}</span>
首先定义一个写文件流ofile,以out | app模式打开。out模式指打开文件作写操作,app模式指每次写之前找到文件尾,即将要写入的数据放在文件的末尾;如果只单独以out模式打开,那么被打开的文件会被清空,丢失数据!
如果工程目录下原本没有1.txt文件,那么程序运行后会自动创建1.txt文本文件,如果有,则打开已有的1.txt文件,准备写入数据。
程序运行后工程目录下有1.txt文件,如下图所示:
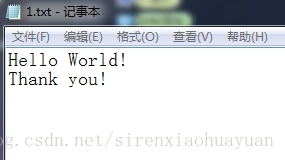
打开1.txt文本文件,内容为
ifstream ifile(strFileName.c_str()) —— 定义一个读文件流ifile,以默认的方式打开。c_str()函数是将string类型的字符串转换成C风格的字符串;
ifile>>str1;
cout<<str1;
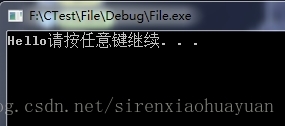
从文件流ifile中获得第一个数据,然后输出,结果为:
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
<span style="font-size:14px;">#include "stdafx.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::fstream;
using std::ofstream;
using std::ifstream;
using std::string;
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
string strFileName("2.txt");
string word;
ofstream ofile(strFileName.c_str(),ofstream::out |ofstream::app);
while(cin>>word)
{
ofile<<word<<endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}</span>
程序运行结果为
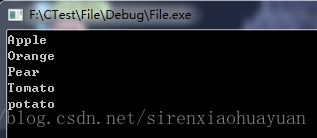
在命令行中连续输入多个字符串,直到输入有效的结束符为止,在工程目录下的2.txt中的内容为
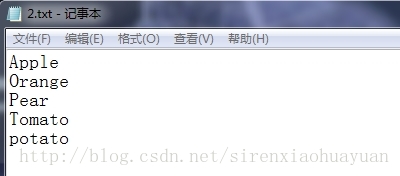
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
<span style="font-size:14px;">#include "stdafx.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::fstream;
using std::ofstream;
using std::ifstream;
using std::string;
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
string strFileName("2.txt");
string word;
ifstream ifile(strFileName.c_str());
while(ifile>>word)
{
cout<<word<<endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}</span>
读取工程目录下的2.txt文件,并将其中的数据全部输出,其输出结果为:
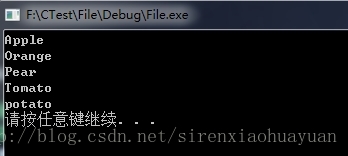





 本文详细介绍了C++中fstream头文件定义的三种文件输入输出类型,并通过实例展示了如何使用这些类型进行文件读写操作。
本文详细介绍了C++中fstream头文件定义的三种文件输入输出类型,并通过实例展示了如何使用这些类型进行文件读写操作。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








