8-1 什么是优先队列
树的不同结构,很灵活。例如之后的树的几个例子:堆,线段树,字典树,并查集。
首先我们来看堆

优先队列的例子
- 计算机的操作系统,动态选择优先级最高的任务执行。
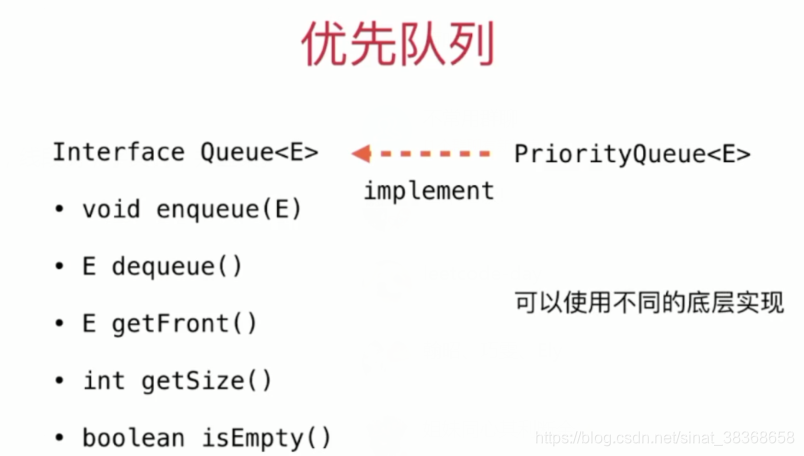
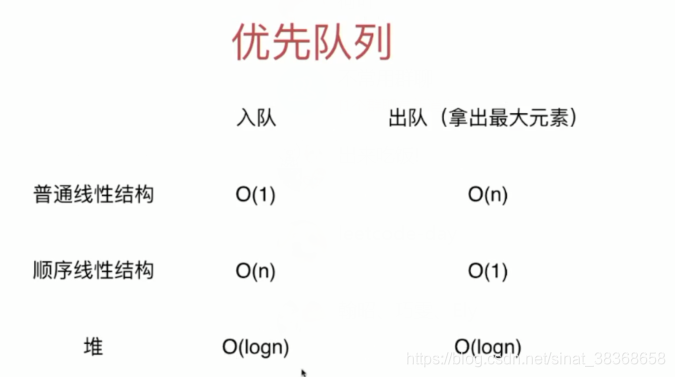
我们使用堆实现优先队列。
8-2 堆的基础表示
- 二叉堆是一个完全二叉树(结点按顺序存放,所以我们可以使用数组来表示完全二叉树)
- 二叉堆堆中某个结点的值总是不大于其父节点的值,最大堆
- 用数组存储二叉堆
注意下标起始的影响
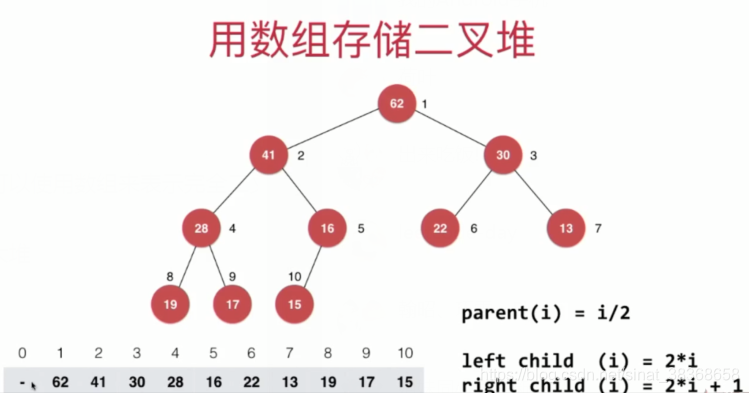
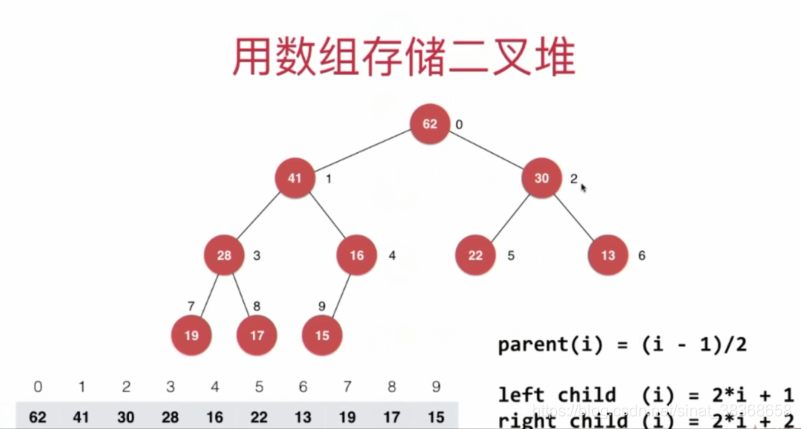
在这里,我们使用一个从0开始的数组表示的二叉堆
public class MaxHeap <E extends Comparable<E>> {
private Array<E> data;
public MaxHeap(int capacity){
data = new Array<>(capacity);
}
public MaxHeap(){
data = new Array<>();
}
//返回堆中的元素个数
public int size(){
return data.getSize();
}
//返回一个布尔值,表示堆中是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return data.isEmpty();
}
// 返回完全二叉树的数组表示中,一个索引所表示的元素的父亲节点的索引
private int parent(int index){
if (index == 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index-0 doesn't hava parent");
return (index-1)/2;
}
// 返回完全二叉树的数组表示中,一个索引所表示的元素的左孩子节点的索引
private int leftChild(int index){
return index * 2 + 1;
}
// 返回完全二叉树的数组表示中,一个索引所表示的元素的右孩子节点的索引
private int rightChild(int index){
return index * 2 + 2;
}
}
8-3 向堆中添加元素和Sift Up
//向堆中添加元素
public void add(E e){
data.addLast(e);
siftUp(data.getSize()-1);
}
private void siftUp(int k){
while (k>0 && data.get(parent(k)).compareTo(data.get(k))<0){
data.swap(k,parent(k));
k = parent(k);
}
}
注意,要在Array里添加swap方法
如下
public void swap(int i, int j){
if(i < 0 || i >= size || j < 0 || j >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Index is illegal.");
E t = data[i];
data[i] = data[j];
data[j] = t;
}
8-4 从堆中取出元素和Sift Down
// 取出堆中最大元素
public E extractMax(){
E ret = findMax();
data.swap(0, data.getSize() - 1);
data.removeLast();
siftDown(0);
return ret;
}
private void siftDown(int k){
while(leftChild(k) < data.getSize()){
int j = leftChild(k); // 在此轮循环中,data[k]和data[j]交换位置
if( j + 1 < data.getSize() &&
data.get(j + 1).compareTo(data.get(j)) > 0 )
j ++;
// data[j] 是 leftChild 和 rightChild 中的最大值
if(data.get(k).compareTo(data.get(j)) >= 0 )
break;
data.swap(k, j);
k = j;
}
}
8-5 Heapify 和 Replace

//取出堆中的最大元素,并且替换成元素e
public E replace(E e){
E ret = findMax();
data.set(0,e);
siftDown(0);
return ret;
}

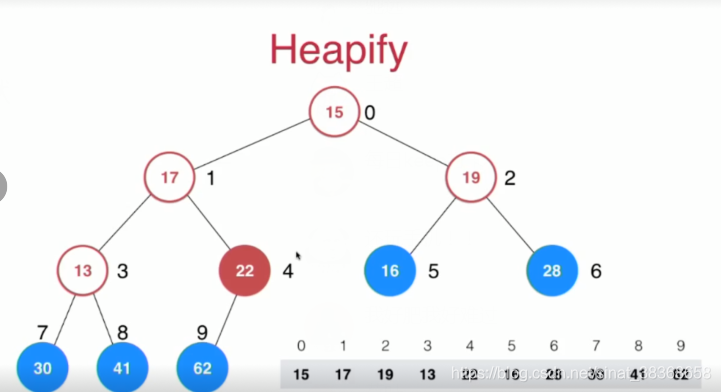
//写成一个构造函数
public MaxHeap(E[] arr){
data = new Array<>(arr);
for (int i = parent(arr.length-1);i>=0;i--)
siftDown(i);
}

比较测试使用heapify的方式创建堆和将数组中的元素逐个添加到空堆中的性能差异
import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
private static double testHeap(Integer[] testData,boolean isHeapify){
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
MaxHeap<Integer> maxHeap;
if (isHeapify)
maxHeap = new MaxHeap<>(testData);
else{
maxHeap = new MaxHeap<>();
for (int num:testData)
maxHeap.add(num);
}
int[] arr = new int[testData.length];
for (int i=0;i<testData.length;i++)
arr[i] = maxHeap.extractMax();
for (int i=1;i<testData.length;i++)
if (arr[i-1]<arr[i])
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Error");
System.out.println("Test MaxHeap completed");
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
return (endTime - startTime)/1000000000.0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 1000000;
Random random = new Random();
Integer[] testData = new Integer[n];
for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
testData[i] = random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
double time1 = testHeap(testData,false);
System.out.println("Without heapify:"+time1+" s");
double time2 = testHeap(testData,true);
System.out.println("Without heapify:"+time2+" s");
}
}
对于百万级的数据量
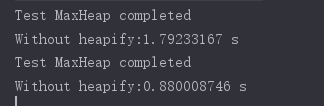
Heapify的复杂度更低。
8-6 基于堆的优先队列
由于优先队列要排优先级,所以必须具有可比较性。
public class PriorityQueue<E extends Comparable<E>> implements Queue<E> {
private MaxHeap<E> maxHeap;
public PriorityQueue(){
maxHeap = new MaxHeap<>();
}
@Override
public int getSize(){
return maxHeap.size();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty(){
return maxHeap.isEmpty();
}
@Override
public E getFront(){
return maxHeap.findMax();
}
@Override
public void enqueue(E e){
maxHeap.add(e);
}
@Override
public E dequeue(){
return maxHe
ap.extractMax();
}
}
8-7 Leetcode上优先队列相关问题
首先我们使用自己定义的PriorityQueue来解决这个问题
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.TreeMap;
class Solution {
private class Freq implements Comparable<Freq>{
public int e,freq;
public Freq(int e,int freq){
this.e = e;
this.freq = freq;
}
@Override
//注意这里应该使用最小堆我们用的是最大堆
//那么这里的这个优先级比较的规则应该是怎么定义的?
public int compareTo(Freq another){
if (this.freq < another.freq)
return 1;
else if (this.freq>another.freq)
return -1;
else
return 0;
}
}
public List<Integer> topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
//首先我们对每个数统计频次
TreeMap<Integer,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
for (int num:nums){
if (map.containsKey(num))
map.put(num,map.get(num)+1);
else
map.put(num,1);
}
//构造优先队列,找出前K个元素
PriorityQueue<Freq> pq = new PriorityQueue<Freq>();
for (int key:map.keySet()){
if (pq.getSize()<k)
pq.enqueue(new Freq(key,map.get(key)));
else if(map.get(key)>pq.getFront().freq){
pq.dequeue();
pq.enqueue(new Freq(key,map.get(key)));
}
}
//存储答案
LinkedList<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>();
while (!pq.isEmpty())
res.add(pq.dequeue().e);
return res;
}
private static void printList(List<Integer> nums){
for (Integer num: nums)
System.out.println(num+" ");
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1,1,1,2,2,3};
int k = 2;
printList((new Solution()).topKFrequent(nums,k));
}
}
8-8 Java中的PriorityQueue
Java中的PriorityQueue和我们自己实现的不太一样,我们这节来看看
首先我们使用Java库中的PriorityQueue来解决上节的leetcode问题
- java的PriorityQueue内容默认是一个最小堆
- 没有getSize()方法,直接是pq.size()
- dequeue对应pq.remove(),enqueue对应pq.add(new Freq(key,map.get(key))),getFront对应pq.peek()
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.PriorityQueue
//我们使用Java库中的PriorityQueue来解决上节的leetcode问题
class Solution2 {
private class Freq implements Comparable<Freq>{
public int e,freq;
public Freq(int e,int freq){
this.e = e;
this.freq = freq;
}
@Override
//注意这里的改变,java维护的是最小堆
public int compareTo(Freq another){
if (this.freq > another.freq)
return 1;
else if (this.freq<another.freq)
return -1;
else
return 0;
}
}
public List<Integer> topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
//首先我们对每个数统计频次
TreeMap<Integer,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
for (int num:nums){
if (map.containsKey(num))
map.put(num,map.get(num)+1);
else
map.put(num,1);
}
//构造优先队列,找出前K个元素
PriorityQueue<Freq> pq = new PriorityQueue<Freq>();
for (int key:map.keySet()){
if (pq.size()<k)
pq.add(new Freq(key,map.get(key)));
else if(map.get(key)>pq.peek().freq){
pq.remove();
pq.add(new Freq(key,map.get(key)));
}
}
//存储答案
LinkedList<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>();
while (!pq.isEmpty())
res.add(pq.remove().e);
return res;
}
private static void printList(List<Integer> nums){
for (Integer num: nums)
System.out.println(num+" ");
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1,1,1,2,2,3};
int k = 2;
printList((new Solution()).topKFrequent(nums,k));
}
}
根据我们的需要,如何改变java标准库中相应类的比较规则。
java的解决方法:设置一个新的类,比较器,实现的是Comprarator接口
只需要覆盖一个方法Compare,同时传入的是两个参数。
import java.util.*;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
//我们使用Java库中的PriorityQueue来解决上节的leetcode问题
class Solution3 {
private class Freq{
public int e,freq;
public Freq(int e,int freq){
this.e = e;
this.freq = freq;
}
}
private class FreqComparator implements Comparator<Freq>{
@Override
public int compare(Freq a,Freq b){
return a.freq - b.freq;
}
}
public List<Integer> topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
//首先我们对每个数统计频次
TreeMap<Integer,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
for (int num:nums){
if (map.containsKey(num))
map.put(num,map.get(num)+1);
else
map.put(num,1);
}
//构造优先队列,找出前K个元素
PriorityQueue<Freq> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new FreqComparator());
for (int key:map.keySet()){
if (pq.size()<k)
pq.add(new Freq(key,map.get(key)));
else if(map.get(key)>pq.peek().freq){
pq.remove();
pq.add(new Freq(key,map.get(key)));
}
}
//存储答案
LinkedList<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>();
while (!pq.isEmpty())
res.add(pq.remove().e);
return res;
}
private static void printList(List<Integer> nums){
for (Integer num: nums)
System.out.println(num+" ");
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1,1,1,2,2,3};
int k = 2;
printList((new Solution()).topKFrequent(nums,k));
}
}
例如,使用上面这种方法,如果优先队列里传的就是字符串,你想有一个自定义的字符串比较规则,此时你不能修改java内部的字符串定义方法,那么可以在外面设置一个字符串的比较规则,传给java的PriorityQueue就好了。
使用匿名类,具有变量捕获capture的能力
import java.util.*;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Solution4 {
private class Freq{
public int e, freq;
public Freq(int e, int freq){
this.e = e;
this.freq = freq;
}
}
public List<Integer> topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
for(int num: nums){
if(map.containsKey(num))
map.put(num, map.get(num) + 1);
else
map.put(num, 1);
}
PriorityQueue<Freq> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Freq>() {
@Override
public int compare(Freq a, Freq b) {
return a.freq - b.freq;
}
});
for(int key: map.keySet()){
if(pq.size() < k)
pq.add(new Freq(key, map.get(key)));
else if(map.get(key) > pq.peek().freq){
pq.remove();
pq.add(new Freq(key, map.get(key)));
}
}
LinkedList<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>();
while(!pq.isEmpty())
res.add(pq.remove().e);
return res;
}
private static void printList(List<Integer> nums){
for(Integer num: nums)
System.out.print(num + " ");
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3};
int k = 2;
printList((new Solution()).topKFrequent(nums, k));
}
}
import java.util.*;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Solution5 {
public List<Integer> topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
for(int num: nums){
if(map.containsKey(num))
map.put(num, map.get(num) + 1);
else
map.put(num, 1);
}
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer a, Integer b) {
return map.get(a) - map.get(b);
}
});
for(int key: map.keySet()){
if(pq.size() < k)
pq.add(key);
else if(map.get(key) > map.get(pq.peek())){
pq.remove();
pq.add(key);
}
}
LinkedList<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>();
while(!pq.isEmpty())
res.add(pq.remove());
return res;
}
private static void printList(List<Integer> nums){
for(Integer num: nums)
System.out.print(num + " ");
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3};
int k = 2;
printList((new Solution()).topKFrequent(nums, k));
}
}
再化简一点,使用拉姆达表达式替代匿名类
import java.util.*;
public class Solution5 {
public List<Integer> topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
for(int num: nums){
if(map.containsKey(num))
map.put(num, map.get(num) + 1);
else
map.put(num, 1);
}
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(
(a, b) -> map.get(a) - map.get(b)
);
for(int key: map.keySet()){
if(pq.size() < k)
pq.add(key);
else if(map.get(key) > map.get(pq.peek())){
pq.remove();
pq.add(key);
}
}
LinkedList<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>();
while(!pq.isEmpty())
res.add(pq.remove());
return res;
}
private static void printList(List<Integer> nums){
for(Integer num: nums)
System.out.print(num + " ");
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3};
int k = 2;
printList((new Solution()).topKFrequent(nums, k));
}
}
8-9 和堆相关的更多话题和广义队列
- d叉堆
- 索引堆
- 二项堆,斐波那契堆
- 广义队列
普通队列,优先队列
栈,也可以理解成一个队列。





 本文围绕堆和优先队列展开,介绍了优先队列的概念,如操作系统动态选最高优先级任务执行。阐述了用堆实现优先队列,包括堆的基础表示、元素添加与取出操作。对比了不同方式创建堆的性能,还探讨了Leetcode相关问题及Java中PriorityQueue的使用,最后提及堆的更多类型和广义队列。
本文围绕堆和优先队列展开,介绍了优先队列的概念,如操作系统动态选最高优先级任务执行。阐述了用堆实现优先队列,包括堆的基础表示、元素添加与取出操作。对比了不同方式创建堆的性能,还探讨了Leetcode相关问题及Java中PriorityQueue的使用,最后提及堆的更多类型和广义队列。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








