- 树是节点的有限集合
- 树的用途:压缩软件 哈夫曼树;人机对战(不断做树得搜索);
二叉树数组
c语言表示:


Tree.h
#ifndef TREE_H_INCLUDED
#define TREE_H_INCLUDED
class Tree
{
public:
Tree(int size,int *pRoot); //创建树
~Tree(); //销毁树
int *SearchNode(int nodeIndex); //根据索引寻找结点
bool AddNode(int nodeIndex,int direction,int *pNode); //添加结点
bool DeleteNode(int nodeIndex,int *pNode); //删除结点
void TreeTraverse(); //遍历结点
private:
int *m_pTree;
int m_iSize;
};
#endif // TREE_H_INCLUDED
Tree.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include"Tree.h"
using namespace std;
Tree::Tree(int size,int *pRoot)
{
m_iSize=size;
m_pTree= new int[size];//从堆中分配了size个int大小的内存,并且pTree指向他
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
m_pTree[i]=0;
}
m_pTree[0]=*pRoot;
}
Tree::~Tree()
{
delete []m_pTree;
m_pTree=NULL;
}
int* Tree::SearchNode(int nodeIndex)
{
if(nodeIndex<0||nodeIndex>=m_iSize)
{
return NULL;
}
if(m_pTree[nodeIndex]==0)
{
return NULL;
}
return &m_pTree[nodeIndex];
}
bool Tree::AddNode(int nodeIndex,int direction,int *pNode)
{
//先找到结点
//nodeindex本身不合法
if(nodeIndex<0||nodeIndex>=m_iSize)
{
return false;
}
if(m_pTree[nodeIndex]==0)
{
return false;
}
if(direction==0)
{
if(nodeIndex*2+1>=m_iSize) //结点范围不合法
{
return false;
}
if(m_pTree[nodeIndex*2+1]!=0)//该节点已有值
{
return false;
}
m_pTree[nodeIndex*2+1]=*pNode;//pNode是指针 *pNode是其内容
}
if(direction==1)//右结点
{
if(nodeIndex*2+2>=m_iSize) //结点范围不合法
{
return false;
}
if(m_pTree[nodeIndex*2+2]!=0)//该节点已有值
{
return false;
}
m_pTree[nodeIndex*2+2]=*pNode;//pNode是指针 *pNode是其内容
}
return true;
}
bool Tree::DeleteNode(int nodeIndex,int *pNode)
{
if(nodeIndex<0||nodeIndex>=m_iSize)
{
return false;
}
if(m_pTree[nodeIndex]==0)// 要删除的地方本身就没有结点
{
return false;
}
*pNode=m_pTree[nodeIndex];
m_pTree[nodeIndex]=0;
return true;
}
void Tree::TreeTraverse() //用数组表示的树,直接循环输出即可
{
for(int i=0;i<m_iSize;i++)
{
cout<<m_pTree[i]<<" ";
}
}
测试
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
#include"Tree.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int root=3;
Tree *pTree = new Tree(10,&root);
int node1=5;
int node2=8;
pTree->AddNode(0,0,&node1);
pTree->AddNode(0,1,&node2);
int node3=2;
int node4=6;
pTree->AddNode(1,0,&node3);
pTree->AddNode(1,1,&node4);
int node5=9;
int node6=7;
pTree->AddNode(2,0,&node5);
pTree->AddNode(2,1,&node6);
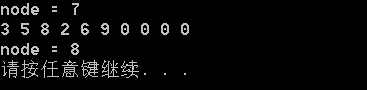
int node=0;
pTree->DeleteNode(6,&node);
cout<<"node = "<<node<<endl;
pTree->TreeTraverse();
int *p=pTree->SearchNode(2);
cout<<endl<<"node = "<<*p<<endl;
delete pTree;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
二叉树链表

Tree.h
#include"Node.h"
#include<stdio.h>
class Tree
{
public:
Tree(); //创建树
~Tree(); //销毁树
Node *SearchNode(int nodeIndex); //搜索结点
bool AddNode(int nodeIndex,int direction,Node *pNode); //添加结点
bool DeleteNode(int nodeIndex,Node *pNode);//删除结点
void PreorderTraversal();
void InorderTraversal();
void PostorderTraversal();
private:
Node *m_pRoot;
};
Tree.cpp
#include"Tree.h"
Tree::Tree()
{
m_pRoot= new Node();
}
Tree::~Tree()
{
DeleteNode(0,NULL);
//m_pRoot->DeleteNode();//也可以
}
Node *Tree::SearchNode(int nodeIndex)
{
return m_pRoot->SearchNode(nodeIndex);
}
bool Tree::AddNode(int nodeIndex,int direction,Node *pNode)
{
Node *temp=SearchNode(nodeIndex);
if(temp==NULL)
{
return false;
}
Node *node= new Node();
if(node==NULL)
{
return false;
}
node->index =pNode->index;
node->data= pNode->data;
node->pParent=temp;// 注意注意::注意在添加时要把父节点也记着
if(direction==0)
{
temp->pLChild=node;
}
if(direction==1)
{
temp->pRChild=node;
}
return true;
}
bool Tree::DeleteNode(int nodeIndex,Node *pNode)
{
Node *temp=SearchNode(nodeIndex);
if(temp==NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(pNode!=NULL)
{
pNode->data=temp->data;
}
temp->DeleteNode();//temp以及以下的子节点都删除
return true;
}
void Tree::PreorderTraversal()
{
m_pRoot->PreorderTraversal();//从根开始遍历
}
void Tree::InorderTraversal()
{
m_pRoot->InorderTraversal();
}
void Tree::PostorderTraversal()
{
m_pRoot->PostorderTraversal();
}
Node.h
#ifndef NODE_H_INCLUDED
#define NODE_H_INCLUDED
class Node
{
public :
Node();
Node *SearchNode(int nodeIndex);
void DeleteNode();
void PreorderTraversal();
void InorderTraversal();
void PostorderTraversal();
int index;
int data;
Node *pLChild;
Node *pRChild;
Node *pParent;
};
#endif // NODE_H_INCLUDED
Node.cpp
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include"Node.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
Node::Node()
{
index = 0;
data=0;
pLChild=NULL;
pRChild=NULL;
pParent=NULL;
}
Node *Node::SearchNode(int nodeIndex)
{
if (this->index == nodeIndex)
{
return this;
}
Node *temp = NULL;
if (this->pLChild != NULL)
{
if (this->pLChild->index == nodeIndex)
{
return this->pLChild;
}
//注意:没找到的情况继续往下找
else
{
temp = this->pLChild->SearchNode(nodeIndex);
if (temp != NULL)
{
return temp;
}
}
}
if (this->pRChild != NULL)
{
if (this->pRChild->index == nodeIndex)
{
return this->pRChild;
}
//注意没找到的情况继续往下找
else
{
temp = this->pRChild->SearchNode(nodeIndex);
if (temp != NULL)
{
return temp;
}
}
}
return NULL;
}
void Node::DeleteNode() //递归的删除结点
{
if(this->pLChild!=NULL) //删除左结点
{
this->pLChild->DeleteNode();
}
if(this->pRChild!=NULL) //删除右结点
{
this->pRChild->DeleteNode();
}
if(this->pParent!=NULL) //找到其父节点
{
if(this->pParent->pLChild==this)//如果该节点是父节点的左结点
{
this->pParent->pLChild=NULL;
}
if(this->pParent->pRChild==this)//如果该节点是父节点的有节点
{
this->pParent->pRChild=NULL;
}
}
delete this;
}
void Node::PreorderTraversal()
{
cout<<this->index<<"---"<<this->data<<endl;
if(this->pLChild!=NULL)
{
this->pLChild->PreorderTraversal();
}
if(this->pRChild!=NULL)
{
this->pRChild->PreorderTraversal();
}
}
void Node::InorderTraversal()
{
if(this->pLChild!=NULL)
{
this->pLChild->InorderTraversal();
}
cout<<this->index<<"---"<<this->data<<endl;
if(this->pRChild!=NULL)
{
this->pRChild->InorderTraversal();
}
}
void Node::PostorderTraversal()
{
if(this->pLChild!=NULL)
{
this->pLChild->PostorderTraversal();
}
if(this->pRChild!=NULL)
{
this->pRChild->PostorderTraversal();
}
cout<<this->index<<"---"<<this->data<<endl;
}
测试:
demo.cpp
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"Tree.h"
#include"Node.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
/*
(0)
5(1) 8(2)
2(3) 6(4) 9(5) 7(6)
*/
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Node *node1 = new Node();
node1->index=1;node1->data=5;
Node *node2= new Node();
node2->index=2;node2->data=8;
Node *node3 = new Node();
node3->index=3;node3->data=2;
Node *node4= new Node();
node4->index=4;node4->data=6;
Node *node5 = new Node();
node5->index=5;node5->data=9;
Node *node6= new Node();
node6->index=6;node6->data=7;
Tree *tree =new Tree();
tree->AddNode(0,0,node1);
tree->AddNode(0,1,node2);
tree->AddNode(1,0,node3);
tree->AddNode(1,1,node4);
tree->AddNode(2,0,node5);
tree->AddNode(2,1,node6);
// tree->DeleteNode(6,NULL);
// tree->DeleteNode(5,NULL);
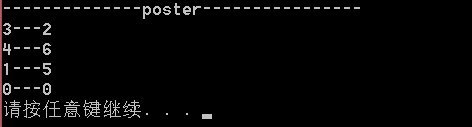
tree->DeleteNode(2,NULL);
// cout<<"--------------pre----------------"<<endl;
// tree->PreorderTraversal();
// cout<<"--------------in----------------"<<endl;
// tree->InorderTraversal();
cout<<"--------------poster----------------"<<endl;
tree->PostorderTraversal();
delete tree;
system("pause");
return 0;
}





 本文详细介绍了如何使用C++实现二叉树的数据结构,包括数组和链表两种方式,涵盖了创建、添加、删除节点及遍历等操作。
本文详细介绍了如何使用C++实现二叉树的数据结构,包括数组和链表两种方式,涵盖了创建、添加、删除节点及遍历等操作。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








