参考:
【2】https://mp.youkuaiyun.com/console/editor/html/105208262
————————————————————————
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//C语言向文件存入数据
void writeFile()
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("0501.txt", "w");
if (!fp)
{
printf("文件打开失败\n");
return;
}
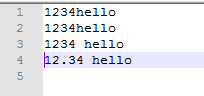
fprintf(fp, "%s\n", "1234hello");
fprintf(fp, "%s\n", "1234hello");
fprintf(fp, "%s\n", "1234 hello");
fprintf(fp, "%s\n", "12.34 hello");
fclose(fp);
printf("数据存储完成\n");
}
//使用C语言读取文件
void ReadFile1()
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("0501.txt", "r");
if (!fp)
{
printf("文件打开失败\n");
return;
}
//读取第一行:fgets
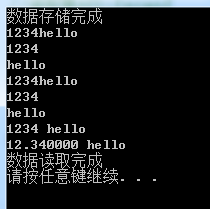
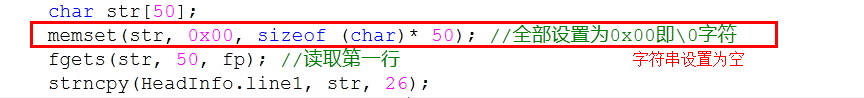
char str1[20];
fgets(str1, 10, fp);
cout << str1 << endl;
//分解第一行
//char str1_1[20] = { 0 }; //初始化为空
char str1_1[20];
memset(str1_1, '\0', sizeof(char)* 20); //初始化为空
strncpy(str1_1, str1, 4);
cout << str1_1 << endl;
char str1_2[20] = { 0 };
strncpy(str1_2, str1 + 4, 5);
cout << str1_2 << endl;
//读取第2行:fscanf
char str2[20];
fscanf(fp, "%s", str2);
cout << str2 << endl;
char str2_1[20] = { 0 };
strncpy(str2_1, str2, 4);
cout << str2_1 << endl;
char str2_2[20] = { 0 };
strncpy(str2_2, str2 + 4, 5);
cout << str2_2 << endl;
//读取第三行:fscanf
int str3_1;
char str3_2[20];
fscanf(fp, "%d %s", &str3_1, str3_2);
printf("%d %s\n", str3_1, str3_2);
//读取第4行:fscanf
float str4_1;
char str4_2[20];
fscanf(fp, "%f %s", &str4_1, str3_2);
printf("%f %s\n", str4_1, str3_2);
fclose(fp);
printf("数据读取完成\n");
}
int main()
{
writeFile();//使用C语言写文件
ReadFile1();//使用C语言读取文件
return 0;
}
%===20200508 补充===
1】
2】
方式1:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(void)
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("0501.txt", "r");
char ch1;
//char ch2[10];
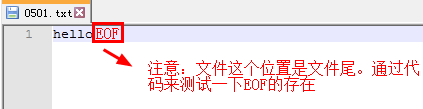
while (!feof(fp))
{
ch1 = fgetc(fp);
printf("%c", ch1);
//strcpy(ch2 , fgets(ch2,10,fp));
}
fclose(fp);
system("pause");
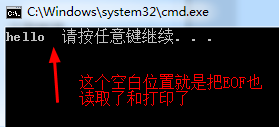
return 0;
}
方式2:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(void)
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("0501.txt", "r");
char ch1;
while (!feof(fp))
{
ch1 = fgetc(fp);
if (ch1 == EOF)
{
break;
}
printf("%c", ch1);
}
fclose(fp);
system("pause");
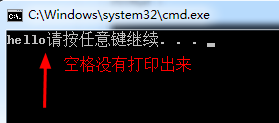
return 0;
}
方式3:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(void)
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("0501.txt", "r");
char ch1;
while ((ch1=fgetc(fp))!= EOF)
{
printf("%c", ch1);
}
fclose(fp);
system("pause");
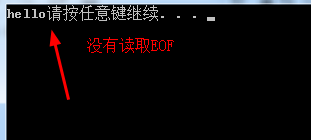
return 0;
}







 本文详细介绍如何使用C语言进行文件的读写操作,包括文件的打开、关闭、数据的写入和读取等基本流程,并提供了具体的代码示例,展示了如何通过fgets、fscanf等函数处理文本文件。
本文详细介绍如何使用C语言进行文件的读写操作,包括文件的打开、关闭、数据的写入和读取等基本流程,并提供了具体的代码示例,展示了如何通过fgets、fscanf等函数处理文本文件。
















 7803
7803

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








