#参照网址 https://github.com/PacktPublishing/Natural-Language-Processing-with-TensorFlow/blob/master/ch8/lstms_for_text_generation.ipynb
import re
import collections
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
filename = '射雕英雄传.txt'
def handle_file():
documents = []
document = []
with open(filename, encoding='gb2312',errors='ignore') as f:
i=0
for line in f:
i+=1
if len(line.strip())>0:
if not re.search("第.{0,3}回", line) and len(line.strip()) > 0:
document.extend(list(line.strip()))
elif re.search("第.{0,3}回", line):
if document:
print("document: ", "".join(document[:100]))
documents.append(document) # 手动添加了虚拟的第四十一回,为了保证第四十回放到列表中。
document = []
if "第四十一回" not in line:
print('\n', line)
else:
print("未知行:", i, line)
return documents
def build_dataset(documents):
chars = []
data_list = []
for d in documents:
chars.extend(d)
print('%d Characters found.' % len(chars))
count = []
count.extend(collections.Counter(chars).most_common())
# Start with 'UNK' that is assigned to too rare words
dictionary = dict({'UNK': 0})
for char, c in count:
# Only add a char to dictionary if its frequency is more than 10
if c > 10:
dictionary[char] = len(dictionary)
unk_count = 0
# Traverse through all the text we have
# to replace each string word with the ID of the word
for d in documents:
data = list()
for char in d:
# If word is in the dictionary use the word ID,
# else use the ID of the special token "UNK"
if char in dictionary:
index = dictionary[char]
else:
index = dictionary['UNK']
unk_count += 1
data.append(index)
data_list.append(data)
reverse_dictionary = dict(zip(dictionary.values(), dictionary.keys()))
return data_list, count, dictionary, reverse_dictionary
class DataGeneratorOHE(object):
def __init__(self, text, batch_size, num_unroll):
# Text where a bigram is denoted by its ID
self._text = text
# Number of bigrams in the text
self._text_size = len(self._text)
# Number of datapoints in a batch of data
self._batch_size = batch_size
# Num unroll is the number of steps we unroll the RNN in a single training step
# This relates to the truncated backpropagation we discuss in Chapter 6 text
self._num_unroll = num_unroll
# We break the text in to several segments and the batch of data is sampled by
# sampling a single item from a single segment
self._segments = self._text_size // self._batch_size
self._cursor = [offset * self._segments for offset in range(self._batch_size)]
def next_batch(self):
'''
Generates a single batch of data
'''
# Train inputs (one-hot-encoded) and train outputs (one-hot-encoded)
batch_data = np.zeros((self._batch_size, vocabulary_size), dtype=np.float32)
batch_labels = np.zeros((self._batch_size, vocabulary_size), dtype=np.float32)
# Fill in the batch datapoint by datapoint
for b in range(self._batch_size):
# If the cursor of a given segment exceeds the segment length
# we reset the cursor back to the beginning of that segment
if self._cursor[b] + 1 >= self._text_size:
self._cursor[b] = b * self._segments
# Add the text at the cursor as the input
batch_data[b, self._text[self._cursor[b]]] = 1.0
# Add the preceding bigram as the label to be predicted
batch_labels[b, self._text[self._cursor[b] + 1]] = 1.0
# Update the cursor
self._cursor[b] = (self._cursor[b] + 1) % self._text_size
return batch_data, batch_labels
def unroll_batches(self):
'''
This produces a list of num_unroll batches
as required by a single step of training of the RNN
'''
unroll_data, unroll_labels = [], []
for ui in range(self._num_unroll):
data, labels = self.next_batch()
unroll_data.append(data)
unroll_labels.append(labels)
return unroll_data, unroll_labels
def reset_indices(self):
'''
Used to reset all the cursors if needed
'''
self._cursor = [offset * self._segments for offset in range(self._batch_size)]
documents = handle_file()
data_list, count, dictionary, reverse_dictionary = build_dataset(documents)
num_files = len(data_list)
vocabulary_size = len(dictionary)
# 隐状态神经元个数
num_nodes = 128
# 批次
batch_size = 64
#时间序列的长度
num_unrollings = 50
# 留存率
dropout = 0.0
tf.reset_default_graph()
# 训练数据集输入,标签,shape=(num_unrollings*batch_size*num_nodes)
train_inputs, train_labels = [],[]
for ui in range(num_unrollings):
train_inputs.append(tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[batch_size,vocabulary_size],name='train_inputs_%d'%ui))
train_labels.append(tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[batch_size,vocabulary_size], name='train_labels_%d'%ui))
# 验证集输入,标签,shape=(1*batch_size*num_nodes)
valid_inputs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[1,vocabulary_size],name='valid_inputs')
valid_labels = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[1,vocabulary_size], name = 'valid_labels')
# 测试输入,标签,shape=(1*batch_size*num_nodes)
test_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[1, vocabulary_size], name = 'test_input')
# 输入门的权重Wix,Whh,Wib
ix = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([vocabulary_size, num_nodes], stddev=0.02))
im = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([num_nodes, num_nodes], stddev=0.02))
ib = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1, num_nodes],-0.02, 0.02))
# 忘记门的权重Wfx,Wfm,Wfb
fx = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([vocabulary_size, num_nodes], stddev=0.02))
fm = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([num_nodes, num_nodes], stddev=0.02))
fb = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1, num_nodes],-0.02, 0.02))
# 候选状态c~_t的权重Wcx,Wcm,Wfb
cx = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([vocabulary_size, num_nodes], stddev=0.02))
cm = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([num_nodes, num_nodes], stddev=0.02))
cb = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1, num_nodes],-0.02,0.02))
# 输出门的权重Wox,Wom,Wob
ox = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([vocabulary_size, num_nodes], stddev=0.02))
om = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([num_nodes, num_nodes], stddev=0.02))
ob = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1, num_nodes],-0.02,0.02))
# LSTM输出值output的w,b
w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([num_nodes, vocabulary_size], stddev=0.02))
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([vocabulary_size],-0.02,0.02))
# 保存训练集隐藏层的output,state
saved_output = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([batch_size, num_nodes]), trainable=False, name='train_hidden')
saved_state = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([batch_size, num_nodes]), trainable=False, name='train_cell')
# 保存验证集隐藏层的output,state
saved_valid_output = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, num_nodes]),trainable=False, name='valid_hidden')
saved_valid_state = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, num_nodes]),trainable=False, name='valid_cell')
# 保存测试集隐藏层的output,state
saved_test_output = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, num_nodes]),trainable=False, name='test_hidden')
saved_test_state = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, num_nodes]),trainable=False, name='test_cell')
# 定义LSTM神经元
def lstm_cell(i, o, state):
input_gate = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(i, ix) + tf.matmul(o, im) + ib)
forget_gate = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(i, fx) + tf.matmul(o, fm) + fb)
update = tf.matmul(i, cx) + tf.matmul(o, cm) + cb
state = forget_gate * state + input_gate * tf.tanh(update)
output_gate = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(i, ox) + tf.matmul(o, om) + ob)
return output_gate * tf.tanh(state), state
# 保存隐藏层的outputs, shape=(num_unrollings,batch_size,num_nodes)
outputs = list()
output = saved_output
state = saved_state
for i in train_inputs:
output, state = lstm_cell(i, output, state)
output = tf.nn.dropout(output, keep_prob=1.0 - dropout)
outputs.append(output)
# 计算outputs的logits score,shape=(num_unrollings*batch_size,num_nodes)
logits = tf.matmul(tf.concat(axis=0, values=outputs), w) + b
# 计算outputs预测概率,shape=(num_unrollings*batch_size,num_nodes)
train_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(logits)
# 计算训练集困惑度.
train_perplexity_without_exp = tf.reduce_sum(
tf.concat(train_labels, 0) * -tf.log(tf.concat(train_prediction, 0) + 1e-10)) / (num_unrollings * batch_size)
# 同上
valid_output, valid_state = lstm_cell(
valid_inputs, saved_valid_output, saved_valid_state)
valid_logits = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(valid_output, w, b)
# 保存上一次的output,state作为下一次迭代的输入
with tf.control_dependencies([saved_valid_output.assign(valid_output),
saved_valid_state.assign(valid_state)]):
valid_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(valid_logits)
valid_perplexity_without_exp = tf.reduce_sum(valid_labels * -tf.log(valid_prediction + 1e-10))
# 同上
test_output, test_state = lstm_cell(
test_input, saved_test_output, saved_test_state)
with tf.control_dependencies([saved_test_output.assign(test_output),
saved_test_state.assign(test_state)]):
test_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(tf.nn.xw_plus_b(test_output, w, b))
# 计算训练集的loss
with tf.control_dependencies([saved_output.assign(output),
saved_state.assign(state)]):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(
logits=logits, labels=tf.concat(axis=0, values=train_labels)))
# 学习率调整,梯度修剪
gstep = tf.Variable(0,trainable=False,name='global_step')
inc_gstep = tf.assign(gstep, gstep+1)
tf_learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(0.001,gstep,decay_steps=1, decay_rate=0.5)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(tf_learning_rate)
gradients, v = zip(*optimizer.compute_gradients(loss))
gradients, _ = tf.clip_by_global_norm(gradients, 5.0)
optimizer = optimizer.apply_gradients(
zip(gradients, v))
# 重置训练集,验证集,测试集的output,state
reset_train_state = tf.group(tf.assign(saved_state, tf.zeros([batch_size, num_nodes])),
tf.assign(saved_output, tf.zeros([batch_size, num_nodes])))
reset_valid_state = tf.group(tf.assign(saved_valid_state, tf.zeros([1, num_nodes])),
tf.assign(saved_valid_output, tf.zeros([1, num_nodes])))
reset_test_state = tf.group(
saved_test_output.assign(tf.random_normal([1, num_nodes],stddev=0.05)),
saved_test_state.assign(tf.random_normal([1, num_nodes],stddev=0.05)))
decay_threshold = 5
decay_count = 0
min_perplexity = 1e10
# 调整学习率的衰减函数,先调整困惑度,当困惑度不能下降则主动调整学习率
def decay_learning_rate(session, v_perplexity):
global decay_threshold, decay_count, min_perplexity
if v_perplexity < min_perplexity:
decay_count = 0
min_perplexity= v_perplexity
else:
decay_count += 1
if decay_count >= decay_threshold:
print('\t Reducing learning rate')
decay_count = 0
session.run(inc_gstep)
# 保存困惑度的变化过程
train_perplexity_ot = []
valid_perplexity_ot = []
session = tf.InteractiveSession()
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
print('Initialized Global Variables ')
# beamsearch的深度和每步的结果。
beam_length = 5
beam_neighbors = 5
# beamsearch的输入值,shape=(beam_neighbors,1,vocabulary_size)
# beamsearch结果索引,shape=(beam_neighbors,)
sample_beam_inputs = [tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[1, vocabulary_size]) for _ in range(beam_neighbors)]
best_beam_index = tf.placeholder(shape=None, dtype=tf.int32)
best_neighbor_beam_indices = tf.placeholder(shape=[beam_neighbors], dtype=tf.int32)
# 保存beamsearch的output,sate,shape=(beam_neighbors,1,num_nodes)
saved_sample_beam_output = [tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, num_nodes])) for _ in range(beam_neighbors)]
saved_sample_beam_state = [tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, num_nodes])) for _ in range(beam_neighbors)]
# 重置beamsearch的output,sate,shape=(beam_neighbors,1,num_nodes)
reset_sample_beam_state = tf.group(
*[saved_sample_beam_output[vi].assign(tf.zeros([1, num_nodes])) for vi in range(beam_neighbors)],
*[saved_sample_beam_state[vi].assign(tf.zeros([1, num_nodes])) for vi in range(beam_neighbors)]
)
# 堆积beamsearch的output,sate,shape=(beam_neighbors,1,num_nodes)
stacked_beam_outputs = tf.stack(saved_sample_beam_output)
stacked_beam_states = tf.stack(saved_sample_beam_state)
# 根据beamsearch的结果索引找到outputs,states并用它们进行更新。
update_sample_beam_state = tf.group(
*[saved_sample_beam_output[vi].assign(tf.gather_nd(stacked_beam_outputs, [best_neighbor_beam_indices[vi]])) for vi
in range(beam_neighbors)],
*[saved_sample_beam_state[vi].assign(tf.gather_nd(stacked_beam_states, [best_neighbor_beam_indices[vi]])) for vi in
range(beam_neighbors)]
)
# 计算每次beamsearch的output,state,shape=(beam_neighbors,1,num_nodes)
sample_beam_outputs, sample_beam_states = [], []
for vi in range(beam_neighbors):
tmp_output, tmp_state = lstm_cell(
sample_beam_inputs[vi], saved_sample_beam_output[vi], saved_sample_beam_state[vi]
)
sample_beam_outputs.append(tmp_output)
sample_beam_states.append(tmp_state)
# 保存beamsearch的预测结果,shape= (beam_neighbors,1,vocabulary_size)
sample_beam_predictions = []
for vi in range(beam_neighbors):
with tf.control_dependencies([saved_sample_beam_output[vi].assign(sample_beam_outputs[vi]),
saved_sample_beam_state[vi].assign(
sample_beam_states[vi])]):
sample_beam_predictions.append(tf.nn.softmax(tf.nn.xw_plus_b(sample_beam_outputs[vi], w, b)))
def get_beam_prediction(session):
# 根据beamsearch的生成对应深度(beam_length)的文字
# 举例说明:假设有3类 beam_neighbors=2 (最佳候选用*表示,次之用`表示)
# *的概率为0.5,`的概率为0.2
# a` b* c <--- root level
# / | \ / | \ / | \
# a b c a* b` c a b c <--- depth 1
# / | \ / | \ / | \ / | \ / | \ / | \ / | \ / | \ / | \
# a b c a b c a b c a*b c a`b c a b c a b c a b c a b c <--- depth 2
# 深度为2的beamsearch结果为b-a-a和b-b-a
global test_word
global sample_beam_predictions
global update_sample_beam_state
# 计算根候选字,复制了5份一样的根候选字
feed_dict = {}
for b_n_i in range(beam_neighbors):
feed_dict.update({sample_beam_inputs[b_n_i]: test_word})
# 计算beamsearch的预测结果,由于输入的根候选字是一样的,只取一份
# shape=(1,1,vocabulary_size)
sample_preds_root = session.run(sample_beam_predictions, feed_dict=feed_dict)
sample_preds_root = sample_preds_root[0]
# 取topK的索引值,例如根级别的b,a的索引值
this_level_candidates = (np.argsort(sample_preds_root, axis=1).ravel()[::-1])[:beam_neighbors].tolist()
# 取topK的预测概率值,对应根级别的0.5,0.2
this_level_probs = sample_preds_root[0, this_level_candidates]
# 根据根级别的候选者更新对应的字并组成短语,结果为['b','a']
test_sequences = ['' for _ in range(beam_neighbors)]
for b_n_i in range(beam_neighbors):
test_sequences[b_n_i] += reverse_dictionary[this_level_candidates[b_n_i]]
# 根据beamsearch搜索深度beam_length计算保留的短语序列以及最后一个字
for b_i in range(beam_length - 1):
test_words = [] # 每次beam的候选者
pred_words = [] # 每次beam的预测字
# 根据上一层级候选者的索引this_level_candidates[p_idx]找到对应的字one-hot编码作为LSTM输入
# sample_beam_inputs[0]: b, sample_beam_inputs[1]:a
# sample_beam_inputs.shape=(beam_neighbors,1,vocabulary_size)
feed_dict = {}
for p_idx, pred_i in enumerate(this_level_candidates):
test_words.append(np.zeros((1, vocabulary_size), dtype=np.float32))
test_words[p_idx][0, this_level_candidates[p_idx]] = 1.0
feed_dict.update({sample_beam_inputs[p_idx]: test_words[p_idx]})
# Calculating predictions for all neighbors in beams
# This is a list of vectors where each vector is the prediction vector for a certain beam
# For level 1 in our example, the prediction values for
# b a (previous beam search results)
# [a, b, c], [a, b, c] (current level predictions) would be
# [0.1,0.1,0.1],[0.5,0.2,0]
# 计算beamsearch的输出概率,shape=(beam_neighbors,1,vocabulary_size)
sample_preds_all_neighbors = session.run(sample_beam_predictions, feed_dict=feed_dict)
#将beam_search的输出概率变为一列,shape=(1,beam_neighbors*vocabulary_size)
sample_preds_all_neighbors_concat = np.concatenate(sample_preds_all_neighbors, axis=1)
# Update this_level_candidates to be used for the next iteration
# And update the probabilities for each beam
# In our example these would be [3,4] (indices with maximum value from above vector)
# 取beam_neighbors个结果输出概率,找到对应的索引值
this_level_candidates = np.argsort(sample_preds_all_neighbors_concat.ravel())[::-1][:beam_neighbors]
# 找到对应父结点(即上一层级)的索引值(0~4之间),例子的结果是[1,1]
parent_beam_indices = this_level_candidates // vocabulary_size
# 找到子结点预测的候选值,shape=(5,),索引值范围在(0~vocabulary_size-1之间),例子的结果为[0,1]
this_level_candidates = (this_level_candidates % vocabulary_size).tolist()
# 由于之前通过sample_beam_predictions已经计算了sample_beam_output,sample_beam_state的结果
# 更新saved_sample_beam_output,saved_sample_beam_state的结果
session.run(update_sample_beam_state, feed_dict={best_neighbor_beam_indices: parent_beam_indices})
# 用临时变量保存this_level_probs,例子为[0.5,0.2]
# 用临时变量保存test_sequences,例子为['b','a']
tmp_this_level_probs = np.asarray(this_level_probs)
tmp_test_sequences = list(test_sequences)
for b_n_i in range(beam_neighbors):
# 父结点的索引值parent_beam_indices[b_n_i]为[1,1]
# 找到父结点的概率值,例子为[0.5,0.5]
this_level_probs[b_n_i] = tmp_this_level_probs[parent_beam_indices[b_n_i]]
# 用乘法合并父结点和子结点的概率值,例子结果为[0.5*0.5, 0.5*0.2] = [0.25,0.1]
this_level_probs[b_n_i] *= sample_preds_all_neighbors[parent_beam_indices[b_n_i]][
0, this_level_candidates[b_n_i]]
# 基于预测结果parent_beam_indices[b_n_i]更新父结点的test_sequences,例子为['b','a']
test_sequences[b_n_i] = tmp_test_sequences[parent_beam_indices[b_n_i]]
# 基于子结点的预测索引this_level_candidates[b_n_i]更新当前的test_sequences,例子为['ba','bb']
test_sequences[b_n_i] += reverse_dictionary[this_level_candidates[b_n_i]]
# 给当前层的候选字创建onehot编码,目的是为beam_length下一次的输入做准备。
# shape=(5,1,vocabulary_size)
pred_words.append(np.zeros((1, vocabulary_size), dtype=np.float32))
pred_words[b_n_i][0, this_level_candidates[b_n_i]] = 1.0
# 基于概率分布找到最好的那个字索引best_beam_id
rand_cand_ids = np.argsort(this_level_probs)[-3:]
rand_cand_probs = this_level_probs[rand_cand_ids] / np.sum(this_level_probs[rand_cand_ids])
random_id = np.random.choice(rand_cand_ids, p=rand_cand_probs)
best_beam_id = parent_beam_indices[random_id]
# 更新output,state为下一次预测做准备
session.run(update_sample_beam_state,
feed_dict={best_neighbor_beam_indices: [best_beam_id for _ in range(beam_neighbors)]})
# 最佳beam的最后一个字
test_word = pred_words[best_beam_id]
# 返回beam_length的短语(包含最初的输入值)
return test_sequences[best_beam_id]
num_steps = 26 # 26
steps_per_document = 100
valid_summary = 1
train_doc_count = len(data_list)
docs_per_step = 10
beam_nodes = []
beam_train_perplexity_ot = []
beam_valid_perplexity_ot = []
session = tf.InteractiveSession()
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
print('Initialized')
average_loss = 0
# We use the first 10 documents that has
# more than 10*steps_per_document bigrams for creating the validation dataset
# Identify the first 10 documents following the above condition
long_doc_ids = []
for di in range(num_files):
if len(data_list[di]) > 10 * steps_per_document:
long_doc_ids.append(di)
if len(long_doc_ids) == 10:
break
data_gens = []
valid_gens = []
for fi in range(num_files-1):
if fi not in long_doc_ids:
data_gens.append(DataGeneratorOHE(data_list[fi], batch_size, num_unrollings))
else:
data_gens.append(DataGeneratorOHE(data_list[fi][:-steps_per_document], batch_size, num_unrollings))
valid_gens.append(DataGeneratorOHE(data_list[fi][-steps_per_document:], 1, 1))
feed_dict = {}
for step in range(num_steps):
for di in np.random.permutation(train_doc_count)[:docs_per_step]:
doc_perplexity = 0
for doc_step_id in range(steps_per_document):
u_data, u_labels = data_gens[di].unroll_batches()
for ui, (dat, lbl) in enumerate(zip(u_data, u_labels)):
feed_dict[train_inputs[ui]] = dat
feed_dict[train_labels[ui]] = lbl
_, l, step_perplexity = session.run([optimizer, loss, train_perplexity_without_exp],
feed_dict=feed_dict)
doc_perplexity += step_perplexity
average_loss += step_perplexity
# 打印训练集的文档索引
print('(%d).' % di, end='')
# session.run(reset_train_state) # 重置每次迭代文档的state,output
print('')
if (step + 1) % valid_summary == 0:
# 计算loss均值,即每个字的平均损失。
average_loss = average_loss / (docs_per_step * steps_per_document * valid_summary)
# 打印每个epoch的损失值、困惑度,困惑度计算方式exp(loss)并保存。
print('Average loss at step %d: %f' % (step + 1, average_loss))
print('\tPerplexity at step %d: %f' % (step + 1, np.exp(average_loss)))
beam_train_perplexity_ot.append(np.exp(average_loss))
# 重置loss
average_loss = 0
valid_loss = 0
# 计算valid perplexity
for v_doc_id in range(10):
for v_step in range(steps_per_document):# 与原书代码//2不同
#uvalid_data,uvalid_labels shape=[1,1,vocabulary_size]
uvalid_data, uvalid_labels = valid_gens[v_doc_id].unroll_batches()
v_perp = session.run(
valid_perplexity_without_exp,
feed_dict={valid_inputs: uvalid_data[0], valid_labels: uvalid_labels[0]}
)
valid_loss += v_perp
session.run(reset_valid_state)
valid_gens[v_doc_id].reset_indices()
print()
v_perplexity = np.exp(valid_loss / (steps_per_document * 10.0))
print("Valid Perplexity: %.2f\n" % v_perplexity)
beam_valid_perplexity_ot.append(v_perplexity)
# 衰减学习率
decay_learning_rate(session, v_perplexity)
# 根据射雕英雄传第40章首字生成第40章。
chars_in_segment = len(data_list[-1])// beam_length
print("'======================== The chapter40 =========================='")
test_word = np.zeros((1,vocabulary_size))
test_word[:, data_list[-1][0]]= 1
print("", reverse_dictionary[data_list[-1][0]], end='')
for _ in range(chars_in_segment):
test_sequence = get_beam_prediction(session)
print(test_sequence, end='')
print("")
session.run([reset_sample_beam_state])
print('====================================================================')
print("")
session.close()
运行结果如下:总体看语义完全不通,训练次数到一定次数loss,perplexity无法下降,代码待改进之处多多。
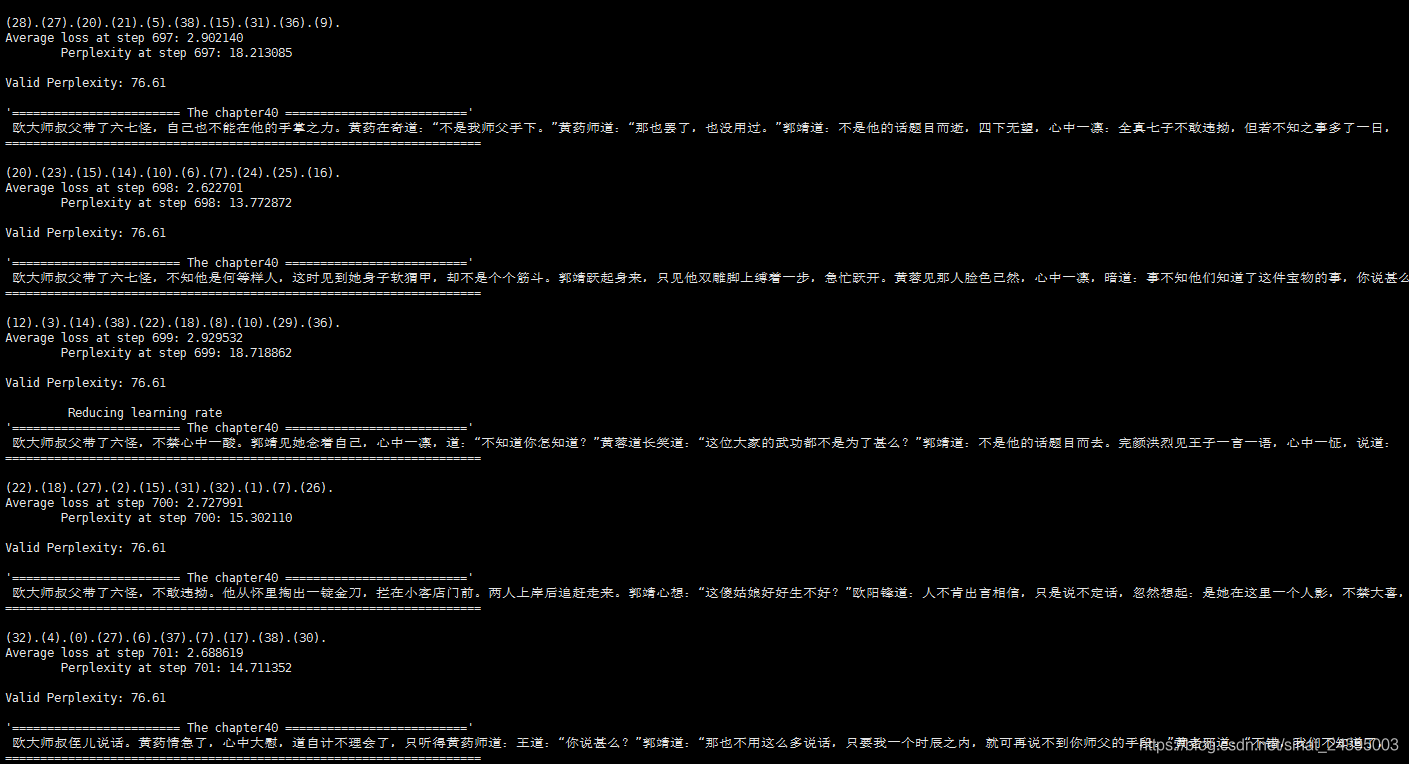





 本博客介绍了一个基于TensorFlow的长短期记忆(LSTM)网络模型,用于从《射雕英雄传》文本中生成新的章节内容。模型通过预处理文本、构建数据集、设置LSTM单元和训练过程,实现了文本的自动续写。尽管生成的文本在语法和语义上仍有待改进,但展示了LSTM在文本生成任务上的应用。
本博客介绍了一个基于TensorFlow的长短期记忆(LSTM)网络模型,用于从《射雕英雄传》文本中生成新的章节内容。模型通过预处理文本、构建数据集、设置LSTM单元和训练过程,实现了文本的自动续写。尽管生成的文本在语法和语义上仍有待改进,但展示了LSTM在文本生成任务上的应用。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








