调试代码搭建参考
断点为LogAspects类与MathCalculator每个方法 debug执行方法

进入断点,intercept方法
@Override
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Class<?> targetClass = null;
Object target = null;
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we
// "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool...
target = getTarget();
if (target != null) {
targetClass = target.getClass();
}
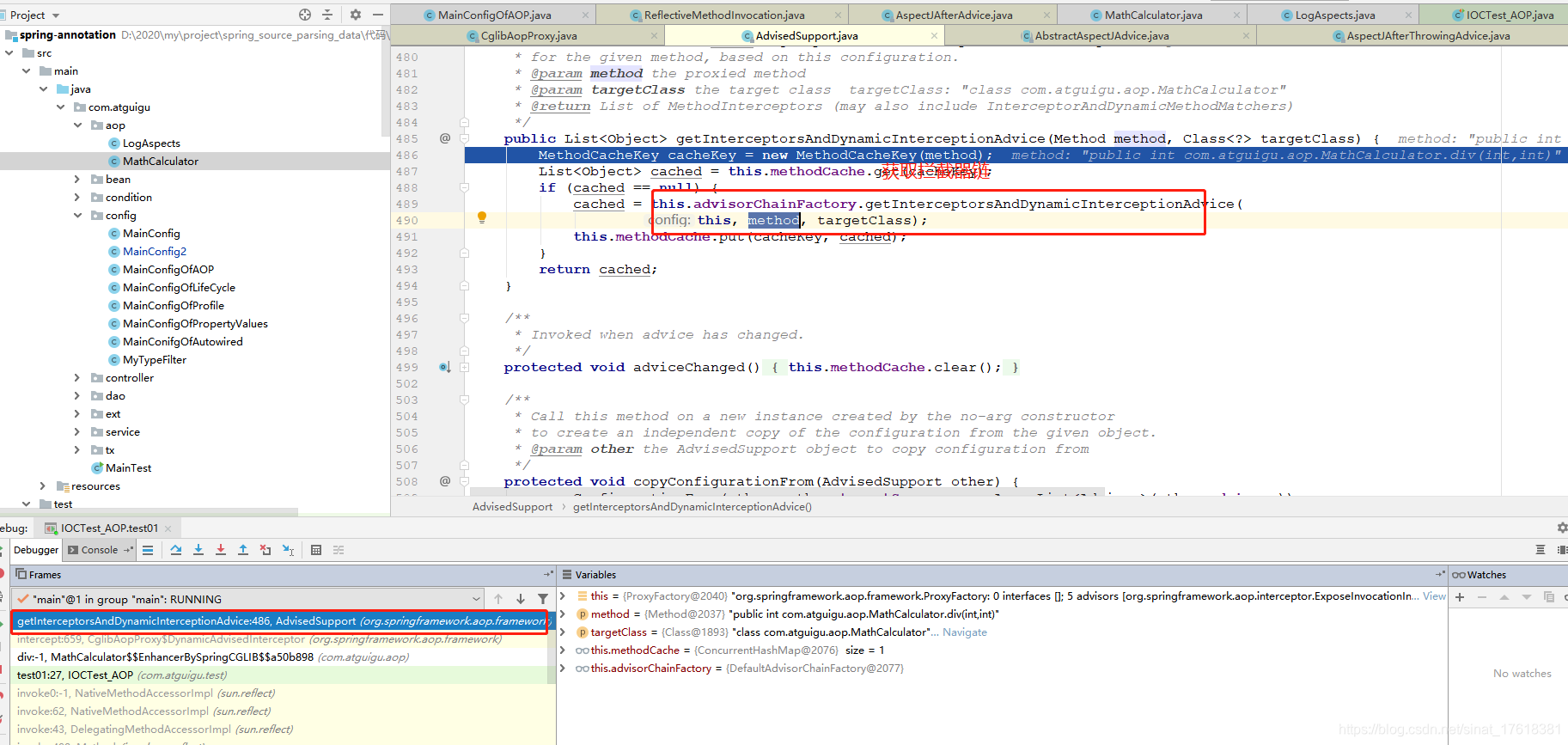
//1.获取拦截器链
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,
// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.
if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly.
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know
// it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot
// swapping or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
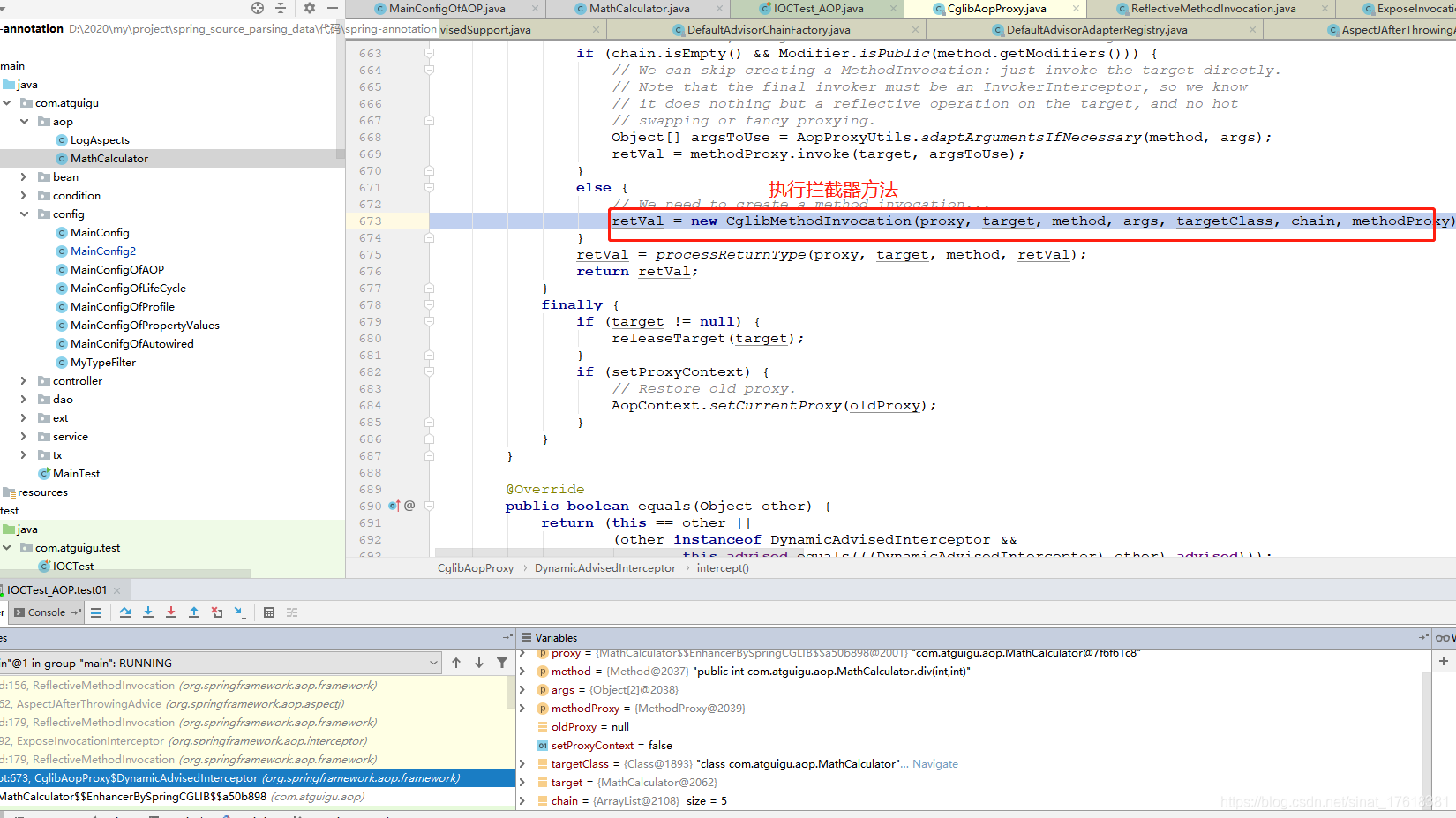
//2.执行拦截器链的方法
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null) {
releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
1.获取拦截器链
2.执行拦截器链的方法
后面就不截图了,就是一个拦截器链的执行过程,有兴趣可以看看,比较简单,通过拦截器链的执行顺序控制代理的通知方法的执行顺序。
总结:
容器中保存了组件的代理对象(cglib增强后的对象),这个对象里面保存了详细信息(比如增强器,目标对象,xxx);
1)、CglibAopProxy.intercept();拦截目标方法的执行
2)、根据ProxyFactory对象获取将要执行的目标方法拦截器链;
List chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
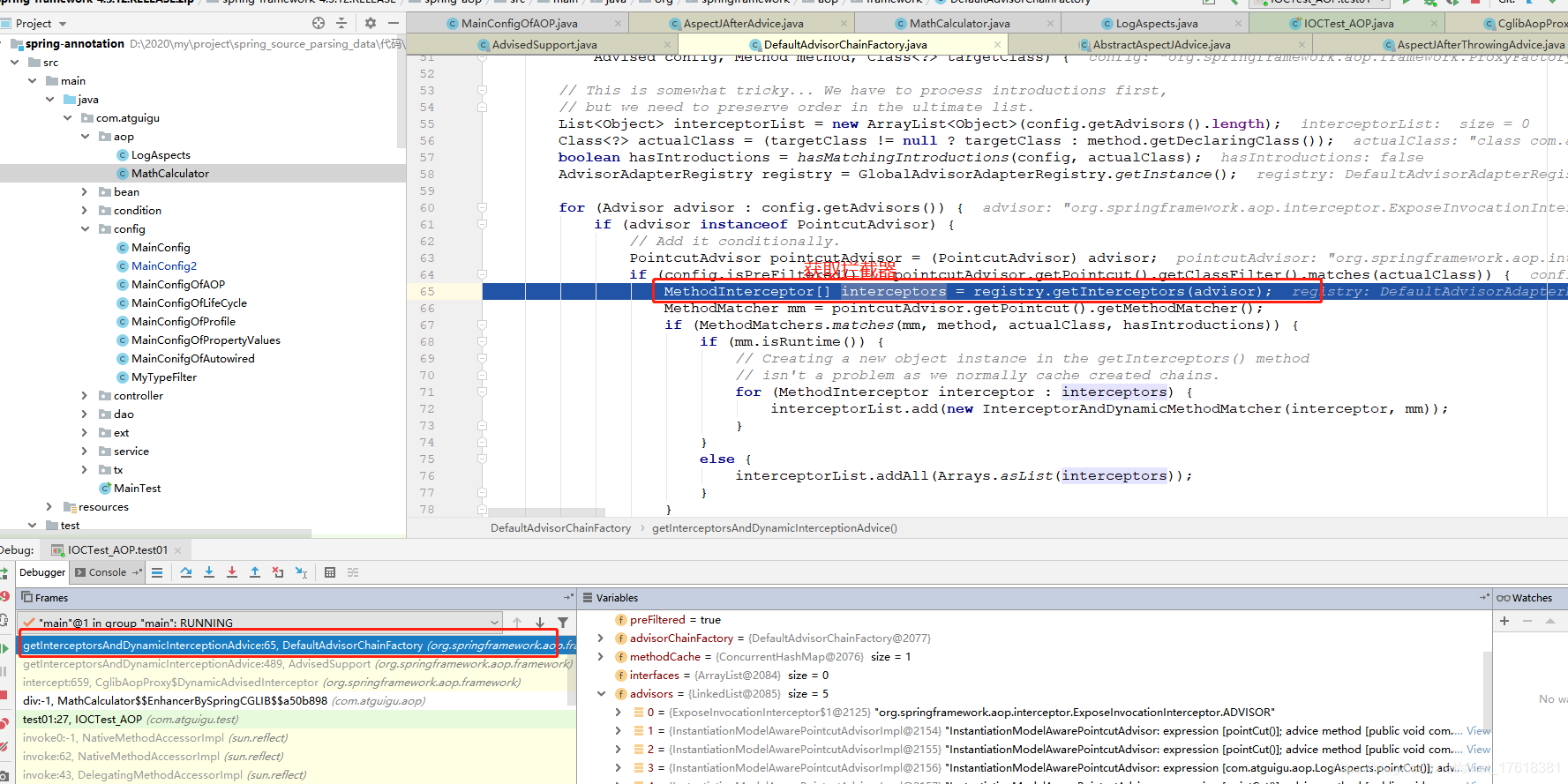
1)、List interceptorList保存所有拦截器 5
一个默认的ExposeInvocationInterceptor 和 4个增强器;
2)、遍历所有的增强器,将其转为Interceptor;
registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
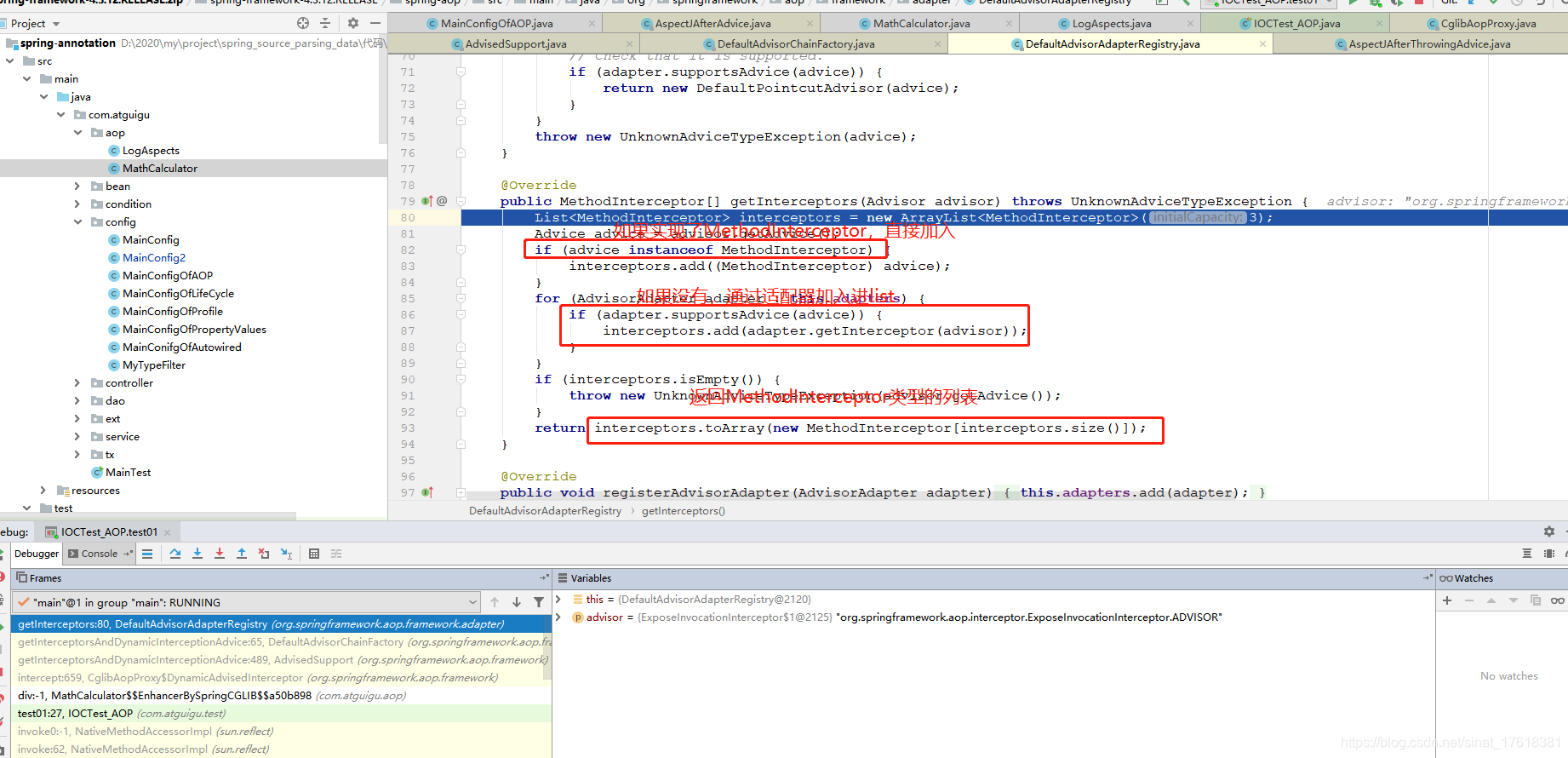
3)、将增强器转为List;
如果是MethodInterceptor,直接加入到集合中
如果不是,使用AdvisorAdapter将增强器转为MethodInterceptor;
转换完成返回MethodInterceptor数组;
3)、如果没有拦截器链,直接执行目标方法;
拦截器链(每一个通知方法又被包装为方法拦截器,利用MethodInterceptor机制)
4)、如果有拦截器链,把需要执行的目标对象,目标方法,
拦截器链等信息传入创建一个 CglibMethodInvocation 对象,
并调用 Object retVal = mi.proceed();
5)、拦截器链的触发过程;
1)、如果没有拦截器执行执行目标方法,或者拦截器的索引和拦截器数组-1大小一样(指定到了最后一个拦截器)执行目标方法;
2)、链式获取每一个拦截器,拦截器执行invoke方法,每一个拦截器等待下一个拦截器执行完成 返回以后再来执行;拦截器链的机制,保证通知方法与目标方法的执行顺序;







 本文详细解析了AOP原理及Cglib在Spring框架中的应用,阐述了如何通过CglibAopProxy.intercept()方法拦截目标方法执行,获取并执行拦截器链,确保通知方法与目标方法正确有序地执行。
本文详细解析了AOP原理及Cglib在Spring框架中的应用,阐述了如何通过CglibAopProxy.intercept()方法拦截目标方法执行,获取并执行拦截器链,确保通知方法与目标方法正确有序地执行。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








