假设我的QContent文章实体类中infoSourceType是来源类型。
public Map findbyIds(List<String> ids){
Predicate predicate1 = QContent.id.in(ids).and(QContent.infoSourceType.eq("微博"));
//来源统计
Long ins = queryFactory.select(QContent.id).where(predicate1).from(QContent).fetchCount();
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("ins",ins);
return map;
}
实现的sql语句为:
select count(id) from content ct
where (ct.id in (100,1005,1006) and ct.info_source_type = "微博")
-- 100,1005,1006是id列表
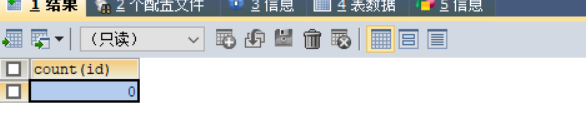
查询结果























 501
501

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








