视频14—介绍对象
对象和结构的区别
对象的内部可以有变量【属性】和函数【方法】,结构通常只有变量。


#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const unsigned int FULL_GAS = 80;
//定义一个类
class car
{
public:
string color;
string engin;
float gas_tank;
unsigned int wheel;
//定义方法【函数】
void fill_gas(float liter);//加油
void setColor(string col);//设置颜色
void setWheel(unsigned int whe);//设置轮子
void setEngin(string eng);//设置引擎
int running();//小车跑着
void warning();//警报
};
void car::warning()
{
cout << "还剩油量:" << 100 * gas_tank / FULL_GAS << '%' << endl;
}
void car::setEngin(string eng)
{
engin = eng;
}
void car::setWheel(unsigned int whe)
{
wheel = whe;
}
void car::setColor(string col)
{
color = col;
}
void car::fill_gas(float liter)
{
gas_tank += liter;
}
int car::running()
{
cout << "小车正在以120的速度跑着!!!" << endl;
gas_tank--;
cout << "当前油量:" << 100 * gas_tank / FULL_GAS << '%' << endl;
return gas_tank;
}
int main()
{
char ch;//存储加油命令
car mycar;
mycar.setColor("Black");
mycar.setWheel(4);
mycar.setEngin("V8");
mycar.gas_tank = FULL_GAS;//加满油
while ( mycar.running() )
{
if (mycar.running() < 10)
{
mycar.warning();
cout << "是否需要加油【Y/N】:" << endl;
cin >> ch;
switch (ch)
{
case 'Y':
case 'y':
mycar.fill_gas(FULL_GAS);
break;
case 'N':
case 'n':
cout << "不加就不加" << endl;
default:
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}视频15—构造器和析构器


每个类至少有一个构造器,如果自己没有定义的话,编译器会自动定义一个相应的空的构造器;相应的销毁对象的时候,会调用析构器



构造器和析构器实现文件操作
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>//字符串操作
#include <fstream>//文件操作
class StoreQuote
{
public:
StoreQuote();//构造器
~StoreQuote();//析构器
string quote, speaker;//存储名言和作者
ofstream OutFile;//写入文件类
void inputQuote();
void inputSpeaker();
bool write();
bool ifwrite();
private:
};
//构造器:事先完成初始化和准备工作
StoreQuote::StoreQuote()
{
OutFile.open("test.txt", ios::app);//追加的方式写入文件
}
//析构器:完成时候的清理工作
StoreQuote::~StoreQuote()
{
OutFile.close();//关闭文件
}
void StoreQuote::inputQuote()
{
getline(cin, quote);//getline是string中的类
}
void StoreQuote::inputSpeaker()
{
getline(cin, speaker);
}
bool StoreQuote::write()
{
//判断文件是否打开
if (OutFile.is_open())
{
OutFile << quote << "………………" << speaker << endl;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool StoreQuote::ifwrite()
{
char ch;
cout << "是否写入格言【Y/N】:" << endl;
cin >> ch;
cin.ignore(100, '\n');//忽略100个字符,除非遇到回车
switch (ch)
{
case 'Y':
case 'y':
cout << "将格言写入文件" << endl;
return true;
break;
case 'N':
case 'n':
cout << "格言不写入文件" << endl;
return false;
break;
default:
return false;
break;
}
}
int main()
{
StoreQuote quote;
while ( quote.ifwrite() )
{
cout << "请输入一句格言:" << endl;
quote.inputQuote();
cout << "请输入作者的姓名:" << endl;
quote.inputSpeaker();
if (quote.write())
{
cout << "数据写入成功!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "数据写入失败!" << endl;
}
}
system("pause");//等待一下
return 0;
}视频16—this指针和类的继承



继承:基类(父类)和子类
/*继承:基类和子类*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>
//基类(父类)动物
class Animal
{
public:
//属性
string mouth;
//方法
void eat();
void sleep();
void drool();
};
//子类1猪猪
class Pig : public Animal
{
public:
void climb();
};
//子类2王八
class Turtle : public Animal
{
public:
void swim();
};
//基类中方法定义
void Animal::eat()
{
cout << "I am eating!!!" << endl;
}
void Animal::sleep()
{
cout << "I am sleeping!!!" << endl;
}
void Animal::drool()
{
cout << "I am drooling!!!" << endl;
}
//子类中方法定义
void Pig::climb()
{
cout << "我是一只漂亮的小母猪,我会上树,我正在爬树!" << endl;
}
void Turtle::swim()
{
cout << "我是一只小甲鱼,当母猪想抓我的时候,我就游到海里,哈哈!" << endl;
}
int main()
{
Pig pig;
Turtle turtle;
//子类自有的方法
pig.eat();
turtle.eat();
//子类继承基类中的方法
pig.climb();
turtle.swim();
system("pause");
return 0;
}视频17—继承中的构造器和析构器
/*继承中的构造器和析构器:基类和子类*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>
//基类(父类)动物
class Animal
{
public:
//属性
string mouth;
string name;
Animal(string theName);
//方法
void eat();
void sleep();
void drool();
};
//子类1猪猪
class Pig : public Animal
{
public:
void climb();
Pig(string theName);//构造器
};
//子类2王八
class Turtle : public Animal
{
public:
void swim();
Turtle(string theName);
};
Animal::Animal(string theName)
{
name = theName;
}
//基类中方法定义
void Animal::eat()
{
cout << "I am eating!!!" << endl;
}
void Animal::sleep()
{
cout << "I am sleeping!!!" << endl;
}
void Animal::drool()
{
cout << "I am drooling!!!" << endl;
}
//子类中方法定义
void Pig::climb()
{
cout << "我是一只漂亮的小母猪,我会上树,我正在爬树!" << endl;
}
Pig::Pig(string theName) : Animal(theName)//子类构造器定义
{
}
void Turtle::swim()
{
cout << "我是一只小甲鱼,当母猪想抓我的时候,我就游到海里,哈哈!" << endl;
}
Turtle::Turtle(string theName):Animal(theName)//子类构造器定义
{
}
int main()
{
Pig pig("小猪猪");
Turtle turtle("小甲鱼");
cout << "这只猪的名字叫" << pig.name << endl;
cout << "这只王八的名字叫" << turtle.name << endl;
//子类自有的方法
pig.eat();
turtle.eat();
//子类继承基类中的方法
pig.climb();
turtle.swim();
system("pause");
return 0;
}基类、子类构造器和析构器的调用顺序
顺序:基类构造器—>子类构造器—>子类中的方法—>子类析构器—>基类析构器
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>
class BaseClass
{
public:
BaseClass();//构造器
~BaseClass();//析构器
void DoThing();
};
class SubClass : public BaseClass
{
public:
SubClass();//构造器
~SubClass();//析构器
};
//构造器定义
BaseClass::BaseClass()
{
cout << "进入基类构造器……" << endl;
cout << "我在基类构造器里面do thing" << endl;
}
//析构器定义
BaseClass::~BaseClass()
{
cout << "进入基类析构器……" << endl;
cout << "我在基类析构器里面do thing" << endl;
}
//定义基类方法
void BaseClass::DoThing()
{
cout << "我干了某些事!" << endl;
}
//子类构造器
SubClass::SubClass()
{
cout << "进入子类构造器……" << endl;
cout << "我在子类构造器里面do thing" << endl;
}
//子类析构器
SubClass::~SubClass()
{
cout << "进入子类析构器……" << endl;
cout << "我在子类析构器里面do thing" << endl;
}
int main()
{
SubClass subclass;
subclass.DoThing();
cout << "完事,收工" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
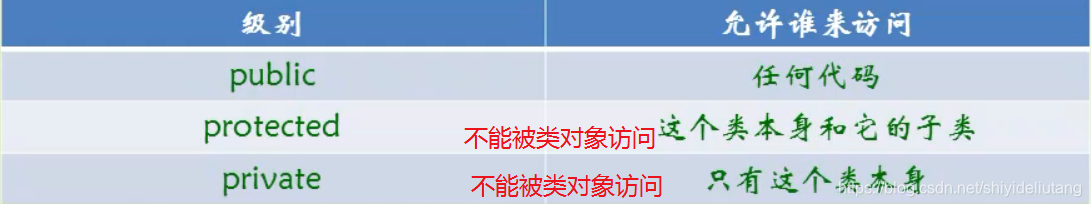
视频18—访问控制

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>
//基类(父类)动物
class Animal
{
public:
//属性
string mouth;
Animal(string theName);
//方法
void eat();
void sleep();
void drool();
protected:
string name;//这里定义name为保护的了,只有Animal本身以及其子类才可以修改
};
//子类1猪猪
class Pig : public Animal
{
public:
void climb();
Pig(string theName);//构造器
};
//子类2王八
class Turtle : public Animal
{
public:
void swim();
Turtle(string theName);
};
Animal::Animal(string theName)
{
name = theName;
}
//基类中方法定义
void Animal::eat()
{
cout << "I am eating!!!" << endl;
}
void Animal::sleep()
{
cout << "I am sleeping!!!" << endl;
}
void Animal::drool()
{
cout << "I am drooling!!!" << endl;
}
//子类中方法定义
void Pig::climb()
{
cout << "我是一只漂亮的小母猪,我会上树,我正在爬树!" << endl;
}
Pig::Pig(string theName) : Animal(theName)//子类构造器定义
{
}
void Turtle::swim()
{
cout << "我是一只小甲鱼,当母猪想抓我的时候,我就游到海里,哈哈!" << endl;
}
Turtle::Turtle(string theName):Animal(theName)//子类构造器定义
{
}
int main()
{
Pig pig("小猪猪");
Turtle turtle("小甲鱼");
pig.name = "小甲鱼";
cout << "这只猪的名字叫" << pig.name << endl;
cout << "这只王八的名字叫" << turtle.name << endl;
//子类自有的方法
pig.eat();
turtle.eat();
//子类继承基类中的方法
pig.climb();
turtle.swim();
system("pause");
return 0;
}PS:以上程序运行报错,因为在基类Animal中定义name为protected,即只能由基类Animal本身和其子类修改。https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/Tostick/article/details/80685482
视频19——覆盖和重载方法
1、覆盖
子类继承了基类中的一个方法,但是对于子类而言该方法和基类中的方法不完全一样,eg动物共有方法“吃”,但是小猪的“吃”和王八的“吃”不一样。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>
//基类(父类)动物
class Animal
{
public:
//属性
string mouth;
Animal(string theName);
//方法
void eat();
void sleep();
void drool();
protected:
string name;//这里定义name为保护的了,只有Animal本身以及其子类才可以修改
};
//子类1猪猪
class Pig : public Animal
{
public:
void climb();
void eat();//子类中覆盖基类中的方法
Pig(string theName);//构造器
};
//子类2王八
class Turtle : public Animal
{
public:
void swim();
void eat();//子类中覆盖基类中的方法
Turtle(string theName);
};
Animal::Animal(string theName)
{
name = theName;
}
//基类中方法定义
void Animal::eat()
{
cout << "I am eating!!!" << endl;
}
void Animal::sleep()
{
cout << "I am sleeping!!!" << endl;
}
void Animal::drool()
{
cout << "I am drooling!!!" << endl;
}
//子类中方法定义
void Pig::climb()
{
cout << "我是一只漂亮的小母猪,我会上树,我正在爬树!" << endl;
}
void Pig::eat()
{
Animal::eat();//小技巧,不需要在定义
cout << name << "正在吃草" << endl;
}
Pig::Pig(string theName) : Animal(theName)//子类构造器定义
{
}
void Turtle::swim()
{
cout << "我是一只小甲鱼,当母猪想抓我的时候,我就游到海里,哈哈!" << endl;
}
void Turtle::eat()
{
Animal::eat();//小技巧,不需要在定义
cout << name << "我正在吃鱼" << endl;
}
Turtle::Turtle(string theName):Animal(theName)//子类构造器定义
{
}
int main()
{
Pig pig("小猪猪");
Turtle turtle("小甲鱼");
//子类自有的方法
pig.eat();
turtle.eat();
//子类继承基类中的方法
pig.climb();
turtle.swim();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2、重载

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>
//基类(父类)动物
class Animal
{
public:
//属性
string mouth;
Animal(string theName);
//方法
void eat();
void eat(int eatcount);
void sleep();
void drool();
protected:
string name;//这里定义name为保护的了,只有Animal本身以及其子类才可以修改
};
//子类1猪猪
class Pig : public Animal
{
public:
void climb();
Pig(string theName);//构造器
};
//子类2王八
class Turtle : public Animal
{
public:
void swim();
Turtle(string theName);
};
Animal::Animal(string theName)
{
name = theName;
}
//基类中方法定义
void Animal::eat(int eatcount)
{
cout << "我吃了" << eatcount << "馄饨" << endl;
}
void Animal::eat()
{
cout << "I am eating!!!" << endl;
}
void Animal::sleep()
{
cout << "I am sleeping!!!" << endl;
}
void Animal::drool()
{
cout << "I am drooling!!!" << endl;
}
//子类中方法定义
void Pig::climb()
{
cout << "我是一只漂亮的小母猪,我会上树,我正在爬树!" << endl;
}
Pig::Pig(string theName) : Animal(theName)//子类构造器定义
{
}
void Turtle::swim()
{
cout << "我是一只小甲鱼,当母猪想抓我的时候,我就游到海里,哈哈!" << endl;
}
Turtle::Turtle(string theName):Animal(theName)//子类构造器定义
{
}
int main()
{
Pig pig("小猪猪");
Turtle turtle("小甲鱼");
//子类继承基类中的方法
pig.eat();
turtle.eat();
pig.eat(5);//重载
turtle.eat(10);
//子类自有的方法
pig.climb();
turtle.swim();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3、覆盖和重载区别

在基类继承来的方法中进行重载,如下程序所示,将会报错!!!!
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>
//基类(父类)动物
class Animal
{
public:
//属性
string mouth;
Animal(string theName);
//方法
void eat();
void sleep();
void drool();
protected:
string name;//这里定义name为保护的了,只有Animal本身以及其子类才可以修改
};
//子类1猪猪
class Pig : public Animal
{
public:
void climb();
Pig(string theName);//构造器
void eat(int eatcount);//在继承基类中进行重载
};
//子类2王八
class Turtle : public Animal
{
public:
void swim();
Turtle(string theName);
};
Animal::Animal(string theName)
{
name = theName;
}
//基类中方法定义
void Animal::eat()
{
cout << "I am eating!!!" << endl;
}
void Animal::sleep()
{
cout << "I am sleeping!!!" << endl;
}
void Animal::drool()
{
cout << "I am drooling!!!" << endl;
}
//子类中方法定义
void Pig::climb()
{
cout << "我是一只漂亮的小母猪,我会上树,我正在爬树!" << endl;
}
void Pig::eat(int eatcount)
{
cout << "我吃了" << eatcount << "馄饨" << endl;
}
Pig::Pig(string theName) : Animal(theName)//子类构造器定义
{
}
void Turtle::swim()
{
cout << "我是一只小甲鱼,当母猪想抓我的时候,我就游到海里,哈哈!" << endl;
}
Turtle::Turtle(string theName):Animal(theName)//子类构造器定义
{
}
int main()
{
Pig pig("小猪猪");
Turtle turtle("小甲鱼");
//子类继承基类中的方法
pig.eat();
turtle.eat();
pig.eat(5);//重载
//子类自有的方法
pig.climb();
turtle.swim();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
视频20——友元关系

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>
//基类
class Lovers
{
public://所有类均可以访问
Lovers(string theName);//构造器
//方法
void kiss(Lovers * lover);//这里可以不用指针,直接用Lovers lover
void ask(Lovers *lover, string sonmething);
protected://只有该类和其子类可以访问
string name;
friend class Others;//友元关系
};
//基类构造器的定义
Lovers::Lovers(string theName)
{
name = theName;
}
//基类中方法定义
void Lovers::kiss(Lovers * lover)
{
cout << name << "成功kiss到了" << lover->name << endl;
}
void Lovers::ask(Lovers * lover, string sonmething)
{
cout << name << ":" << lover->name << sonmething << endl;
}
//子类1
class Boyfriend : public Lovers
{
public:
Boyfriend(string theName);//子类构造器
};
//子类构造器定义:这里务必注意要显式调用父类的构造函数
Boyfriend::Boyfriend(string theName) : Lovers(theName)
{
}
//子类2
class Girlfriend : public Lovers
{
public:
Girlfriend(string theName);
};
//子类构造器定义:这里务必注意要显示调用父类的构造函数
Girlfriend::Girlfriend(string theName) : Lovers(theName)
{
}
//友元类
class Others
{
public:
Others(string theName);
void kiss(Lovers* lover);
protected:
string name;
};
//构造器
Others::Others(string theName)
{
name = theName;
}
//方法定义
void Others::kiss(Lovers* lover)
{
cout << name << "偷偷kiss到了" << lover->name << endl;
}
int main()
{
Boyfriend boyfriend("小明");
Girlfriend girlfriend("小红");
Others others("老王");
girlfriend.kiss(&boyfriend);
girlfriend.ask(&boyfriend, "回家吃饭了!!!");
cout << "老王上线嘞嘞-----------------------" << endl;
others.kiss(&girlfriend);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
子类构造函数的写法
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/zhaolianyun/article/details/45271727





 本文深入探讨C++面向对象编程的核心概念,包括对象、类、构造器、析构器、继承、覆盖与重载方法,以及友元关系。通过实例讲解,如小车类的创建与操作、名言存储类的文件操作、动物类的继承与方法覆盖等,帮助读者理解并掌握面向对象编程的基本原理。
本文深入探讨C++面向对象编程的核心概念,包括对象、类、构造器、析构器、继承、覆盖与重载方法,以及友元关系。通过实例讲解,如小车类的创建与操作、名言存储类的文件操作、动物类的继承与方法覆盖等,帮助读者理解并掌握面向对象编程的基本原理。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








