文章目录
一、Fragment为何被称为第5大组件
1、为何称为第5组件
1)、fragment具有生命周期
2)、fragment比activity更节省内存,ui的切换效果也更加的舒适;
3)、但是fragment必须依附于activity, 加载到activity中去;
2、Fragment加载到activity的两种方式
1)、添加Fragment到activity的布局文件中
2)、动态在activity 中添加fragment
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener{
private Button mTabWeixin;
private Button mTabFriend;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState){
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// 初始化控件和声明事件
mTabWeixin = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button);
mTabFriend = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button2);
mTabWeixin.setOnClickListener(this);
mTabFriend.setOnClickListener(this);
// 设置默认的Fragment
setDefaultFragment();
}
private void setDefaultFragment() {
FragmentTransaction transaction = getFragmentManager().beginTransaction();
transaction.replace(R.id.id_content, new ContentFragment());
transaction.commit();
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v){
// 开启Fragment事务
FragmentTransaction transaction = getFragmentManager().beginTransaction();
switch (v.getId()){
case R.id.button:
// 使用当前Fragment的布局替代id_content的控件
transaction.replace(R.id.id_content, new ContentFragment());
break;
case R.id.button2:
transaction.replace(R.id.id_content, new FriendFragment());
break;
}
transaction.commit();
}
}
public class ContentFragment extends Fragment{
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_content, container, false);
}
}
public class FriendFragment extends Fragment{
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_friend, container, false);
}
}
public class TitleFragment extends Fragment {
private ImageButton mLeftMenu;
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_title, container, false);
mLeftMenu = (ImageButton) view.findViewById(R.id.id_title_left_btn);
mLeftMenu.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(getActivity(), "i am an ImageButton in TitleFragment ! ",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
return view;
}
}
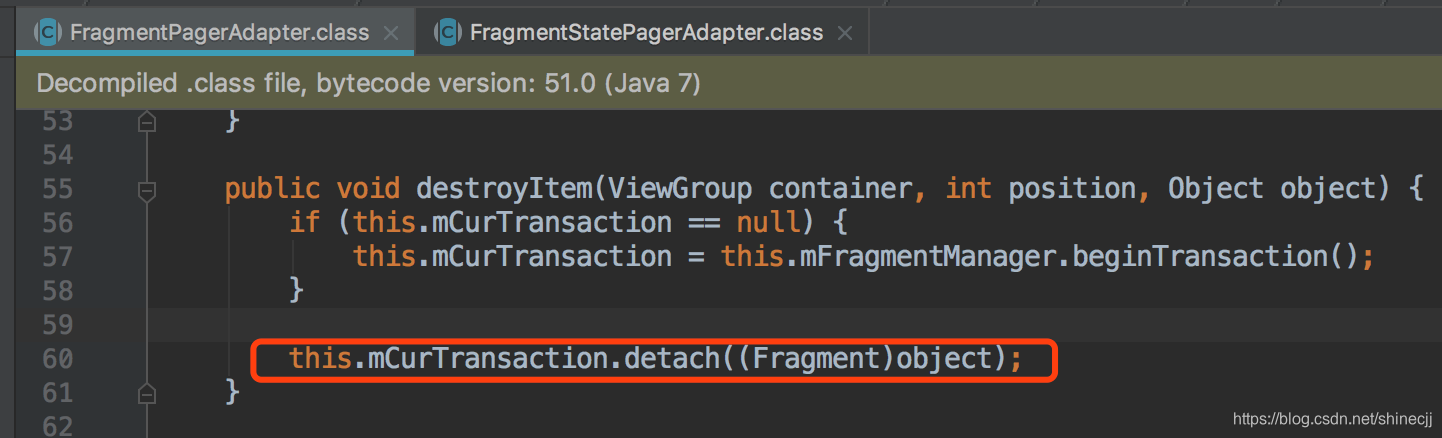
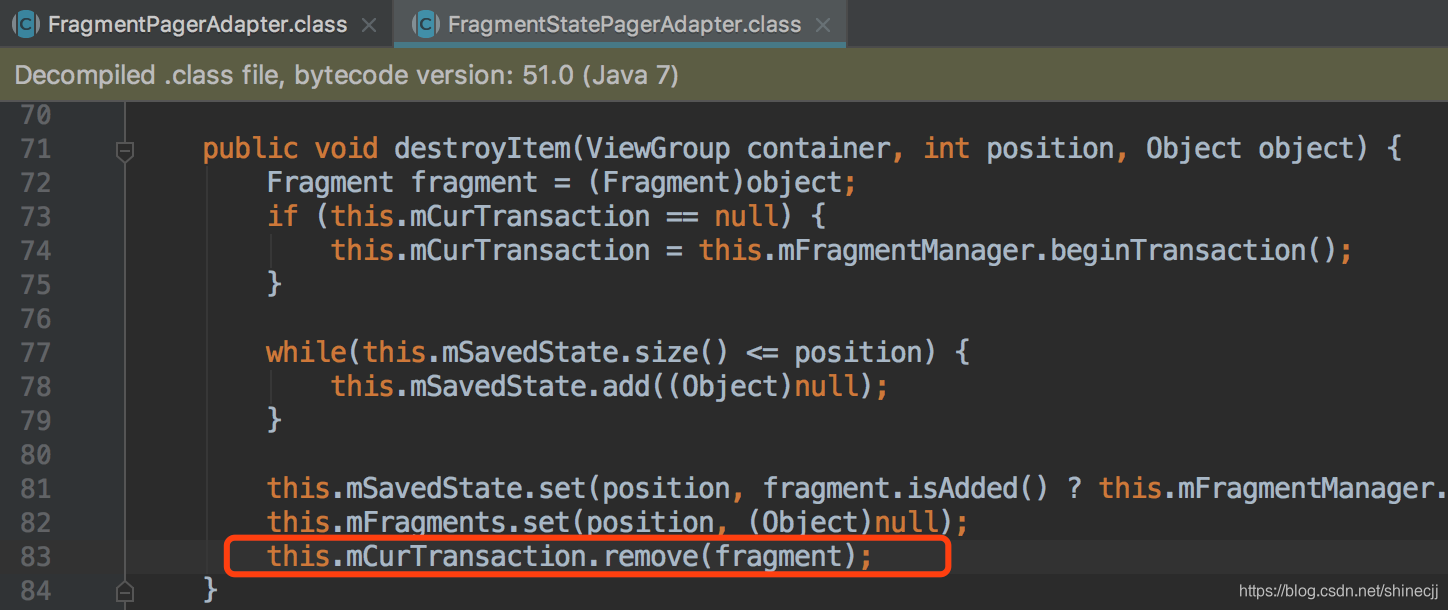
3、FragmentPageAdapter和FragmentStatePageAdapter区别

- 、FragmentPageAdapter适用于页面较少的情况,FragmentStatePageAdapter适用于页面较多的情况
因为FragmentStatePageAdapter每次切换fragment的时候是回收内存的,所以适合页面多情况
因为FragmentPageAdapter每次切换fragment的时候只是分离fragment,适合页面少的情况,也对系统内存没太大的影响。
二、Fragment的生命周期
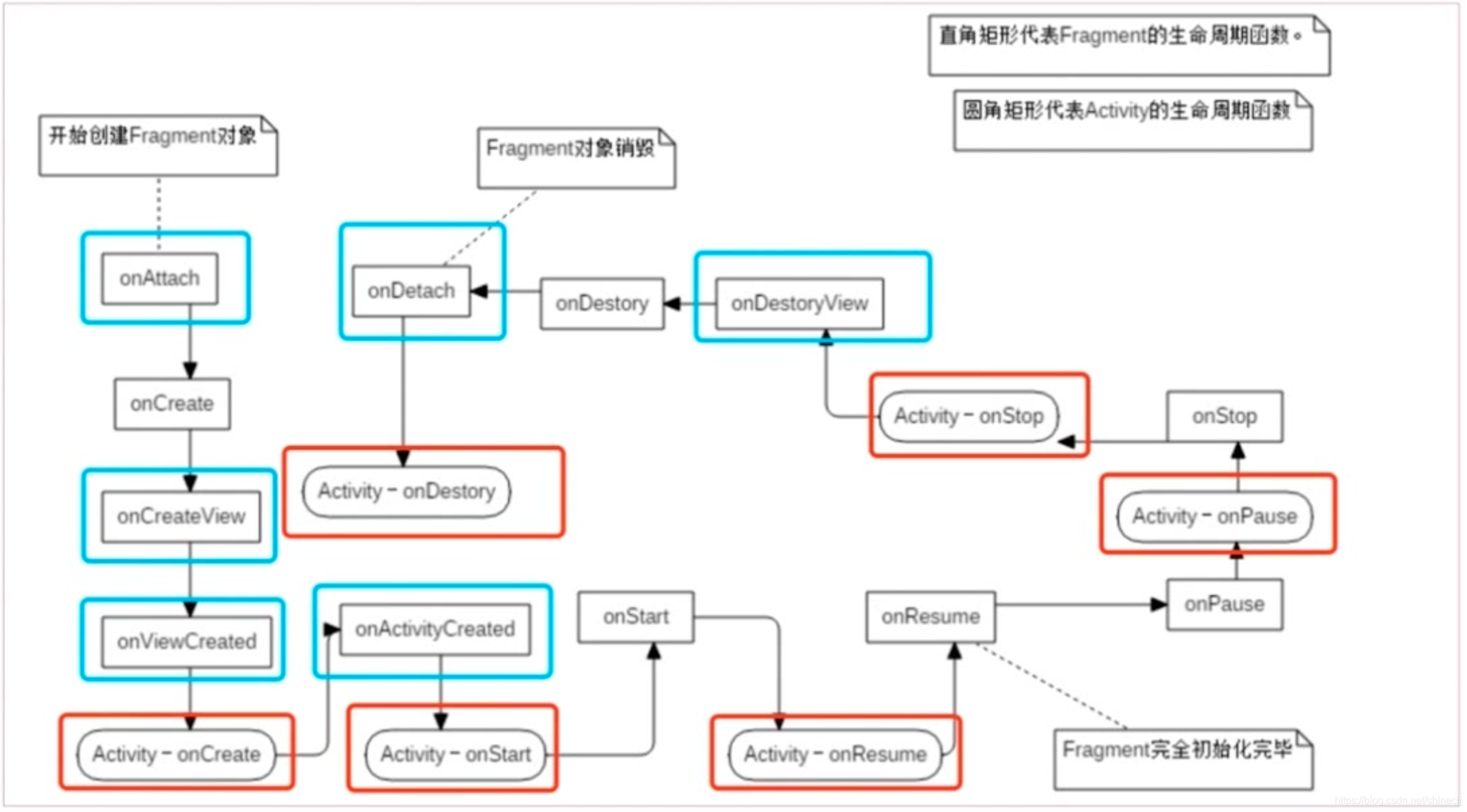
1、onAttach():fragment与Activity关联后调用。
2、onCreate(): 初次创建fragment调用,此时的activity并没有创建完成。
3、onCreateView():系统在Fragment首次绘制用户界面的时候调用,该方法返回的view必须是Fragment布局的根视图。
4、onViewCreated(): Fragment的界面UI被绘制好的时候调用,这时候可以初始化fragment里面的控件资源。
activity的onCreate() : 初始化activity的布局等
5、onActivityCreated() : activity被渲染绘制成功之后调用
activity的onStrart() : acticity可见了
6、onStart() : activity可见之后调用,此时Fragment也是可见的了
activity的onResume() : acticity可交互了
7、onResume() : Fragment可交互了,可以在Fragment上进行滑动,点击等等
到这完成了Fragment从启动到展现的操作;
8、onPause() : fragment不能和用户交互了。
activity的onPause() : acticity不可交互了。
9、onstop():
activity的onstop() :
10、onDestoryView(): Fragment即将结束,会被保存。
11、onDestory():
12、onDetach():Fragment对象被销毁。
activity的onDestory():整个activity被回收了。
三、Fragment的通信

四、Fragment的replace、add、remove
1、add()是将Fragment实例添加到activity的Fragment队列的最上层
2、remove()是将Fragment实例从到activity的Fragment队列中删除
3、replace:内部线remove(实例会被回收掉)然后再add,会始终保持fragment栈中只有一个fragment(并且每次是新建的)。
4、hide:是隐藏了fragment,不会销毁,最消耗内存但是最常用的。
5、detach和atach是鸡肋的,几乎不会用到。因为,detach不会回收fragment,但是会回收fragment中的view。atach会将fragment中的view重新创建。既不剩内存,也不提高性能。






 本文详细解析了Fragment作为Android开发中第五大组件的原因,包括其生命周期、与Activity的交互方式、不同加载方式的区别,以及FragmentStatePagerAdapter与FragmentPagerAdapter的适用场景。同时,深入探讨了Fragment的生命周期、通信机制、replace/add/remove等操作的原理,最后介绍了FragmentManager的管理机制。
本文详细解析了Fragment作为Android开发中第五大组件的原因,包括其生命周期、与Activity的交互方式、不同加载方式的区别,以及FragmentStatePagerAdapter与FragmentPagerAdapter的适用场景。同时,深入探讨了Fragment的生命周期、通信机制、replace/add/remove等操作的原理,最后介绍了FragmentManager的管理机制。
















 1937
1937

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








