三、Statement与ResultSet
- 通过调用 Connection 对象的 createStatement 方法创建该对象
- Statement st = conn.createStatement();
- 该对象用于执行静态的 SQL 语句,并且返回执行结果
- Statement 接口中定义了下列方法用于执行 SQL 语句:
- ResultSet excuteQuery(String sql)
- int excuteUpdate(String sql)
//通用的INSSERT UPDATE DELETE方法(version 1.0)
public void update(String sql){
//1.获取数据库的连接
Connection conn = null;
Statement st = null;
try{
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.提供一个Statement对象,将sql传递给数据库中执行
st = conn.createStatement();
st.execute(sql);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//3.关闭Statement对象及连接
JDBCUtils.close(null, st, conn);
}
}
// 通用的查询方法,返回一个对象(version 1.0)
public <T> T get(String sql, Class<T> clazz) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
T t = null;
try {
t = clazz.newInstance();
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
st = conn.createStatement();
rs = st.executeQuery(sql);
/*
* 通过ResultSet调用getMetaData()返回一个结果集的元数据:ResultSetMetaData
*
* 1.getColumnCount():返回结果集的列数
* 2.getColumnLabel():返回列的别名
*/
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
if (rs.next()) {
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
Object columnVal = rs.getObject(i + 1);// 相应列的值
//String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1);
String columnName = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1);
//使用PropertyUtils将指定对象t的指定属性columnName设置为指定的值columnVal
PropertyUtils.setProperty(t, columnName, columnVal);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(rs, st, conn);
}
return t;
}
//通用的返回多个对象的查询操作(version 1.0)
public <T> List<T> getInstances(String sql,Class<T> clazz){
Connection conn = null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
List<T> list = new ArrayList<T>();
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
st = conn.createStatement();
rs = st.executeQuery(sql);
/*
* 通过ResultSet调用getMetaData()返回一个结果集的元数据:ResultSetMetaData
*
* 1.getColumnCount():返回结果集的列数
* 2.getColumnLabel():返回列的别名
*/
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
while (rs.next()) {
T t = clazz.newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
Object columnVal = rs.getObject(i + 1);// 相应列的值
//String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1);
String columnName = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1);
//使用PropertyUtils将指定对象t的指定属性columnName设置为指定的值columnVal
PropertyUtils.setProperty(t, columnName, columnVal);
}
list.add(t);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(rs, st, conn);
}
return list;
}
流程:
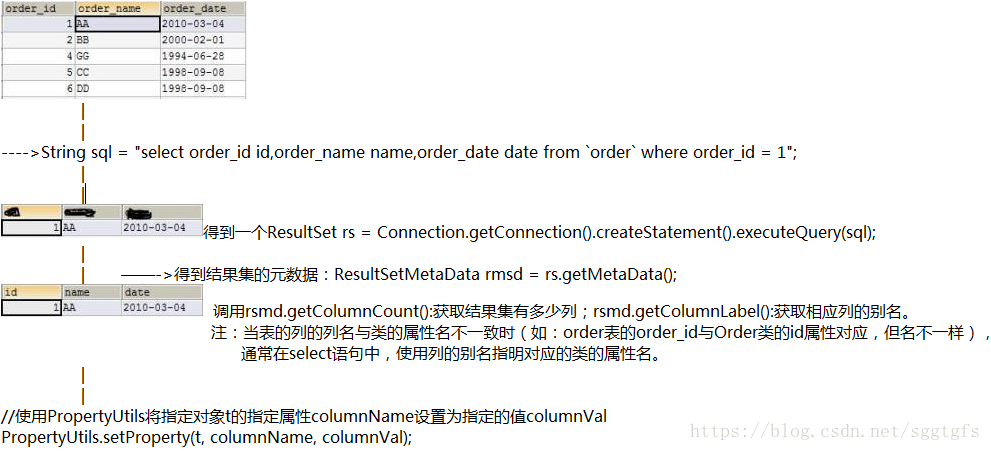
//总结:
两种思想:
- 面向接口编程的思想;
- ORM思想:
* ORM:Object Relational Mapping
* 数据库中的表与java中的一个类对应(如:customers表与Customer类对应)
* 数据库中表的一个列与java类的一个属性对应(如:表中的id列与Customer类的id属性对应)
* 数据库中表的一行(一条数据)与java类的一个对象对应
两个技术:
- 结果集的元数据:ResultSetMetaData;
- PropertyUtils
1.结果集的元数据:ResultSetMetaData
//获取:ResultSet.getMetaData();
//两个方法:1)getColumnCount():获取结果集中有多少列
2)getColumnLabel():获取结果集的相应列的列名,相当于是对应的表的列的别名。
--getColumnName():不用。
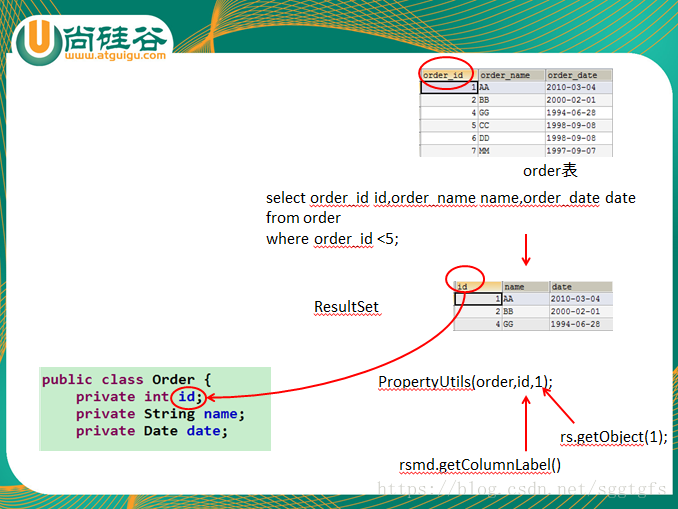
public void testResultSetMetaData(){
Connection conn = null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
String sql = "select order_id id,order_name name,order_date date from `order`";
try{
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
st = conn.createStatement();
rs = st.executeQuery(sql);
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
System.out.println(columnCount);
while(rs.next()){
for(int i = 0;i < columnCount;i++){
System.out.print(rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1) + " ");
System.out.print(rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1) + " ");
System.out.println(rs.getObject(i + 1));
}
System.out.println();
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBCUtils.close(rs, st, conn);
}
}
2.PropertyUtils工具类,使用它的setProperty(Object obj,String FieldName,Object FieldValue)
public void testPropertyUtils() throws Exception{
Order order = new Order();
System.out.println(order);
PropertyUtils.setProperty(order, "id", 1001);
PropertyUtils.setProperty(order, "name", "AA");
PropertyUtils.setProperty(order, "date", new Date(new java.util.Date().getTime()));
System.out.println(order);
}
四、PreparedStatement
PreparedStatement是Statement的子接口
①需要预编译SQL语句:PreparedStatement ps = conn.preparedStatement(sql);
②填充占位符:setObject(int index);//index从1开始
③execute() / executeUpdate() ; executeQuery(); 返回一个ResultSet
1.替换原来的Statement,实现增删改和查的操作
-->Statement的问题:①拼串 不方便,容易出错 ②存在sql注入的问题,可以对数据库进行恶意攻击。
// 实现一个通用的UPDATE INSERT DELETE的操作的方法(version 2.0)
public void update(String sql, Object... args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// 1.获取连接
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
// 2.返回PreparedSt对象,预编译sql语句
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 3.填充占位符
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
ps.execute();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(null, ps, conn);
}
}
// 实现一个通用的查询操作,返回一个对象(version 2.0)
public <T> T getInstance(String sql, Class<T> clazz, Object... args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// 1.获取连接
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
// 2.预编译sql语句,返回PreparedStatement对象
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 3.填充占位符
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
// 4.执行并返回ResultSet的对象
rs = ps.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
// 5.创建T的对象
T t = clazz.newInstance();
// 6.将结果集中的列值作为T的对象的属性,给予赋值
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
Object columnVal = rs.getObject(i + 1);
String columnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1);
PropertyUtils.setProperty(t, columnLabel, columnVal);
}
return t;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 7.关闭相应的操作
JDBCUtils.close(rs, ps, conn);
}
return null;
}
// 实现一个通用的查询操作,返回一个对象的集合(version 2.0)
public <T> List<T> getForList(String sql,Class<T> clazz,Object ... args){
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
List<T> list = new ArrayList<T>();
try{
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i = 0;i < args.length;i++){
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
rs = ps.executeQuery();
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
while(rs.next()){
T t = clazz.newInstance();
for(int i = 0;i < columnCount;i++){
Object columnVal = rs.getObject(i + 1);
String columnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1);
PropertyUtils.setProperty(t, columnLabel, columnVal);
}
list.add(t);
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBCUtils.close(rs, ps, conn);
}
return list;
}
//2.使用PreparedStatement的其他优点
1.实现大数据类型的数据的插入、修改、查询的操作.
setBlob() getBlob();
// 从数据表中将大数据类型的数据取出
@Test
public void testBlob3(){
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
String sql = "select id,name,email,birth,photo from customers where id = ?";
ResultSet rs = null;
InputStream is = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try{
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
fos = new FileOutputStream("ym1.jpg");
ps.setInt(1, 21);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
if(rs.next()){
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
Date birth = rs.getDate("birth");
String email = rs.getString("email");
Customer cust = new Customer(id,name,email,birth);
System.out.println(cust);
}
Blob photo = rs.getBlob(5);
is = photo.getBinaryStream();
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = is.read(b)) != -1){
fos.write(b, 0, len);
}
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(rs, ps, conn);
if(fos != null){
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(is != null){
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 向数据表中修改现有的大数据类型的数据
@Test
public void testBlob2() {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
String sql = "update customers set photo = ? where id = ?";
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setBlob(1, new FileInputStream("ym.jpg"));
ps.setInt(2, 21);
ps.execute();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(null, ps, conn);
}
}
// 向数据库的表中写入大数据类型的数据
@Test
public void testBlob1() {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
String sql = "insert into customers(name,email,birth,photo)values(?,?,?,?)";
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, "杨幂1");
ps.setString(2, "yang@126.com");
ps.setDate(3, new Date(new java.util.Date().getTime()));
ps.setBlob(4, new FileInputStream("1.jpg"));
ps.execute();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(null, ps, conn);
}
}
2.使用PreparedStatement进行批量操作时,效率优于Statement.
//批量操作,主要指的是批量插入。
//oracle是支持批量插入的。
//如何实现最优? ①使用PreparedStatement ②addBatch() executeBatch() clearBatch()
public void test4() {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String sql = "insert into dept values(?,?)";
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
ps.setInt(1, i + 1);
ps.setString(2, "dept_" + (i + 1) + "_name");
//1.“攒”SQL
ps.addBatch();
if( (i + 1) % 250 == 0){
//2.执行sql
ps.executeBatch();
//3.清空sql
ps.clearBatch();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(null, ps, conn);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("花费时间:" + (end - start));//2427
}
本教程由尚硅谷教育大数据研究院出品,如需转载请注明来源。





 本文详细介绍了JDBC中的Statement与PreparedStatement的使用,包括执行SQL语句、获取结果集、元数据处理以及批处理操作。通过示例代码展示了如何创建Statement对象,执行查询和更新操作,以及PreparedStatement的优点,如预编译SQL、防止SQL注入和提高性能。最后,讨论了PreparedStatement在大数据类型处理和批量操作中的应用。
本文详细介绍了JDBC中的Statement与PreparedStatement的使用,包括执行SQL语句、获取结果集、元数据处理以及批处理操作。通过示例代码展示了如何创建Statement对象,执行查询和更新操作,以及PreparedStatement的优点,如预编译SQL、防止SQL注入和提高性能。最后,讨论了PreparedStatement在大数据类型处理和批量操作中的应用。
















 1683
1683

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








