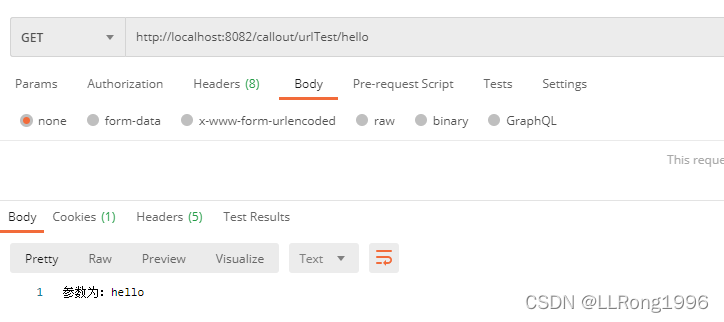
1.请求参数是restful风格,直接将参数放在url路径里,用“/”分割
例如,参数值为hello,完整url为http://localhost:8082/callout/urlTest/hello
get请求与post请求均适用
后端代码为:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/callout/")
@Slf4j
public class CalloutTestController {
//@GetMapping("/urlTest/{testUrl}")
@PostMapping("/urlTest/{testUrl}")
public String urlTest(@PathVariable String testUrl) {
return "参数为:" + testUrl;
}
}postman模拟结果:
2.参数拼接在路径里,用“?”分割
例如,请求参数名为paramStr,跟在路径中的问号后面http://localhost:8082/callout/paramTest/?paramStr=hello
get请求与post请求均适用
后端代码为
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/callout/")
@Slf4j
public class CalloutTestController {
// @GetMapping("/paramTest")
@PostMapping("/paramTest")
public String paramTest(@RequestParam String paramStr) {
return "参数为:" + paramStr;
}
}
postman模拟结果:

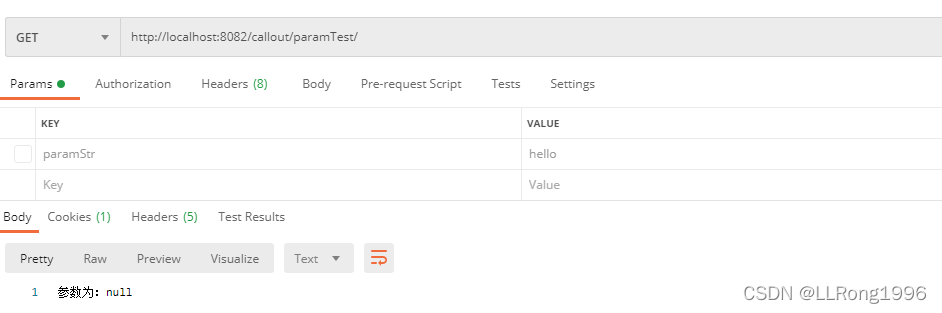
若参数为非必填,可以使用 required = false 标注参数是非必须的,在@RequestParam注解里面设置,否则会报错
后端代码:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/callout/")
@Slf4j
public class CalloutTestController {
@GetMapping("/paramTest")
public String getOne(@RequestParam(required = false) String paramStr) {
return "参数为:" + paramStr;
}
}postman模拟结果:
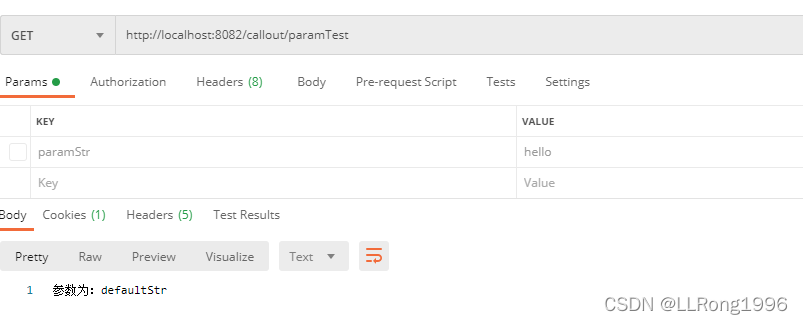
当没有传递参数时可以设定默认值,使用defaultValue = "XXX",在@RequestParam注解里面设置,此时 可以不使用required = false 标注参数
后端代码:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/callout/")
@Slf4j
public class CalloutTestController {
@GetMapping("/paramTest")
public String getOne(@RequestParam(defaultValue = "defaultStr") String paramStr) {
return "参数为:" + paramStr;
}
}postman模拟结果:
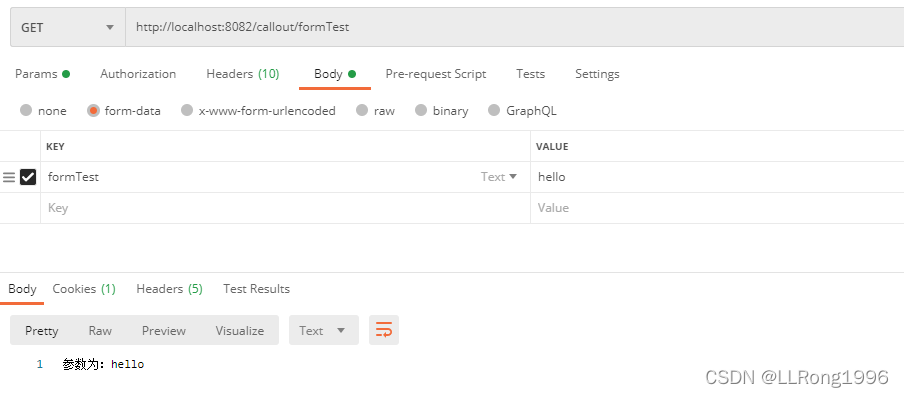
3.使用form表单接收参数
使用form表单接收参数,参数不会拼接在路径中
post请求与get请求均适用
当去掉@RequestParam注解时,这种方式不会校验请求里是否带参数,即下面的formTest不带也会响应成功
后端代码:
//@PostMapping("/formTest")
@GetMapping("/formTest")
public String formTest(@RequestParam String formTest) {
return "参数为:" + formTest;
}postman请求模拟:
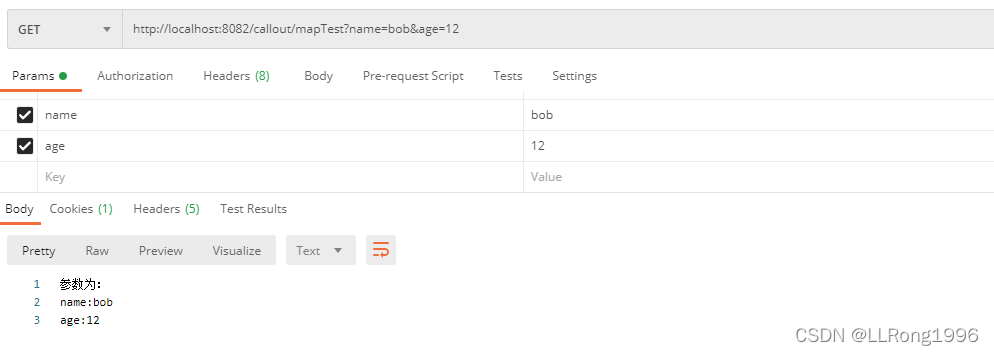
4.使用map接收参数
使用map可以接收多个参数,参数跟在路径中的“?”后面
例如 http://localhost:8082/callout/mapTest?name=bob&age=12
get请求与post请求均适用
后端代码:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/callout/")
@Slf4j
public class CalloutTestController {
//@GetMapping("/mapTest")
@PostMapping("/mapTest")
public String getOne(@RequestParam Map<String, Object> map) {
return "参数为:" + "\n" + "name:" + map.get("name") + "\n"+ "age:"+ map.get("age");
}
}postman模拟结果:
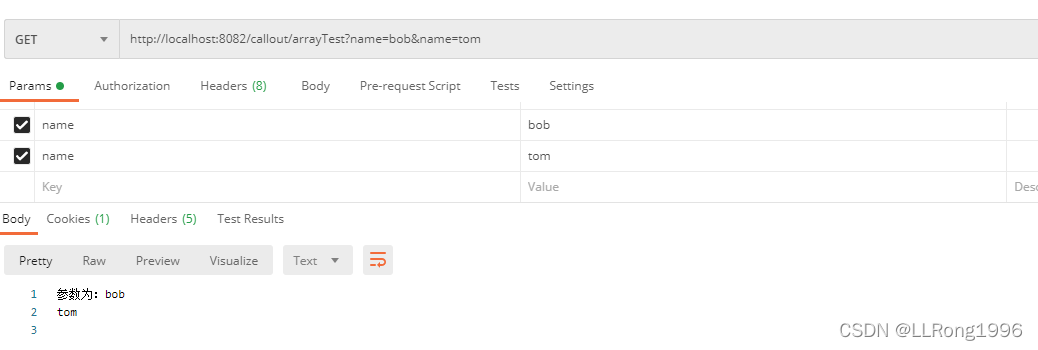
5.使用数组接收参数
当URL路径中有多个同名参数时,可以使用数组进行接收,在使用时,需要在@RequestParam中绑定参数名
例如:http://localhost:8082/callout/arrayTest?name=bob&name=tom
需要在后端绑定name,
@RequestParam("name")get请求与post请求均适用
后端代码:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/callout/")
@Slf4j
public class CalloutTestController {
//@GetMapping("/arrayTest")
@PostMapping("/arrayTest")
public String getOne(@RequestParam("name") String [] array) {
String result = "参数为:";
for(String str : array){
result += str + "\n";
}
return result;
}
}postman模拟:
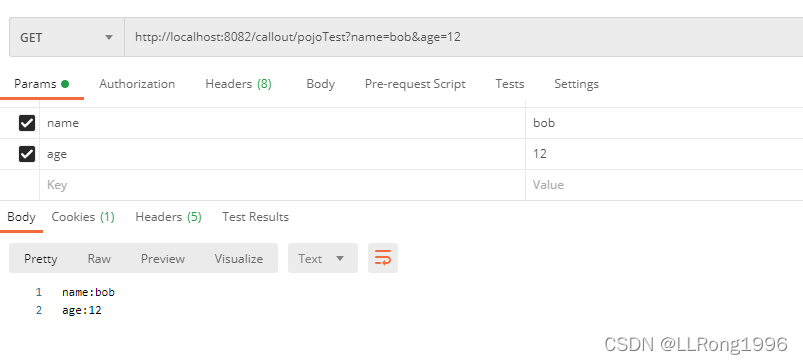
6.使用对象接收参数
如果get请求的参数过多,可以使用对象来获取参数
get请求与post请求均适用
后台代码:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/callout/")
@Slf4j
public class CalloutTestController {
//@GetMapping("/pojoTest")
@PostMapping("/pojoTest")
public String getOne(User user) {
return "name:" + user.getName() + "\n" + "age:" + user.getAge() ;
}
}
@Data
class User{
private String name;
private int age;
}postman模拟结果:
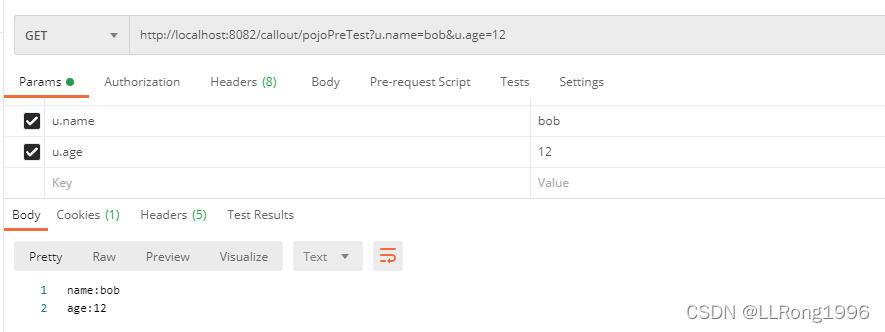
如果请求的参数有前缀,且参数与实体类中的属性命名并不相同,可以使用@ModelAttribute与@InitBinder结合使用,通过参数预处理来指定前缀
当get请求需要接受多个实体类,且不同实体类之间的的属性命名有冲突是也可以使用参数预处理,为不同的实体类指定不同的前缀加以区分
get请求与post请求均适用
后端代码:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/callout/")
@Slf4j
public class CalloutTestController {
//@GetMapping("/pojoPreTest")
@PostMapping("/pojoPreTest")
public String pojoPreTest(@ModelAttribute("user") User user) {
return "name:" + user.getName() + "\n" + "age:" + user.getAge() ;
}
@InitBinder("user")
public void pojoPreTest(WebDataBinder binder) {
binder.setFieldDefaultPrefix("u.");
}
}
@Data
class User{
private String name;
private int age;
}
postman模拟结果:
7. 使用HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse
通过HttpServletRequest对象获取请求参数,post和get方法均适用,
后台代码:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/callout/")
@Slf4j
public class CalloutTestController {
@GetMapping("/httpTest")
//@PostMapping("/httpTest")
public void getOne(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String age = request.getParameter("age");
String str = "参数为:" + "\n" + "name:" + name +"\n" + "age:" + age;
response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache");
response.setContentType("text/XML;charset=UTF-8");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
try {
response.getWriter().write(str);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}postman模拟结果:
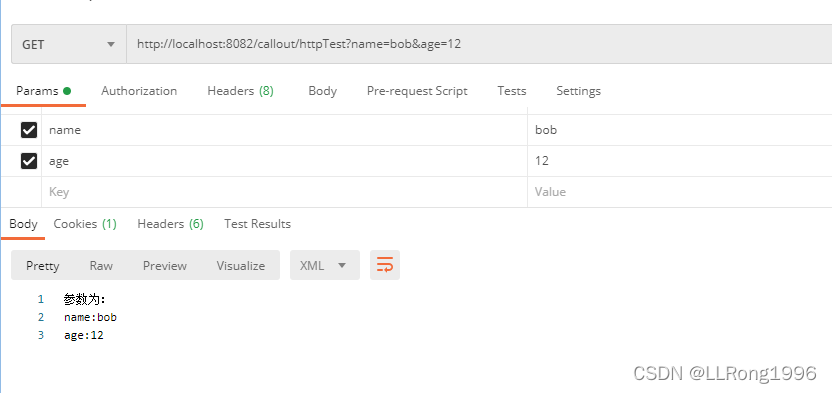
也可以利用HttpServletRequest中的输入流获取请求体,text和json格式都适用
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/callout/")
@Slf4j
public class CalloutTestController {
@GetMapping("/httpTest")
public void getOne(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
String reqBody = getRequestBodyAsString(request);
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(reqBody);
String str = "参数为:" + "\n" + "name:" + jsonObject.getString("name") +"\n" + "age:" + jsonObject.getInteger("age");
response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache");
response.setContentType("text/XML;charset=UTF-8");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
try {
response.getWriter().write(str);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static String getRequestBodyAsString(HttpServletRequest req) {
try (ServletInputStream sir = req.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader isReader = new InputStreamReader(sir, "utf-8");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isReader); ) {
StringBuilder ret = new StringBuilder();
String line;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
ret.append(line);
}
return ret.toString();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Read inputStream from request error: uri = {}, queryString = {}", req.getRequestURI(), req.getQueryString(), e);
}
return null;
}
}postman模拟测试:
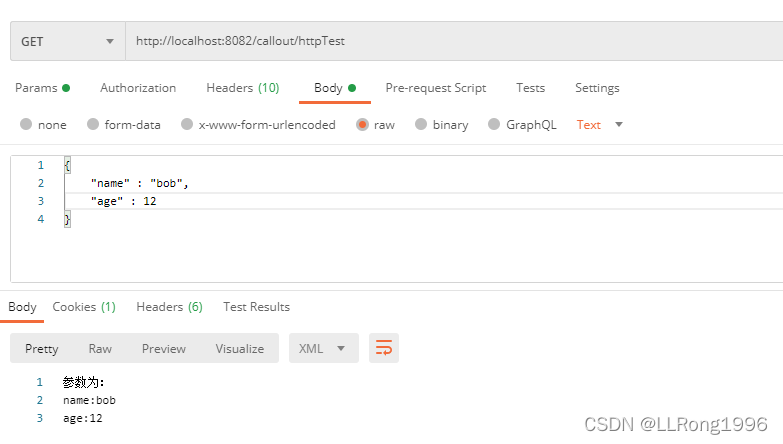
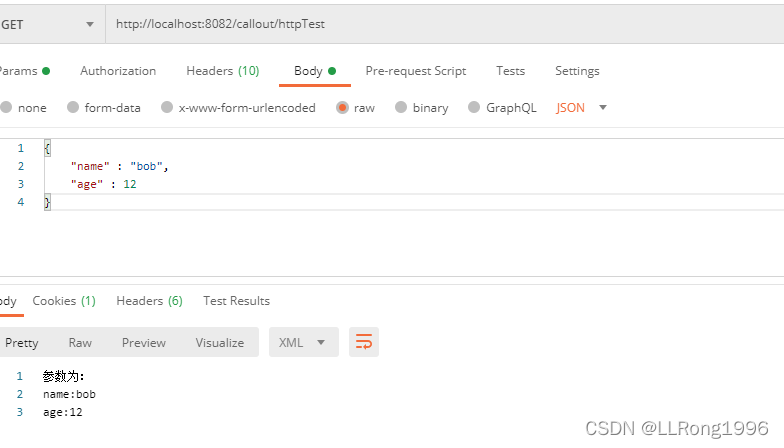
8.使用@RequestBody接收请求体数据
get请求与post请求均适用,但数据格式只能是JSON格式,
可以利用map,bean,list,JSONObject接收数据
后端代码:
//@PostMapping("/bodyTest")
@GetMapping("/bodyTest")
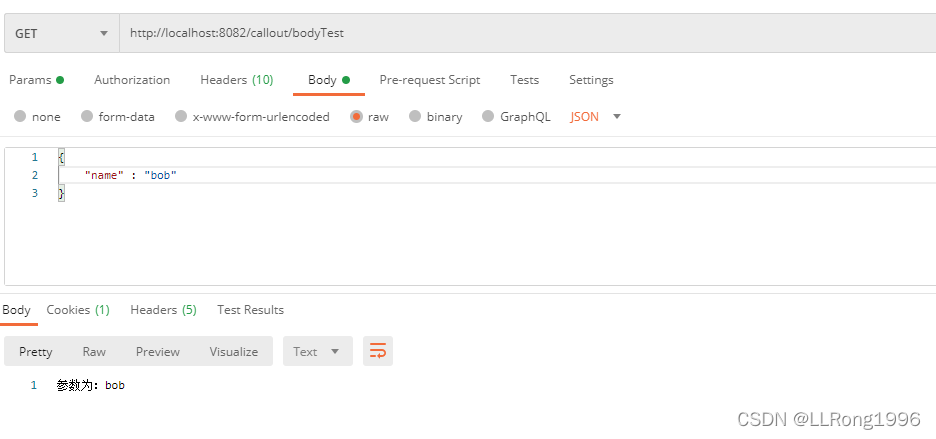
public String bodyTest(@RequestBody JSONObject object) {
return "参数为:" + object.getString("name");
}
postman请求模拟:





 本文详细介绍了SpringBoot在Controller层如何接收不同类型的参数,包括restful风格、路径参数、表单参数、Map、数组、对象、HttpServletRequest及@RequestBody等,并提供了相应的后端代码示例和Postman模拟请求结果。
本文详细介绍了SpringBoot在Controller层如何接收不同类型的参数,包括restful风格、路径参数、表单参数、Map、数组、对象、HttpServletRequest及@RequestBody等,并提供了相应的后端代码示例和Postman模拟请求结果。
















 2785
2785

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








