前言
《Spring Security学习(六)——配置多个Provider》有个很奇怪的现象,如果我们不添加DaoAuthenticationProvider到HttpSecurity中,似乎也能够达到类似的效果。那我们为什么要多此一举呢?从文章的效果来看确实是多此一举,但其实这里面暗藏玄机。也引出了本文的父子AuthenticationManager(ProviderManager)的话题。
探究父子AuthenticationManager(ProviderManager)体系
我们在Spring Security源码的ProviderManager(在org.springframework.security.authentication包中)中,在authenticate方法的以下位置断点调试:

然后查看断点的变量:
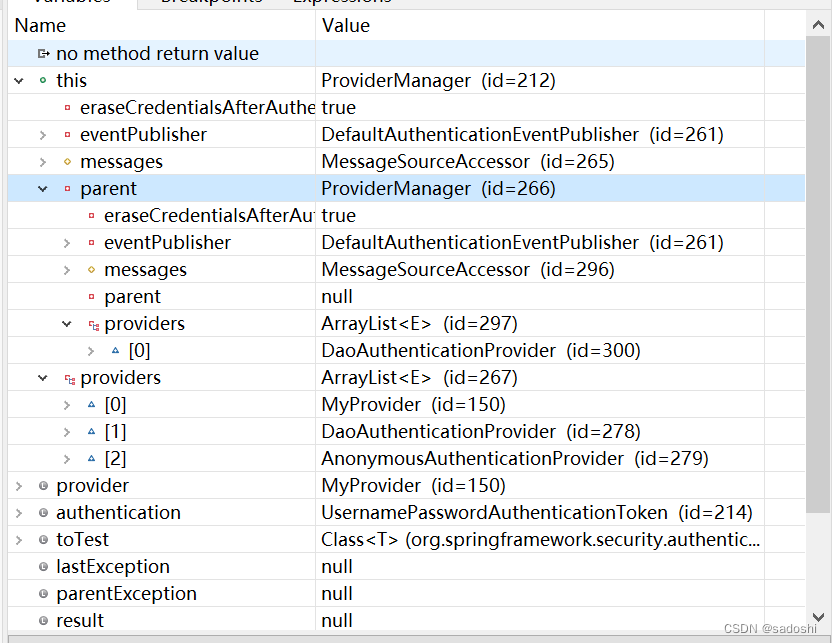
目前程序准备处理MyProvider的authenticate方法,目前providers列表中有三个provider,分别是我们添加的MyProvider和DaoAuthenticationProvider,还有一个AnonymousAuthenticationProvider是Spring Security在HttpSecurity初始化时加进去的(参考HttpSecurityConfiguration的httpSecurity方法)。
重点来了,我们还看到parent,里面有个DaoAuthenticationProvider。parent的ProviderManager和里面的DaoAuthenticationProvider又是什么时候加进去的?这个源码上有点复杂,我也不准备大段大段的粘出来(大概率读者一下子很难看懂),提示一下读者,在HttpSecurityConfiguration的httpSecurity方法的这一行:
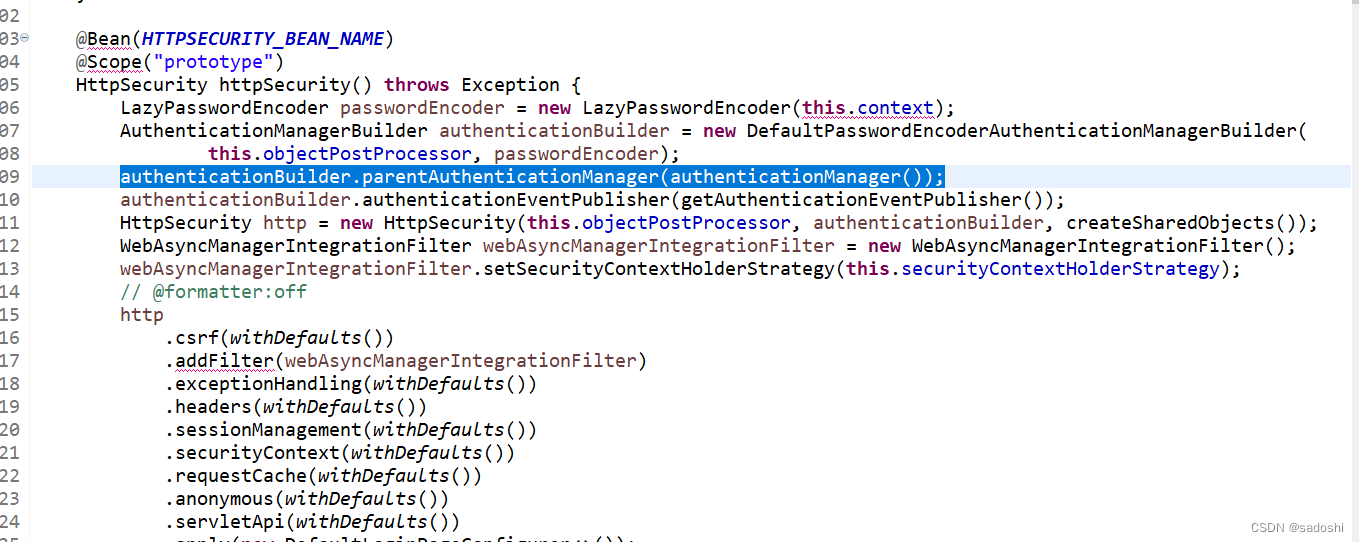
在蓝色标出的位置设置的父ProviderManager。这个父ProviderManager是AuthenticationConfiguration配置中创建InitializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurer到Spring容器中,然后在Spring Security初始化时调用InitializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurer的configue方法获取并设置ProviderManager,在父ProviderManager中设置DaoAuthenticationProvider也是类似的原理。
读者可以尝试删掉《Spring Securi习(六)——配置多个Provider》WebSecurityConfig中添加DaoAuthenticationProvider到HttpSecurity的代码,再断点调试一下。
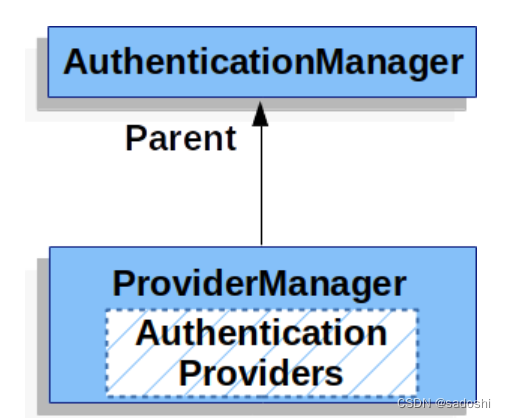
父AuthenticationManager的作用
父子AuthenticationManager的机制是这样的:先对子AuthenticationManager中的AuthenticationProvider列表进行逐个匹配,若都无法匹配,则会对父AuthenticationManager中的AuthenticationProvider列表进行逐个匹配。
下面两张图是来自Spring Security官网文档的:





 本文分析了SpringSecurity中父子AuthenticationManager的工作原理,展示了如何在不添加DaoAuthenticationProvider的情况下实现认证,以及如何自定义父ProviderManager,结合Redis进行用户验证。重点在于理解其内部机制和应用场景。
本文分析了SpringSecurity中父子AuthenticationManager的工作原理,展示了如何在不添加DaoAuthenticationProvider的情况下实现认证,以及如何自定义父ProviderManager,结合Redis进行用户验证。重点在于理解其内部机制和应用场景。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 488
488










