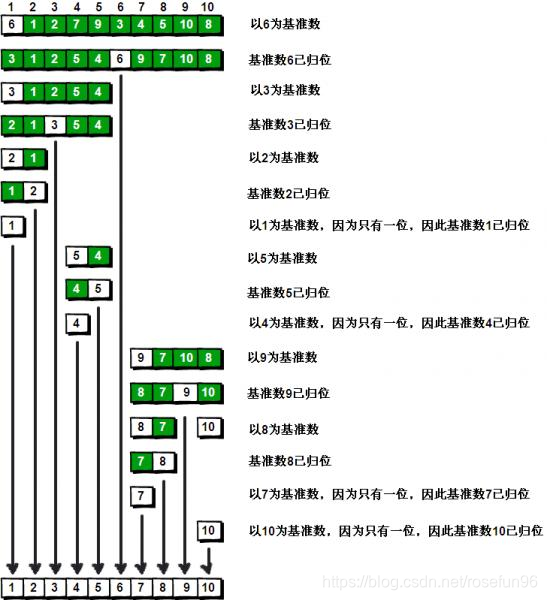
1.思想
以一个数为基准(一般最左边的数),从左到右和从右到左,分别找大于这个基准和小于这个基准的数,若找到就交换,汇合处的数和这个基准交换。多次重复。
以下图为例。
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int a[101], n;//定义全局变量,这两个变量需要在子函数中使用
void quicksort(int left, int right)
{
int i, j, t, temp;
if (left>right)
return;
temp = a[left]; //temp中存的就是基准数
i = left;
j = right;
while (i != j)
{
//顺序很重要,要先从右边开始找
while (a[j] >= temp && i<j)
j--;
//再找右边的
while (a[i] <= temp && i<j)
i++;
//交换两个数在数组中的位置
if (i<j)
{
t = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = t;
}
}
//最终将基准数归位
a[left] = a[i];
a[i] = temp;
quicksort(left, i - 1);//继续处理左边的,这里是一个递归的过程
quicksort(i + 1, right);//继续处理右边的 ,这里是一个递归的过程
}
int main()
{
int i=0, j=0, t;
char c;
//读入数据
cin >> n;
cin.ignore();
for (i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
//cout << endl;
quicksort(0, n-1); //快速排序调用
//输出排序后的结果
for (i = 0;i < n;i++)
cout << a[i] << ' ';
system("pause");
return 0;
}
参考:http://developer.51cto.com/art/201403/430986.htm
























 657
657

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










